
BM_Anomodon_pseudotristis_crop.jpg from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/66_Anomodontaceae.html
Exploring the Fascinating World of Haplohymenium pseudotriste var. robustum Bizot Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play a vital role in many ecosystems around the world. Today, we’ll dive into the captivating world of Haplohymenium pseudotriste var. robustum Bizot, a unique moss species from the Anomodontaceae family, commonly known as Haplohymenium

kobanoitogoke-eda.jpg from: https://mikawanoyasou.org/koke/kobanoitogoke.htm
. Get ready to learn about its distinctive features, global distribution, and ecological importance!
Background on Bryophytes
Before we explore Haplohymenium pseudotriste var. robustum specifically, let’s briefly review what mosses are. Mosses belong to the division

medium.jpg from: https://www.naturalista.mx/taxa/163519
Bryophyta
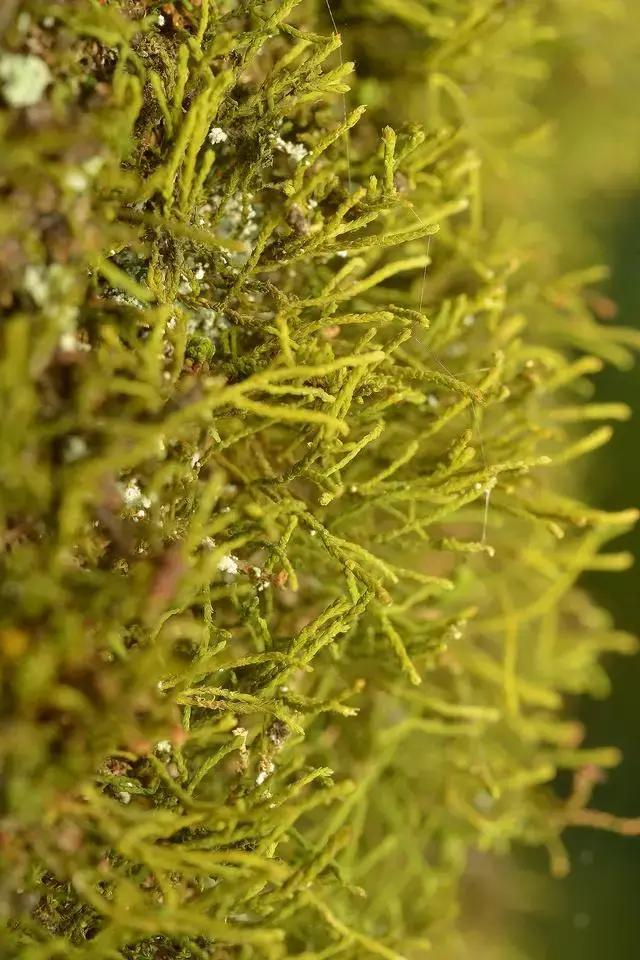

kobanoitogoke150807_1.jpg from: https://soyokaze2jp.blogspot.com/2015/08/blog-post_17.html
, which includes small, non-vascular plants that lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have leaf-like structures called phyllids. Mosses are found in the class

