
06-04-Pohlia-elongata-Helm-Cragg.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/pohlia-elongata/
Exploring the Fascinating World of Pohlia elongata var. greenii Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Pohlia elongata var. greenii (Brid.) A.J.Shaw, a moss in the Mniaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at this fascinating plant, from its unique morphology to its ecological importance. Get ready to dive into the miniature world of Pohlia!
Background on Mosses
Before we focus on P. elongata var. greenii specifically, let’s review some moss basics. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. Unlike other plants, they lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have rhizoids, stems, and phyllids. Mosses are found on every continent and play important roles in water and nutrient cycling.
Morphology and Identification
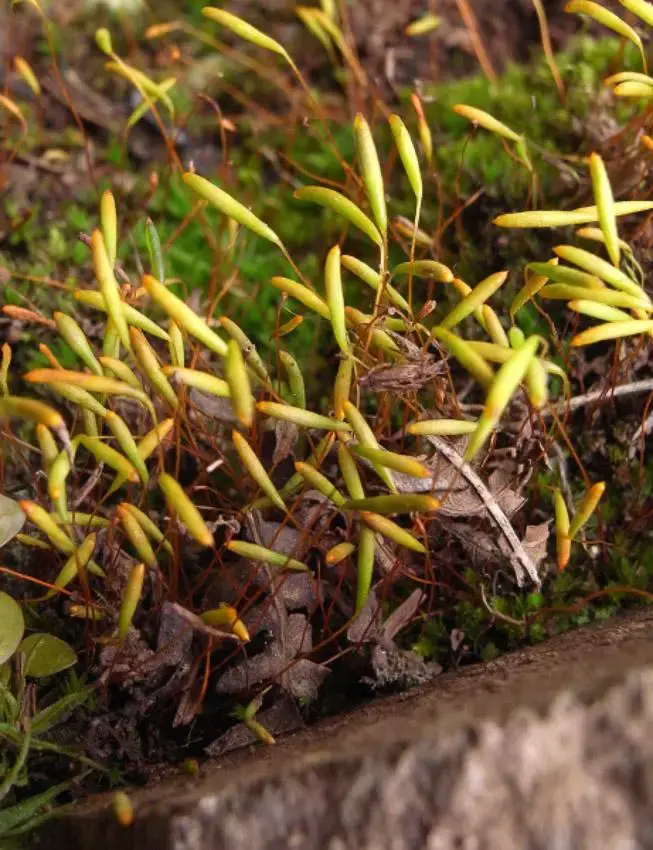
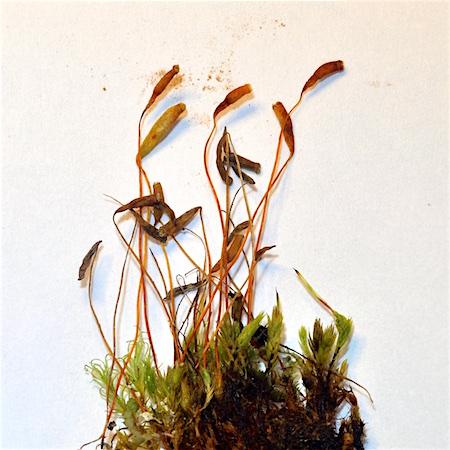
Pohlia elongata var. greenii is a small acrocarpous moss, meaning it produces sporophytes at the tips of the stems. Its stems are

