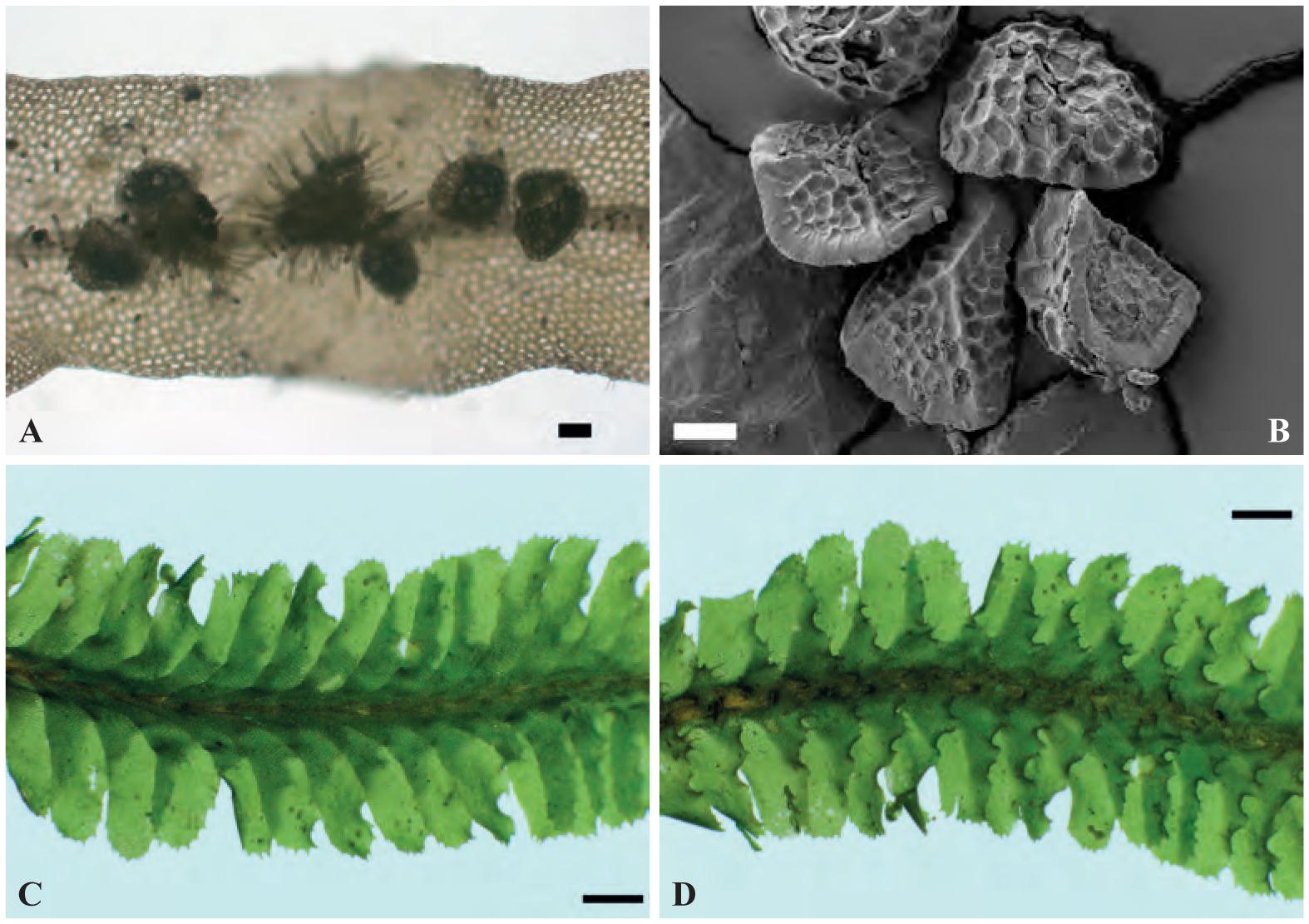
f06_50.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/herzogia/volume-28/issue-1/heia.28.1.2015.50/Additions-to-the-Liverwort-and-Hornwort-Flora-of-São-Tomé/10.13158/heia.28.1.2015.50.full
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Radula ankefinensis Gottsche ex Steph. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Radulaceae family. Often referred to simply as Radula, this unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this diminutive marvel and uncover its secrets.
