
largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281336919_Didymodon_Rigidulus_var_Subulatus_ther_Bartram_Ex_EB_Bartram_RH_Zander_new_to_the_moss_flora_of_Mongolia_and_Asia
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of Tuerckheimia svihlae (E.B.Bartram) R.H.Zander, a captivating moss species belonging to the Pottiaceae family. Also known simply as Tuerckheimia, this tiny yet resilient plant has captured the hearts of bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike. Prepare to embark on a journey through the intricate details of this remarkable moss, where we’ll unravel its secrets and appreciate its unique place in the natural world.
Background
Before we delve into the specifics of Tuerckheimia svihlae, it’s essential to understand the broader context of mosses. These diminutive plants belong to the Bryophyta division, which encompasses a diverse array of non-vascular plants collectively known as bryophytes. Mosses, along with liverworts and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era.
Tuerckheimia_svihlae_4422_label.png from: https://vaplantatlas.org/index.php?do=plant&plant=4422&label=1&search=search
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
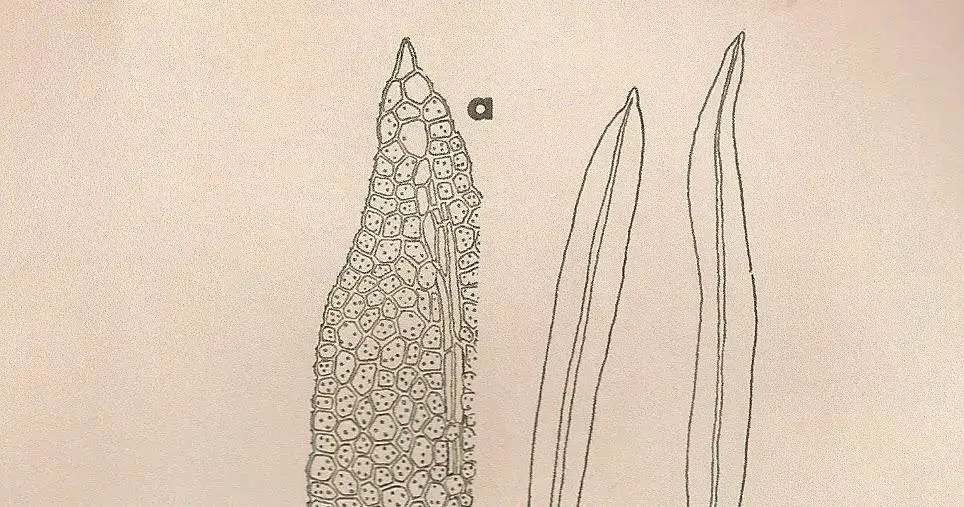
TUERCKHEIMIA%2BLINEARIS.jpg from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/01/musgos-pottiaceae-tuerckheimia-linearis.html
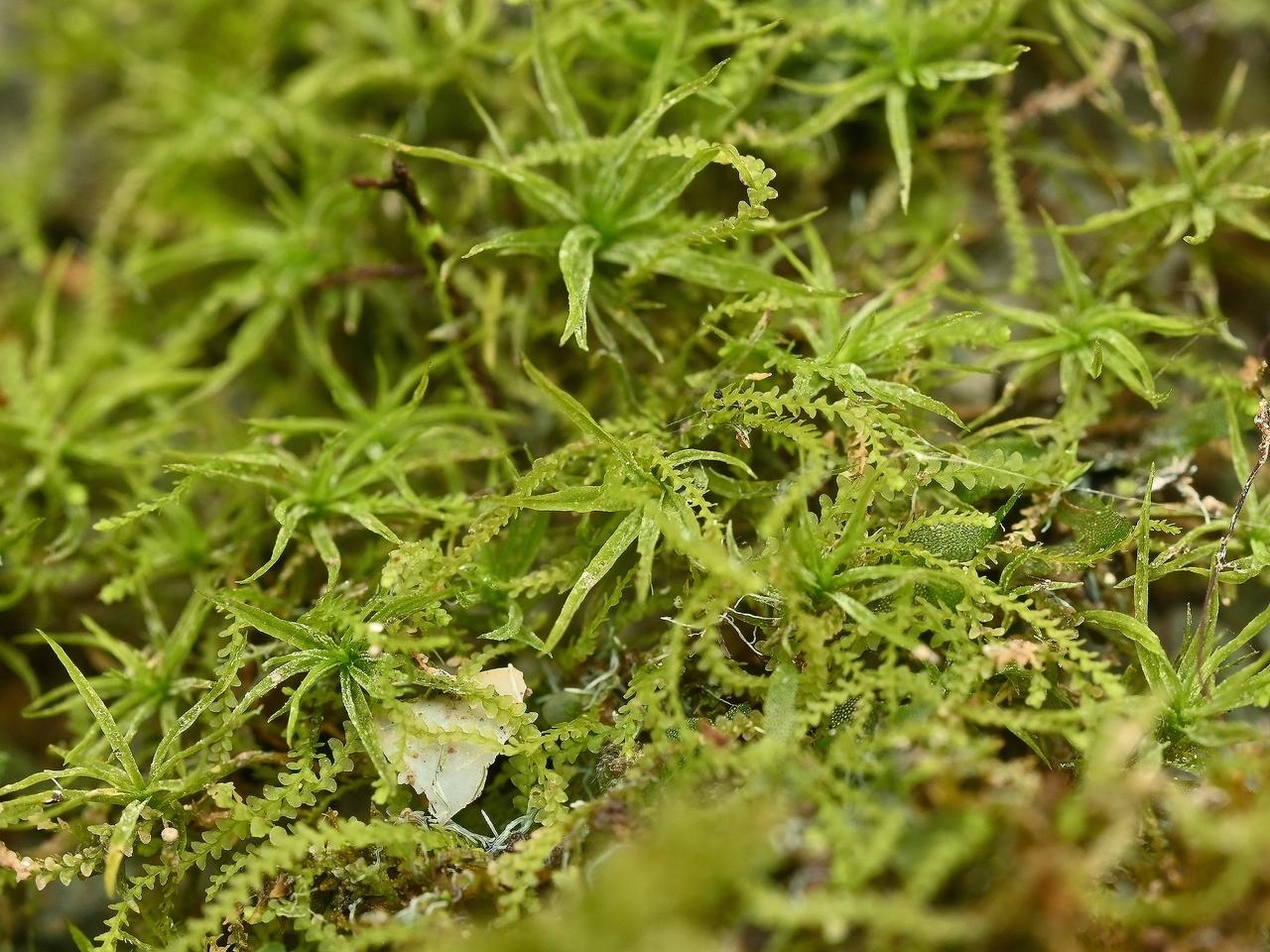
Tuerckheimia svihlae

tnChenia_leptophylla1612031811.jpg from: https://auth1.dpr.ncparks.gov/bryophytes/view.php?checklist_number=219903
is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a short hair point. The leaf margins are often recurved, and the leaf cells are

niseisibaigpke231231_1.jpg from: https://soyokaze2jp.blogspot.com/
quadrate to rectangular in shape.
One of the most striking features of this moss is its capsule, which is cylindrical and erect, supported by a reddish-brown seta (stalk). The
AATXAJxovROpiUe13_hhEh1RMwzw7MEj2EJT-F6_Bw=s900-c-k-c0xffffffff-no-rj-mo from: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCz4j0bAwqUS4ja20fbI1avA