Pohlia_elongata-elon_004.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Pohlia_elongata_var_elongata.html
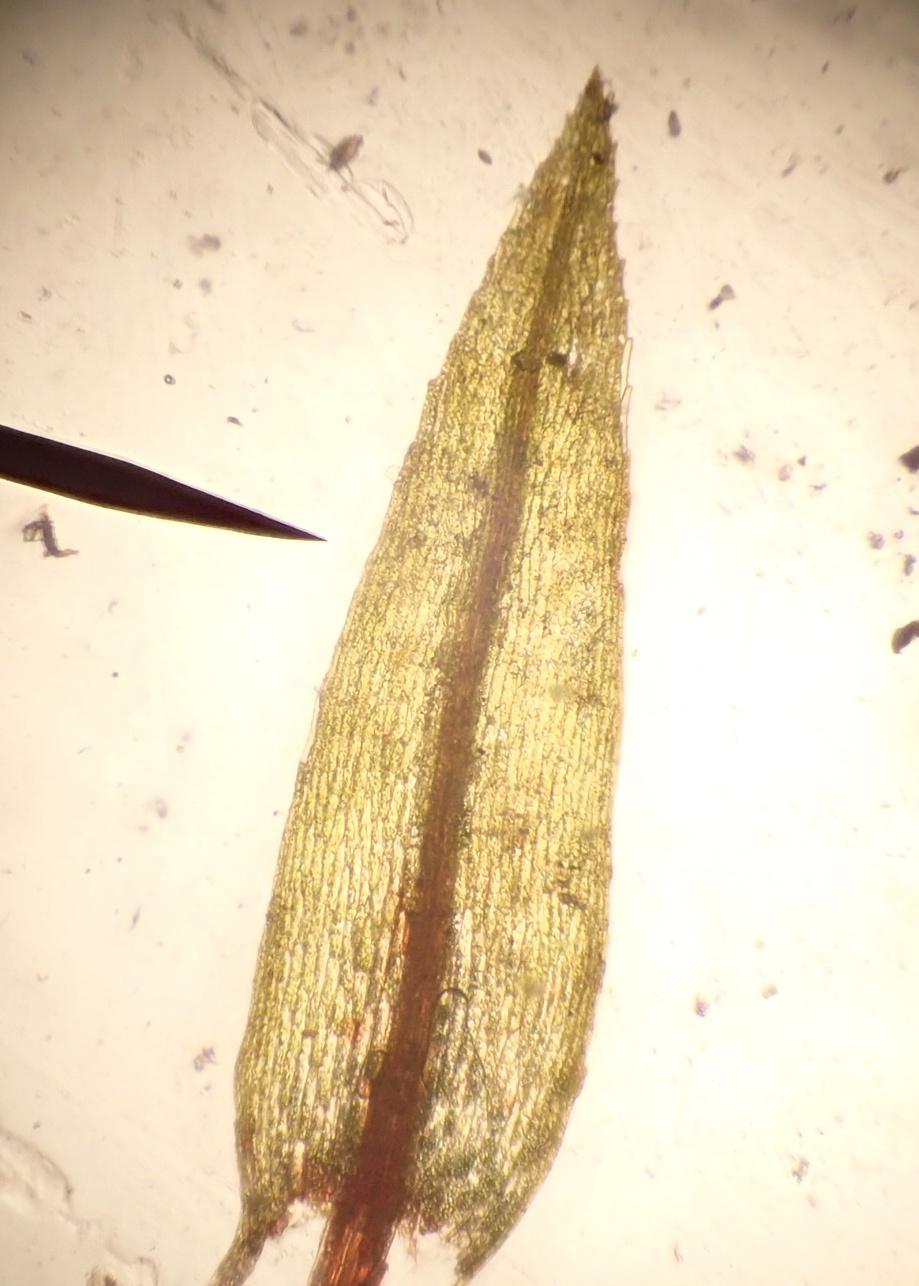
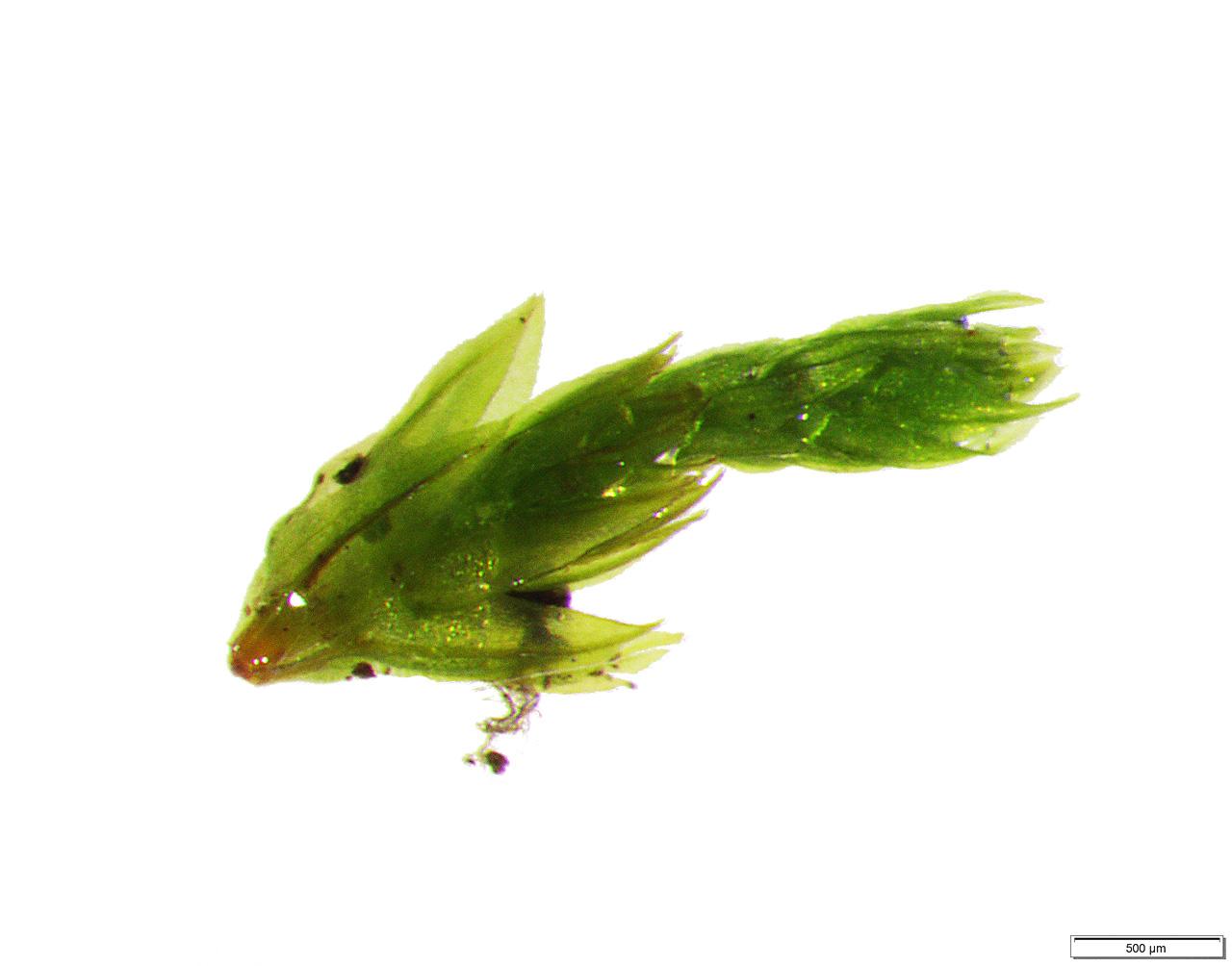
elongated and sparsely branched, reaching 1-4 cm tall. The lanceolate leaves are pale to yellowish-green, with a strong costa (midrib) that often extends beyond the leaf tip.

397479.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4900
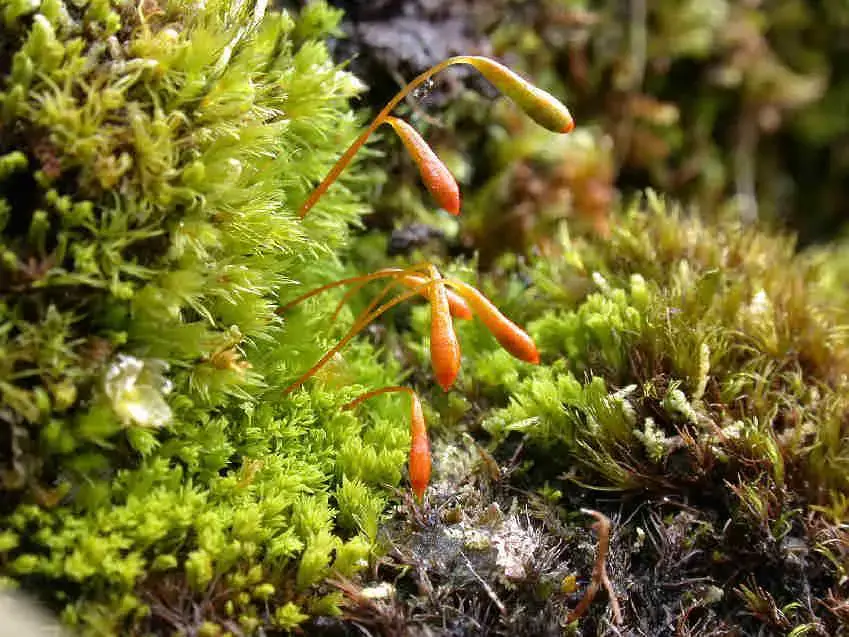
The key identification features of this moss are:
- Elongated stems
- Pale yellowish-green lanceolate leaves
- Strong costa extending past leaf tip
