348059.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5165
Introduction
Welcome, fellow moss enthusiasts! Today, we’re delving into the fascinating world of

p_tectorum1.jpg from: https://admissions.wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/pseudoleskeella_tectorum.html
Pseudoleskeella tectorum (Funck ex Brid.) Kindb. ex Broth., a captivating member of the Pseudoleskeellaceae family. This unassuming yet remarkable moss, commonly known as Pseudoleskeella, has captured the hearts and minds of bryologists worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty details, let’s set the stage. Bryophytes, or mosses, are a diverse group of non-vascular plants that play a crucial role in various ecosystems. These diminutive yet resilient organisms have been around for millions of years, adapting to a wide range of environments and contributing to the intricate web of life on our planet.

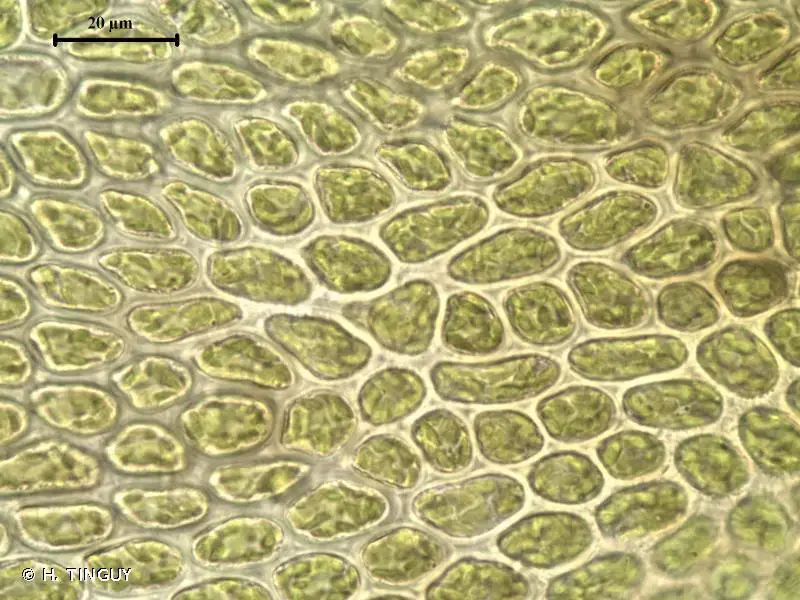
p_tectorum7.jpg from: https://soe.wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/pseudoleskeella_tectorum.html
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
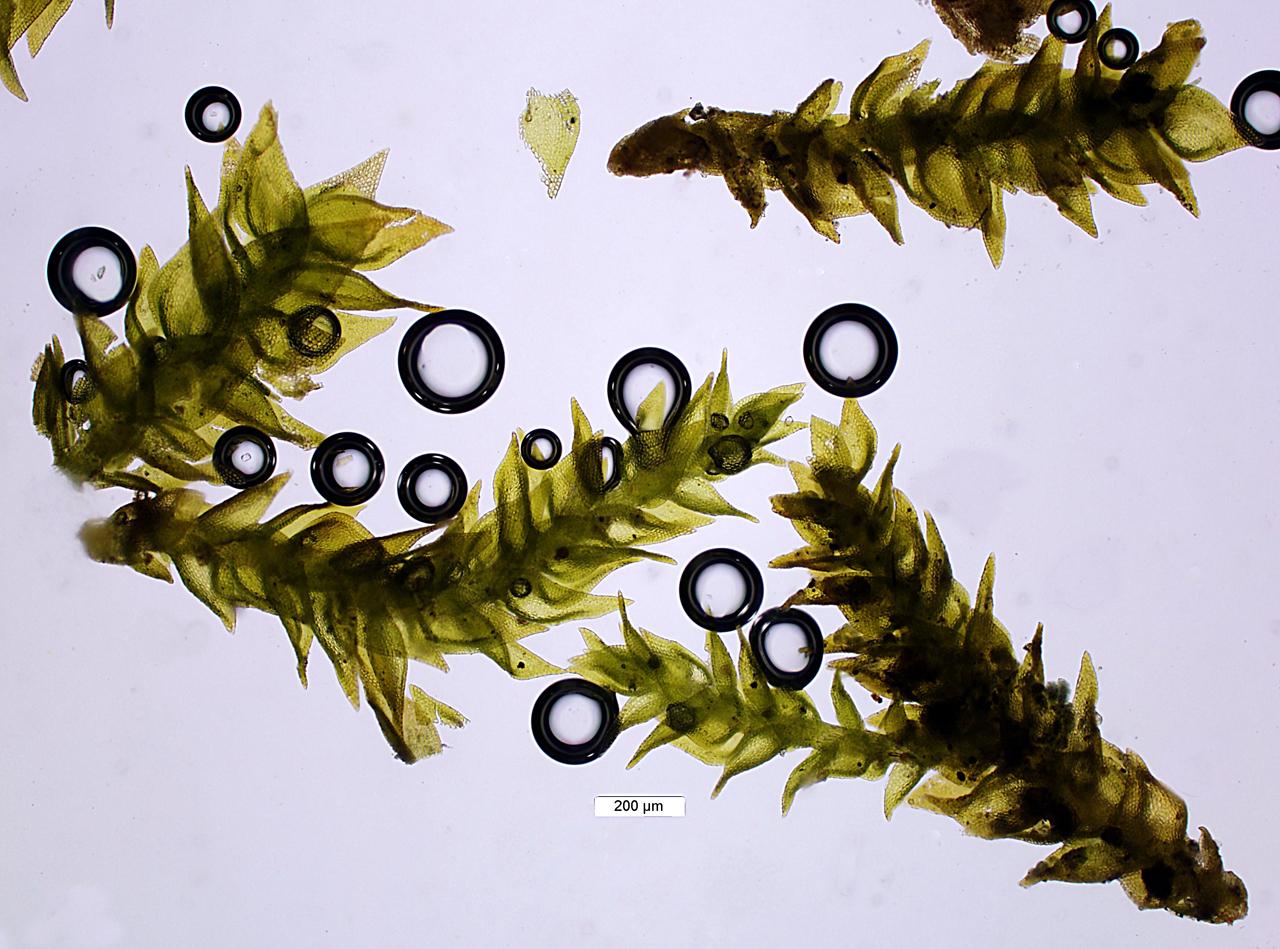
Pseudoleskeella tectorum is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems and branches grow horizontally. Its slender, creeping stems are adorned with delicate, lance-shaped leaves that form a feathery appearance. The leaves are typically