operculum (lid) of the capsule is long-beaked, and the peristome (tooth-like structures) is well-developed, aiding in spore dispersal.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Tuerckheimia svihlae is widely distributed across various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa. It thrives in a variety of habitats, such as calcareous soils, rock crevices, cliff faces, and disturbed areas. This moss is often found in dry, exposed locations, showcasing its remarkable ability to adapt to harsh environmental conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Tuerckheimia svihlae plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, mosses like Tuerckheimia serve as important microhabitats for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of this moss is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, Tuerckheimia svihlae can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. When moisture becomes available, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Rocky Mountains of North America, researchers discovered that Tuerckheimia svihlae played a vital role in stabilizing soil on steep slopes, preventing erosion and facilitating the establishment of other plant species. This highlights the importance of this unassuming moss in maintaining the integrity of fragile ecosystems.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Tuerckheimia
 2330-l.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=13316 |
| Species | svihlae |
Growth Form
 3957250603_0798ab1254_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/62054865@N00/3957250603 |
Acrocarpous |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Margin | Recurved |
| Costa | Extending beyond leaf apex |
| Capsule | Cylindrical, erect |
| Operculum | Long-beaked |
| Peristome | Well-developed |
Conclusion
Tuerckheimia svihlae is a remarkable moss species that deserves our admiration and appreciation. Its ability to thrive in harsh environments, stabilize soils, and provide microhabitats for other organisms showcases the vital role it plays in the intricate web of life. As we continue to explore and understand the world of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these unsung heroes of the plant kingdom, ensuring their continued existence for generations to come?