- Cylindrical capsules on long setae
Global Distribution and Habitat
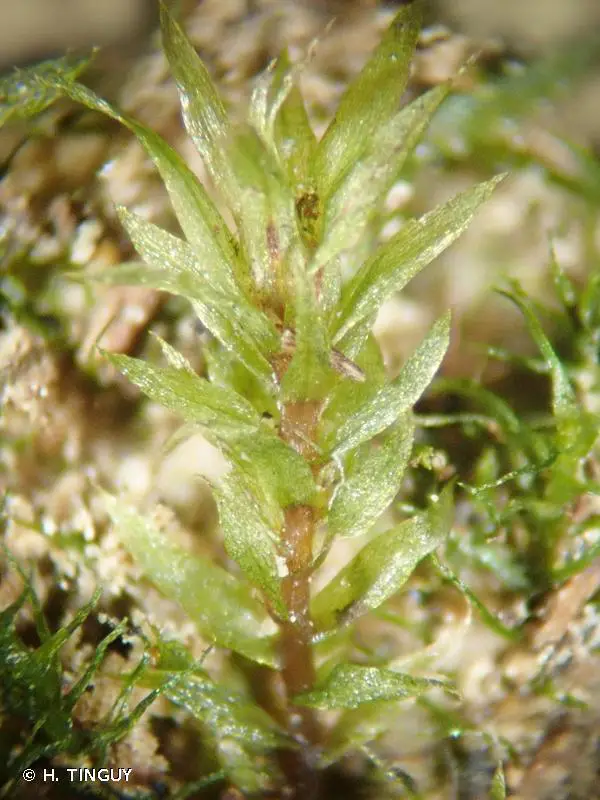
This moss has a wide distribution, found in North America, Europe, and Asia. It typically grows on
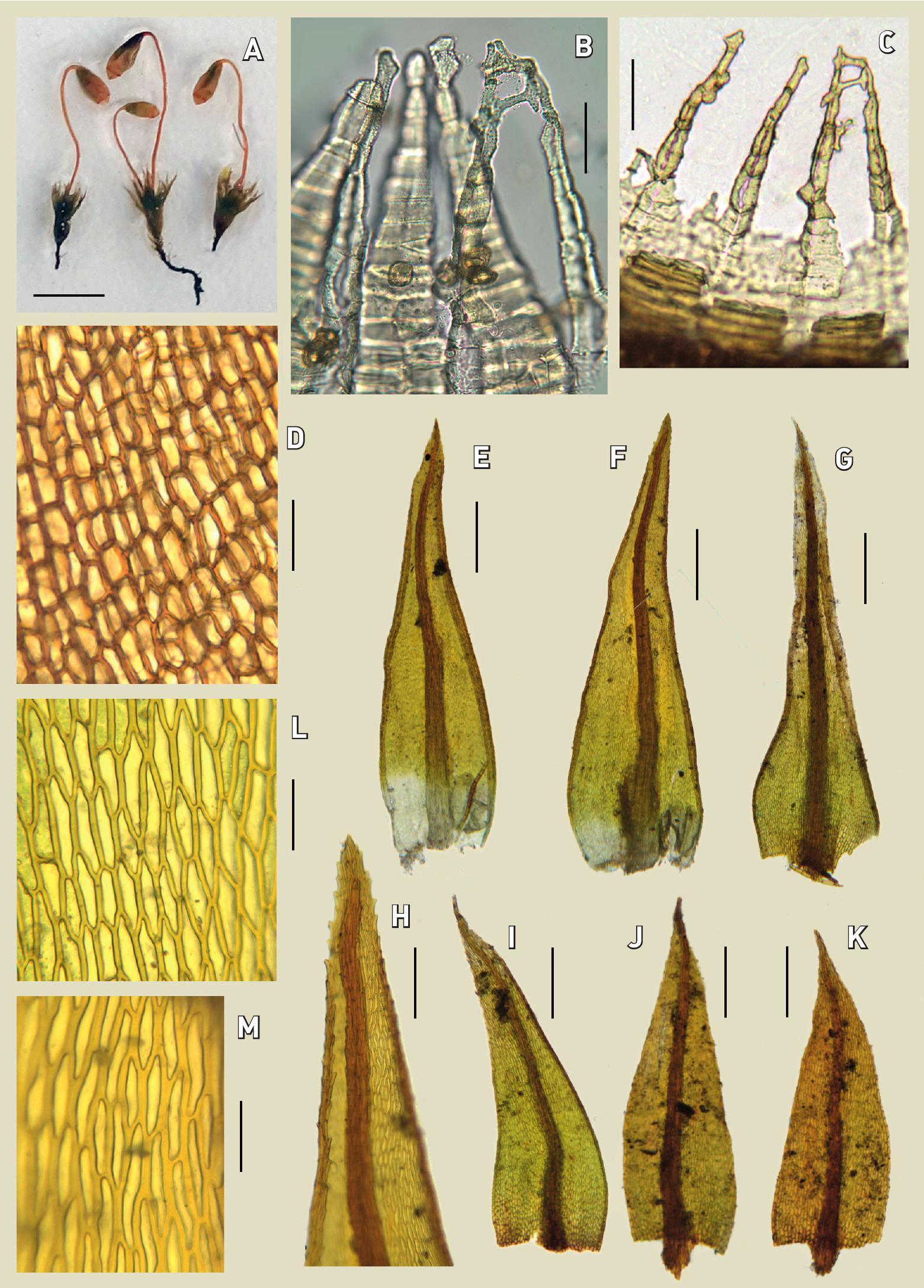
img-z3-3_197.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/herzogia/volume-34/issue-1/heia.34.1.2021.197/Notes-on-the-taxonomy-chorology-and-habitat-of-Pohlia-greenii/10.13158/heia.34.1.2021.197.full
damp, shaded soil, rocks, or rotten wood in forests and ravines from lowlands to subalpine elevations.