141978.jpg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=14107
1-2 mm long and feature a distinctive midrib that extends nearly to the leaf tip. When viewed under a microscope, the leaf cells reveal a intricate pattern of hexagonal shapes, adding to the moss’s unique charm.
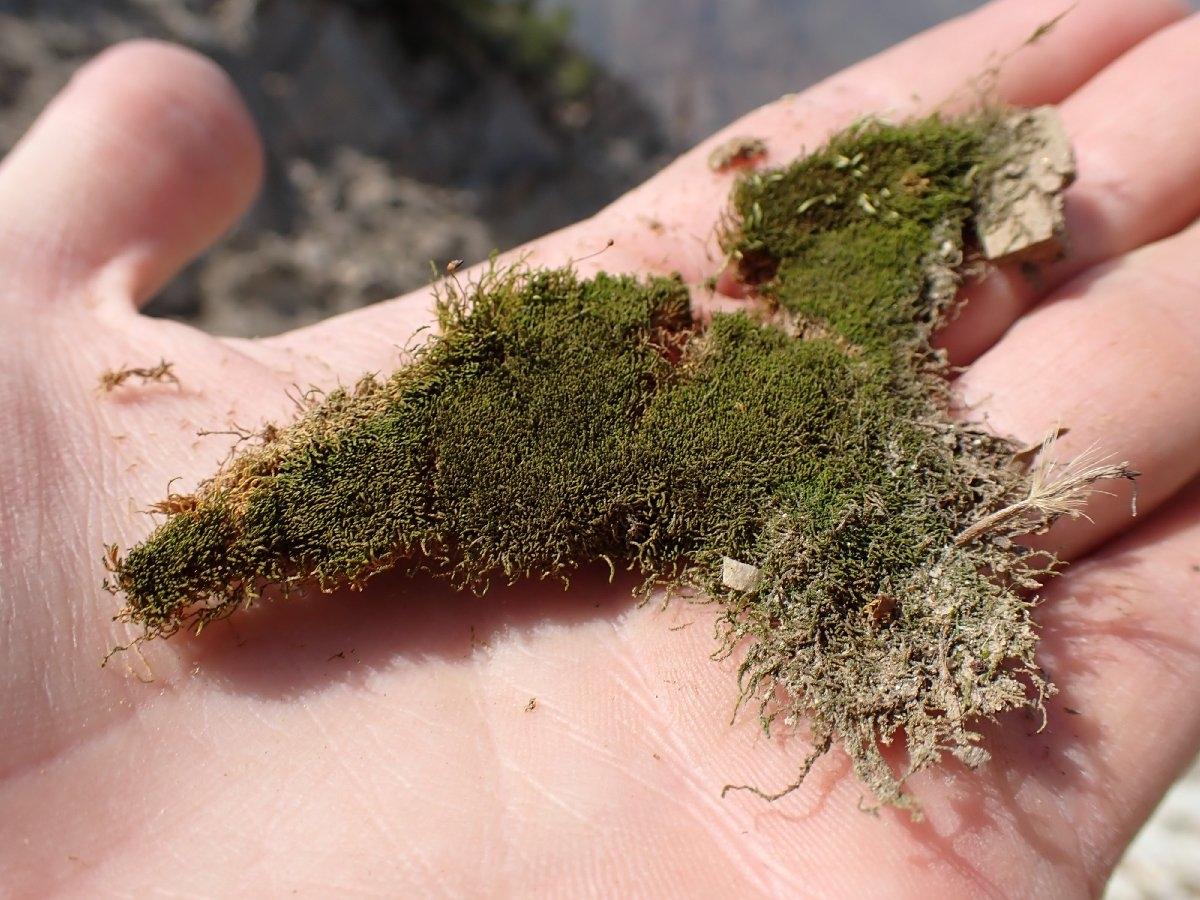
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss is widely distributed across various regions, including Europe, Asia, and North America. