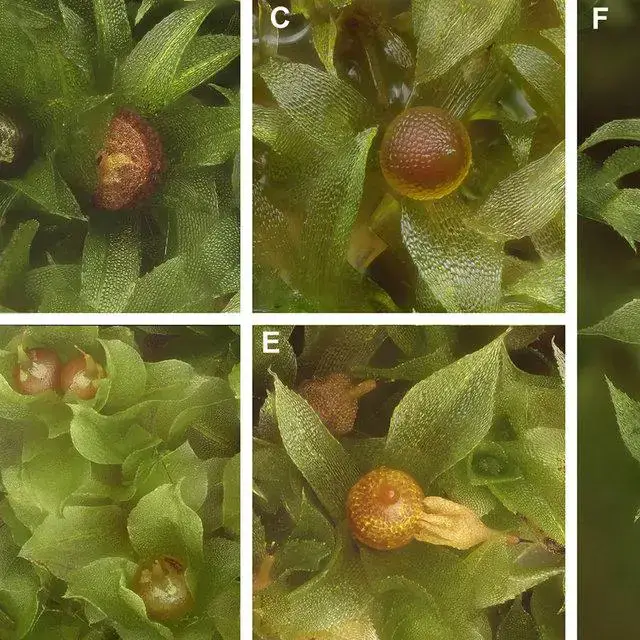

Generic-exemplars-of-the-Physcomitrium-Entosthodon-complex-A-Physcomitrium-pyriforme_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Generic-exemplars-of-the-Physcomitrium-Entosthodon-complex-A-Physcomitrium-pyriforme_fig1_333319642
Exploring the Fascinating World of Entosthodon jamesonii (Taylor) Mitt. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Entosthodon jamesonii (Taylor) Mitt., a moss in the Funariaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the captivating details of this tiny but mighty plant.
Background
Entosthodon jamesonii is a species of moss first described by Thomas Taylor in 1846. It was later transferred to the genus Entosthodon by William Mitten. This moss belongs to the division Bryophyta and the class Bryopsida.
Morphology and Identification
E. jamesonii forms small tufts or cushions, typically reaching heights of 3-10 mm. The leaves are oblong-lanceolate, with entire margins and acute tips. The leaf cells are
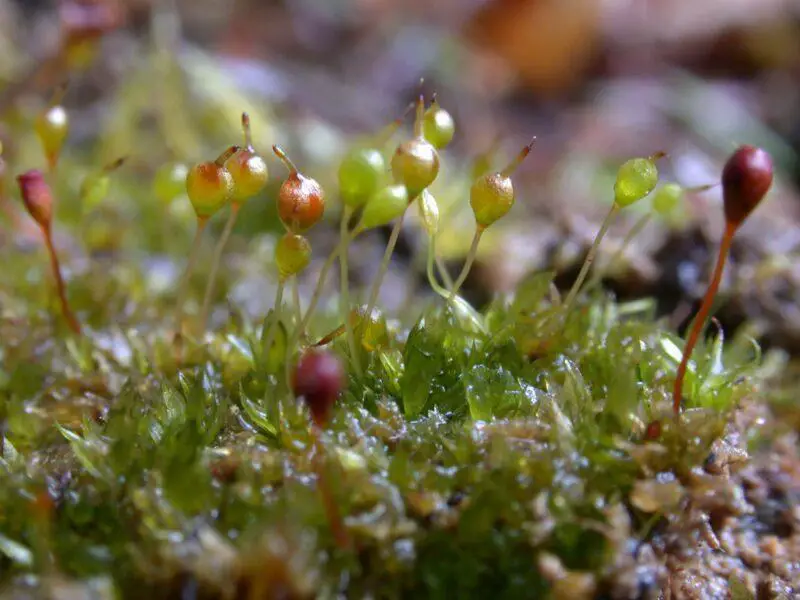

Entosthodon-obtusus-2-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/entosthodon-obtusus/
thin-walled and hexagonal. Capsules are
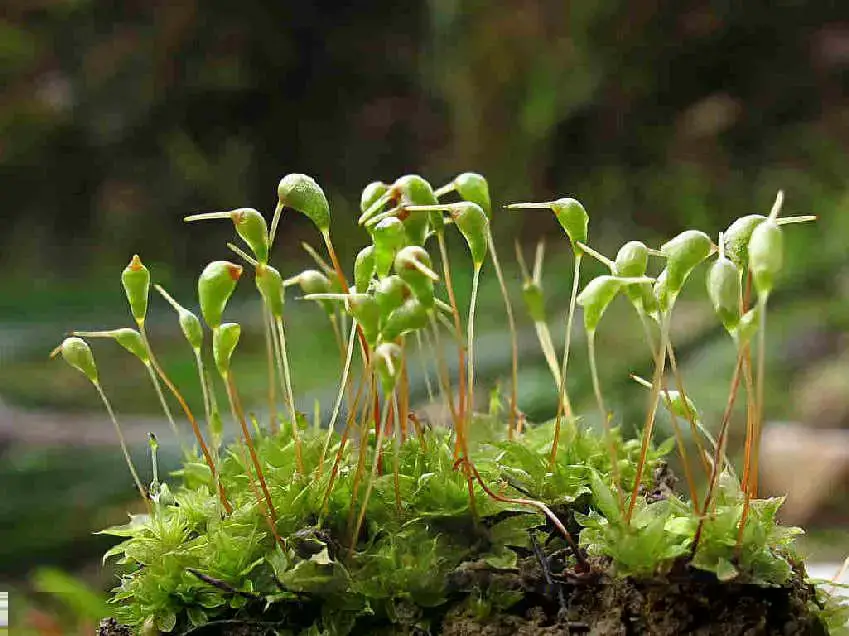