Haplohymenium-longinerve02L.jpg from: https://www.digital-museum.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~museum/habit/moss_habit/Haplohymenium longinerve/Haplohymenium_longinerve.html
Bryopsida. There are over 12,000 moss species worldwide, growing in diverse habitats from the arctic tundra to tropical rainforests.
Morphology and Identification
Haplohymenium pseudotriste var. robustum is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its sporophytes grow laterally from the stem. Its phyllids are ovate-lanceolate in shape and have a distinct costa (midrib). The seta (stalk bearing the capsule) is smooth and reddish-brown. Capsules are erect and cylindrical.
One of the key identifying features of H. pseudotriste var. robustum is the presence of pseudoparaphyllia, small leaf-like structures surrounding the branch buds. These help distinguish it from similar species in the Anomodontaceae family.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Haplohymenium pseudotriste var. robustum has a relatively limited global range. It is found primarily in eastern Asia, including parts of China, Japan, and the Korean peninsula. This moss typically grows on tree trunks and branches in humid forests at low to moderate elevations.
It prefers partially shaded habitats with good air humidity. The species is not currently considered threatened, but like many bryophytes, it is sensitive to environmental disturbances that impact forest ecosystems.
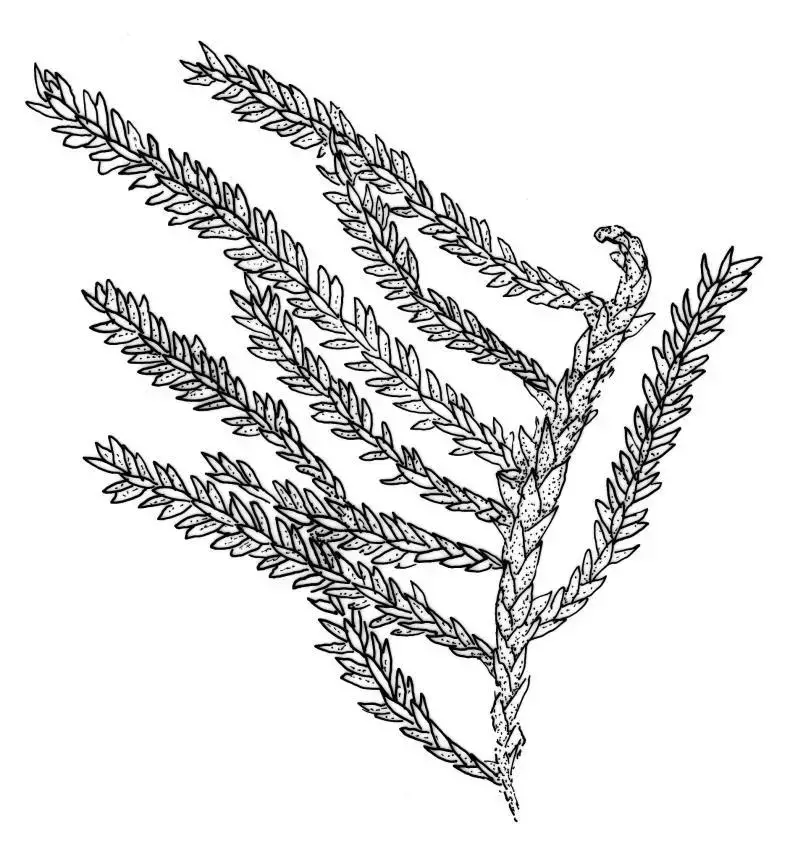