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from shaded rock crevices and tree bark to soil and decaying wood. Pseudoleskeella tectorum is particularly fond of calcareous substrates, making it a common sight in areas with limestone or chalk outcrops.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size,
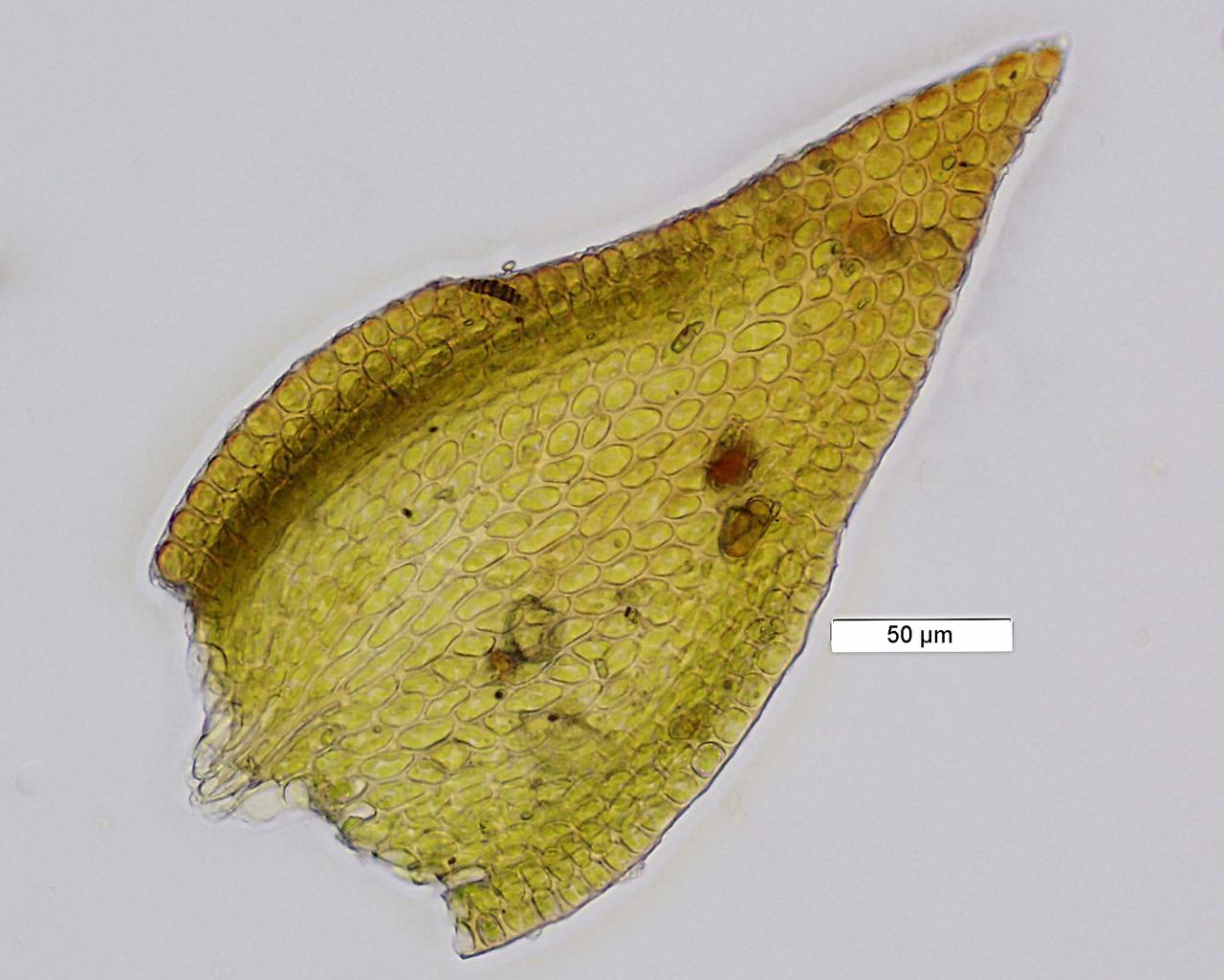