Entosthodon_pulchellus_8d.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Entosthodon_pulchellus.html
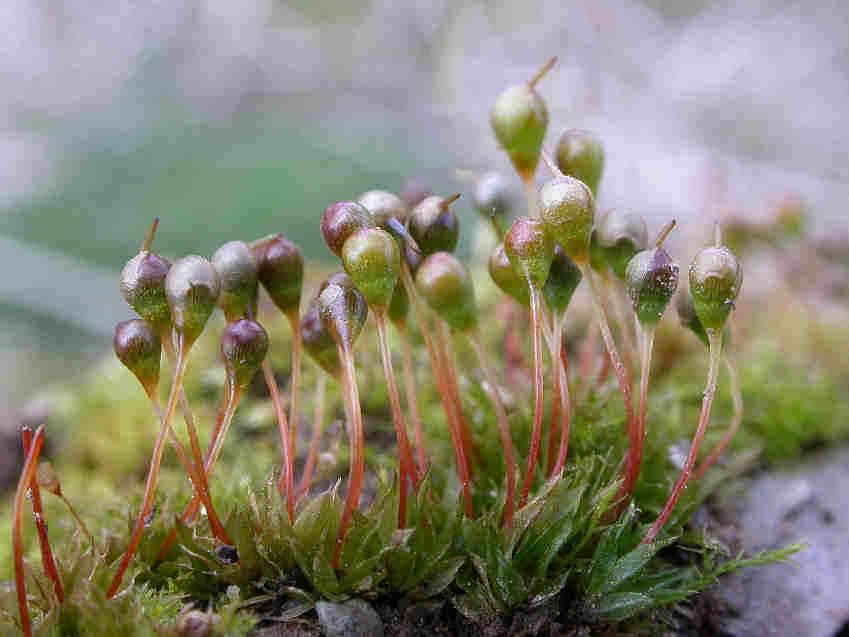
erect and symmetric
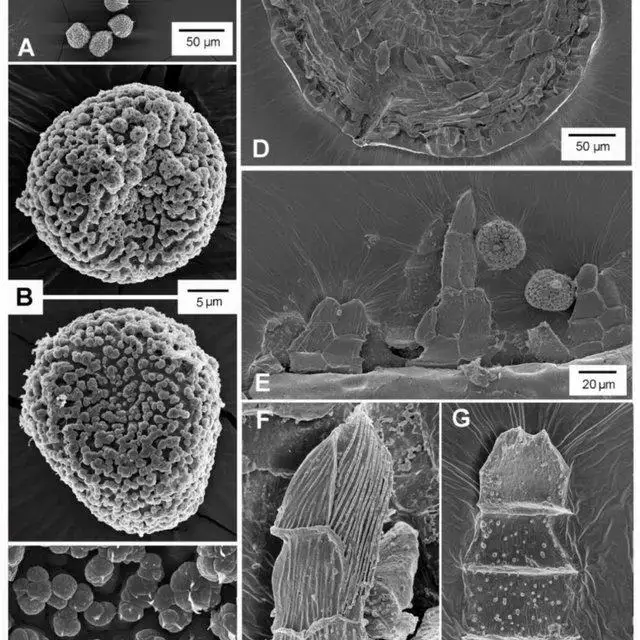