Image1F3Blarge.jpg from: https://www.nzflora.info/factsheet/Taxon/Anomodontaceae.html
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
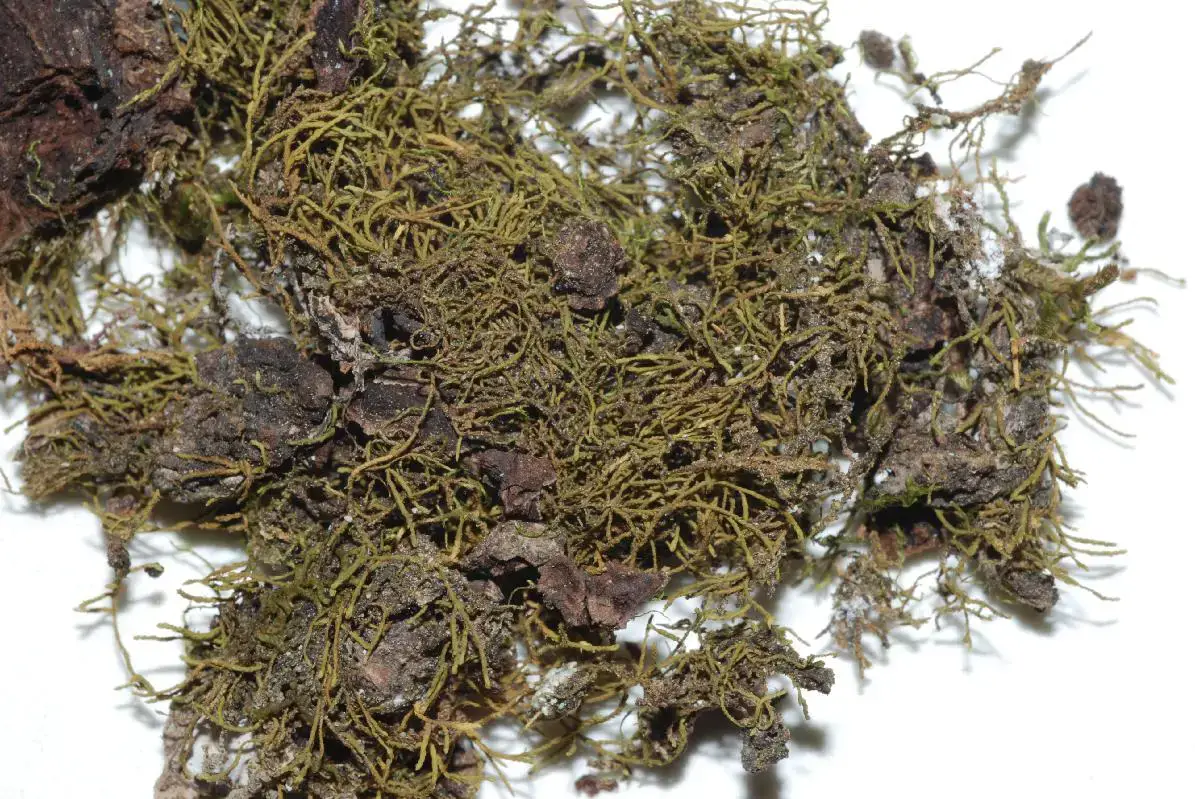

lrHaplohymenium_triste0B123B.jpg from: https://www.james-vankley.com/PineywoodsPlants/Bryophytes_Charophytes/Mosses/Anomodontaceae/Anomodontaceae.html
As an epiphytic moss, H. pseudotriste var. robustum plays several important roles in forest habitats:
- Microhabitats: The dense mats formed by this moss create microhabitats for numerous invertebrates and other small organisms.
kobanoitogoke-papira.jpg from: https://flora-of-mikawa.sakura.ne.jp/koke/kobanoitogoke.htm
- Water and nutrient retention: Moss clumps trap and retain moisture, regulating humidity in the immediate environment. They also accumulate nutrients from the atmosphere, enriching their substrate.

Ctenidium%2Bmolluscum%2Bvar%2Brobustum%2BHepste%2B27012017.JPG from: http://southwalesbryos.blogspot.com/2017/01/homage-in-hepste.html
- Substrate stabilization: By growing on tree bark, H. pseudotriste var. robustum helps stabilize and protect the surface from erosion and damage.
To thrive as an epiphyte, this moss has several adaptations:
- Tolerance of desiccation: Like many bryophytes, H. pseudotriste var. robustum can survive periods of drying out and quickly resume photosynthesis when moisture is available again.
- Efficient water and nutrient uptake: Without true roots, this species relies on specialized structures to absorb water and dissolved nutrients directly through its phyllids and stems.
Conclusion
Haplohymenium pseudotriste var. robustum may be a small and inconspicuous moss, but it is a fascinating component of eastern Asian forest ecosystems. Its unique morphology, niche habitat preferences, and ecological roles make it a compelling subject for bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike.

bwi-b052459.jpg from: https://www.agefotostock.com/age/en/details-photo/peat-moss-sphagnum-robustum-germany/BWI-B052459
Next time you’re walking through a humid forest, take a closer look at the tree trunks and branches around you – you might just spot this marvelous moss! What other amazing bryophytes could be hiding in plain sight, waiting to be appreciated?