p_tectorum2.jpg from: https://www.wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/pseudoleskeella_tectorum.html
Pseudoleskeella tectorum plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating microhabitats for other organisms to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a food source for various invertebrates and provides nesting material for some bird species.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Pseudoleskeella tectorum is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to conserve moisture. Once water becomes available, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
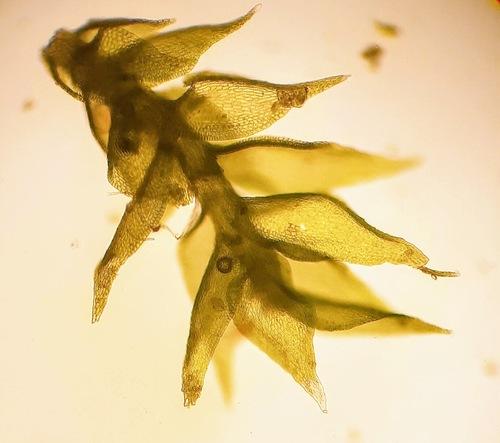

medium.jpg from: https://enciclovida.mx/especies/147128
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Appalachian Mountains, researchers discovered a thriving population of Pseudoleskeella tectorum growing on limestone outcrops. The moss played a crucial role in stabilizing the soil and providing a suitable habitat for other plant species to establish themselves, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
Technical Table
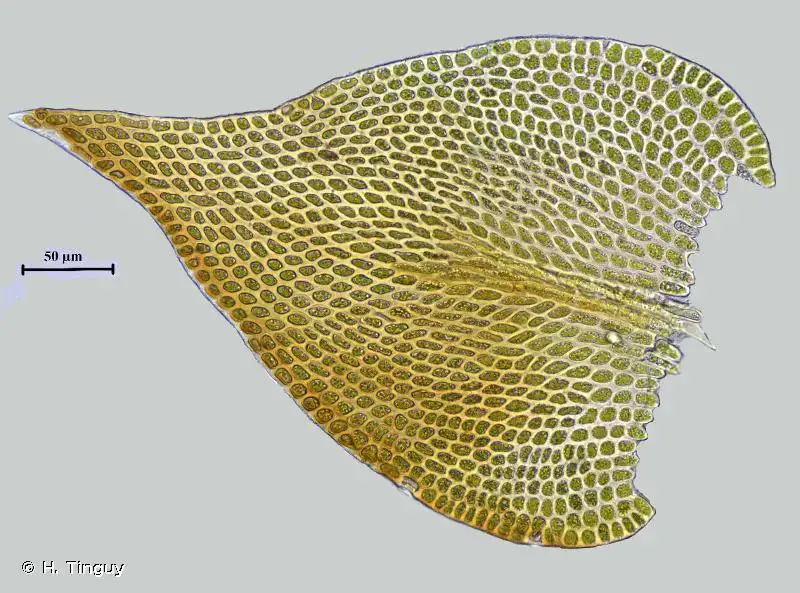

176537.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5161
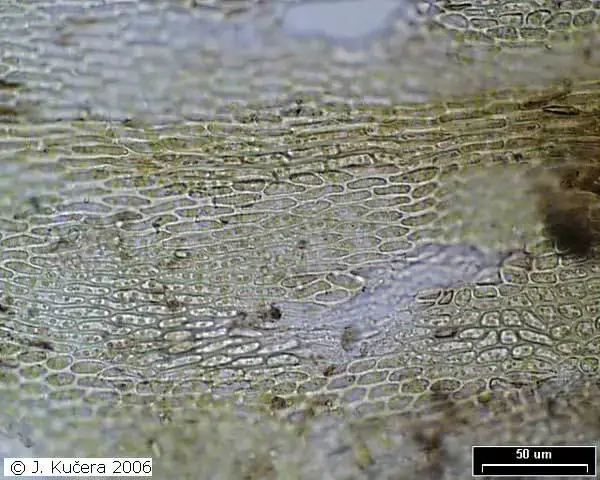