In North America, P. elongata var. greenii occurs across much of Canada and the northern/western United States. Some common habitats include:
- Moist coniferous and deciduous forests
- Shaded streambanks and seeps

pohlia_elongata1.jpg from: http://www.luopioistenkasvisto.fi/Sivut/sammalet/pitkavarstasammal.html
- Crevices of cliffs and boulders
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Pohlia plays several important ecological roles:
- Helps retain moisture in soils
- Provides habitat for micro-organisms
- Cycles nutrients
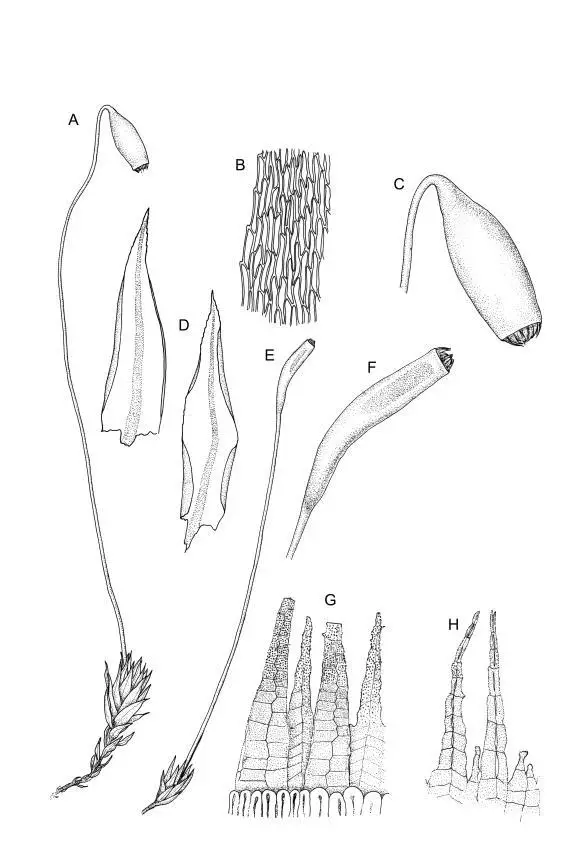
Image3NQZlarge.jpg from: https://www.nzflora.info/factsheet/Taxon/Pohlia-elongata.html
- Serves as a pioneer species in succession
This moss has adaptations that allow it to thrive in its niche, including:
45092901.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/foto/view/45092901/
- Rhizoids for anchoring to substrates
- Ability to absorb water and nutrients over its entire surface
- Desiccation tolerance during dry periods

COLO-B-0043255_lg.jpg from: https://www.gbif.org/pt/species/5711017
| Trait | Adaptation |
|---|---|
| Rhizoids | Anchoring and stability |
| Absorptive surfaces | Efficient water/nutrient uptake |
| Desiccation tolerance | Survival during dry conditions |
Conclusion
Pohlia elongata var. greenii may be small, but this mighty moss is a fascinating part of forest ecosystems. From its distinct morphology to its important ecological roles, it reminds us to appreciate the miniature world beneath our feet.

p_elongata2.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/pohlia_elongata.html
The next time you’re out in nature, take a closer look – you might just spot some

120px-Pohlia_elongata_(b%2C_112725-471212)_6753.JPG from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Pohlia_elongata
Pohlia brightening up a shady patch of soil! What other mini-marvels of the plant kingdom have you encountered?