FIGURE3-SEM-images-of-Entosthodon-elimbatus-WZ-Ma-Shevock-S-He-A-B-spores-under_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/FIGURE3-SEM-images-of-Entosthodon-elimbatus-WZ-Ma-Shevock-S-He-A-B-spores-under_fig3_342665264
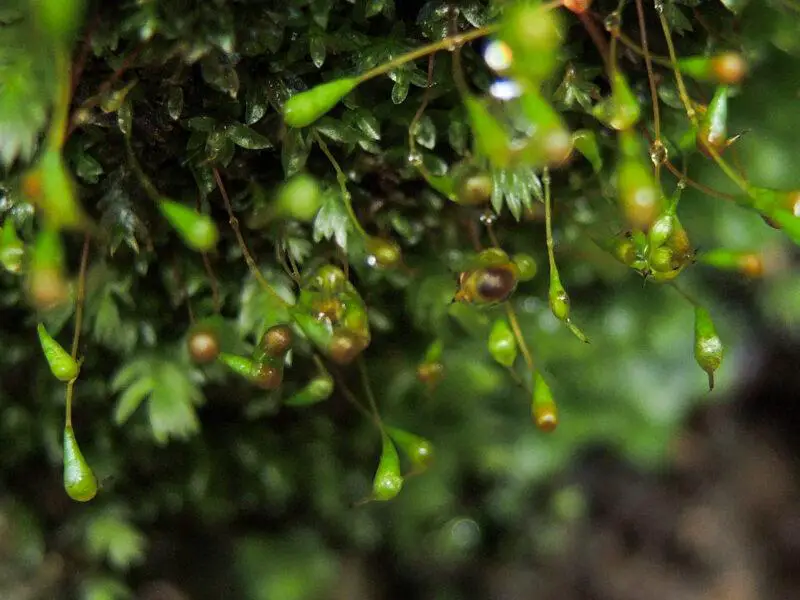
, borne on a seta (stalk) that is 5-15 mm long. The peristome (toothed structure around the capsule mouth) is double, with the outer teeth being short and blunt.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a wide distribution, found in Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. It grows on disturbed soil, banks, and crevices, often in open habitats such as fields, roadsides, and waste ground. E. jamesonii prefers acidic to neutral substrates and can tolerate some drought.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, E. jamesonii plays important roles in soil stabilization, water retention, and nutrient cycling. Its small size allows it to colonize areas where other plants struggle to establish. This moss has adaptations to cope with periodic drying, including the ability to quickly rehydrate and resume photosynthesis when water becomes available.
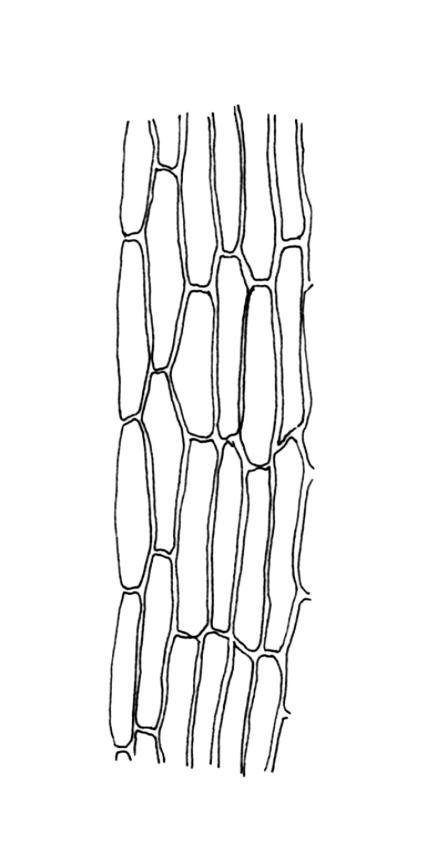
Image30IZlarge.jpg from: https://www.nzflora.info/factsheet/Taxon/Entosthodon-jamesonii-subsp-productus.html
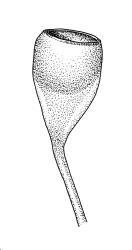
Image30IX.jpg from: https://www.nzflora.info/factsheet/Taxon/Entosthodon-jamesonii.html
17fa27739d84391a6d8a4a0e1eafdc34 from: https://www.europeana.eu/de/item/853/NHMUKXBOTXBM000872646

DSCN9700_Entosthodon-attenuatus-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/entosthodon-attenuatus/

Entosthodon-elimbatus-WZ-Ma-Shevock-S-He-A-dry-plants-with-sporophytes-B-C_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342665264_Entosthodon_elimbatus_Bryophyta_Funariaceae_a_new_species_from_the_sub-alpine_region_in_Yunnan_and_E_physcomitrioides_new_for_mainland_China

Entosthodon_fascicularis_026.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Entosthodon_fascicularis.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Height | 3-10 mm |
| Leaves | Oblong-lanceolate, entire margins, acute tips |
| Leaf Cells | Thin-walled, hexagonal |
| Capsule | Erect, symmetric |
| Seta | 5-15 mm long |
| Peristome | Double, outer teeth short and blunt |
Conclusion
Entosthodon jamesonii may be small, but it is a fascinating and important component of many ecosystems. Its ability to thrive in disturbed habitats and its roles in soil and water dynamics make it a valuable contributor to the environments it inhabits. Next time you’re out for a walk, take a closer look – you might just spot this tiny but remarkable moss! What other small wonders are waiting to be discovered in the world around us?