Pse_rup_cells.jpg from: https://botanika.prf.jcu.cz/bryoweb/klic/genera/pseudoleskeella.html
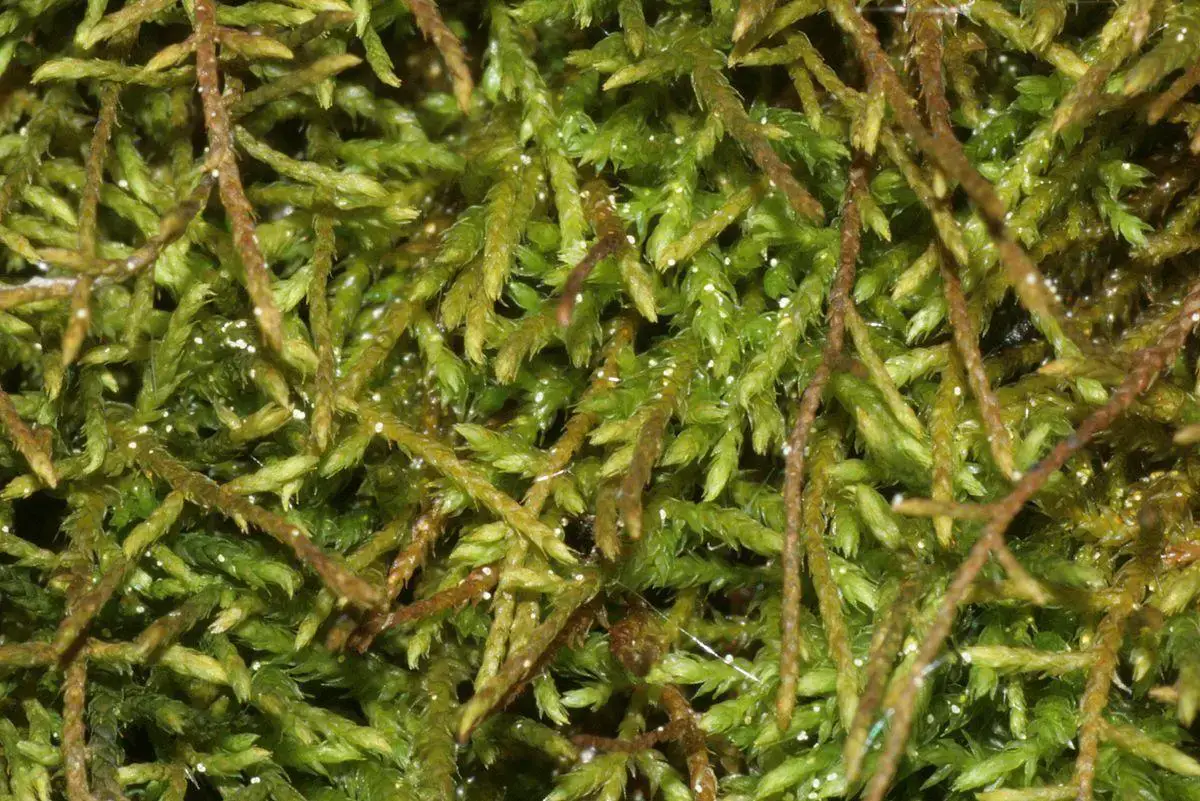

fels-kettenmoos-deu–pseudoleskeella-catenulata.jpg from: https://www.plantsnap.com/plant-encyclopedia/bryophytes/Leskeaceae/pseudoleskeella-papillosa/

original.jpg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/4279191
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Pseudoleskeellaceae |
| Genus | Pseudoleskeella |
| Species | tectorum |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous |
| Leaf Shape | Lance-shaped |
| Leaf Size | 1-2 mm |
| Habitat | Calcareous substrates, rock crevices, tree bark, soil, decaying wood |
Conclusion
Pseudoleskeella tectorum is a true marvel of nature, showcasing the incredible diversity and resilience of the bryophyte world. From its intricate morphology to its vital ecological roles, this unassuming moss deserves our admiration and appreciation. As we continue to explore the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other hidden gems lie waiting to be discovered, and how can we better protect and preserve these invaluable components of our ecosystems?