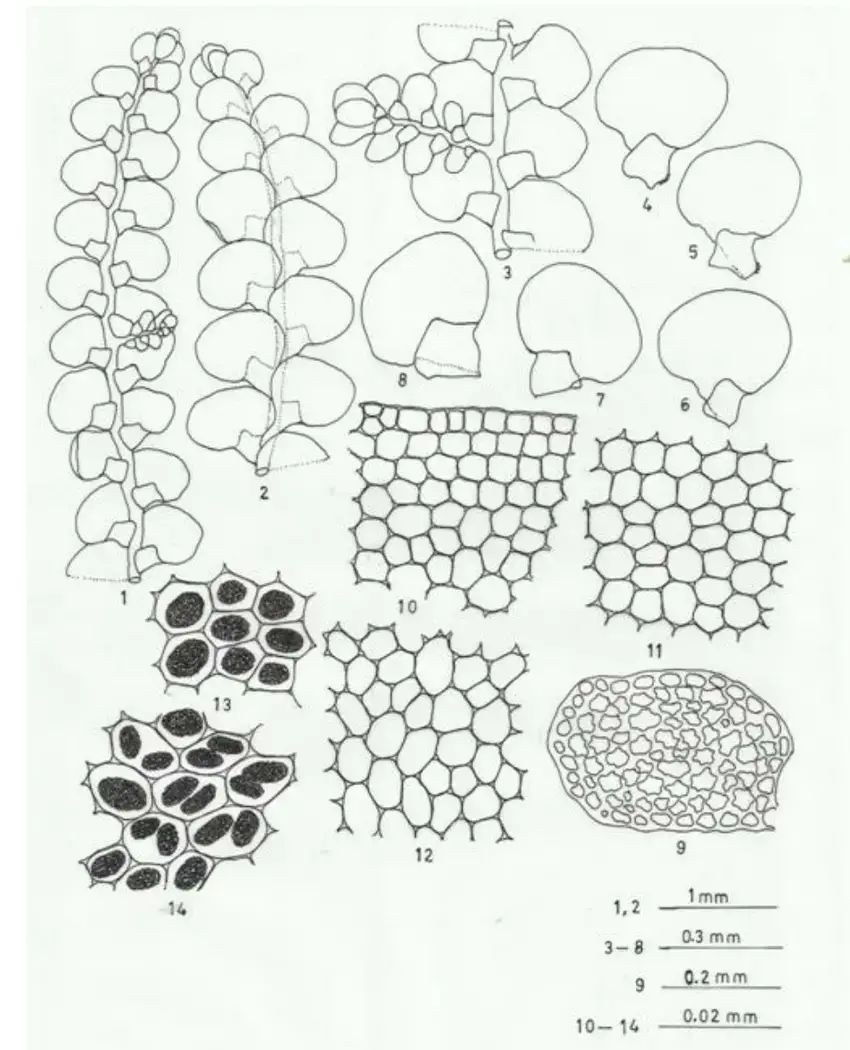
Radula-javanica-Gottsche-Figures-1-14-Figures-1-3-Plants-showing-habit-1-plant-in.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Radula-javanica-Gottsche-Figures-1-14-Figures-1-3-Plants-showing-habit-1-plant-in_fig3_258926968
Background
Before we explore the specifics of
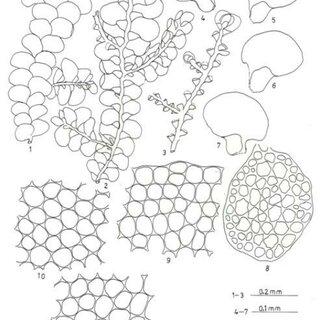
Radula-madagascariensis-Gottsche-Figures-1-11-Figures-1-3-Plant-showing-habit-1_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Radula-madagascariensis-Gottsche-Figures-1-11-Figures-1-3-Plant-showing-habit-1_fig1_258926968
Radula ankefinensis, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. Mosses belong to the division Marchantiophyta
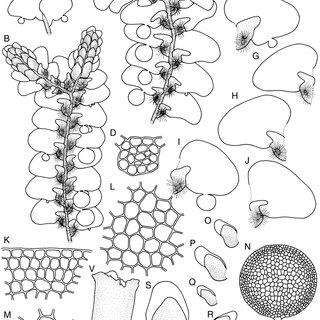
Radula-nymanii-Steph-A-A-portion-of-plant-in-dorsal-view-B-A-portion-of-male-plant_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/292186036_The_genus_Radula_Radulaceae_Marchantiophyta_in_Andaman_Nicobar_Islands_India
, which encompasses liverworts, hornworts, and mosses. These ancient and resilient plants have been around for millions of years, predating even the earliest vascular plants. Within this diverse group, the order Jungermanniopsida houses the leafy liverworts, including the Radulaceae family.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Radula ankefinensis is a tiny, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on various substrates. Its delicate, flattened stems bear overlapping leaves arranged in two rows, giving it a distinctive feathery appearance. The leaves themselves are deeply divided, resembling miniature ferns or fronds. This intricate structure not only adds to the moss’s visual appeal but also plays a crucial role in its ability to absorb and retain moisture.
Global Distribution and Habitat
While Radula ankefinensis is found in various regions around the world, it thrives particularly well in tropical and subtropical environments. This moss can be encountered growing on tree bark, rocks, and even soil in humid forests, where it forms vibrant green carpets. Its ability to adapt to a wide range of habitats is a testament to its resilience and versatility.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Radula ankefinensis plays a vital role in its ecosystem. These mosses act as sponges, absorbing and retaining moisture, creating microhabitats for other organisms to thrive. They also contribute to soil formation and nutrient cycling, making them essential components of healthy forest ecosystems.
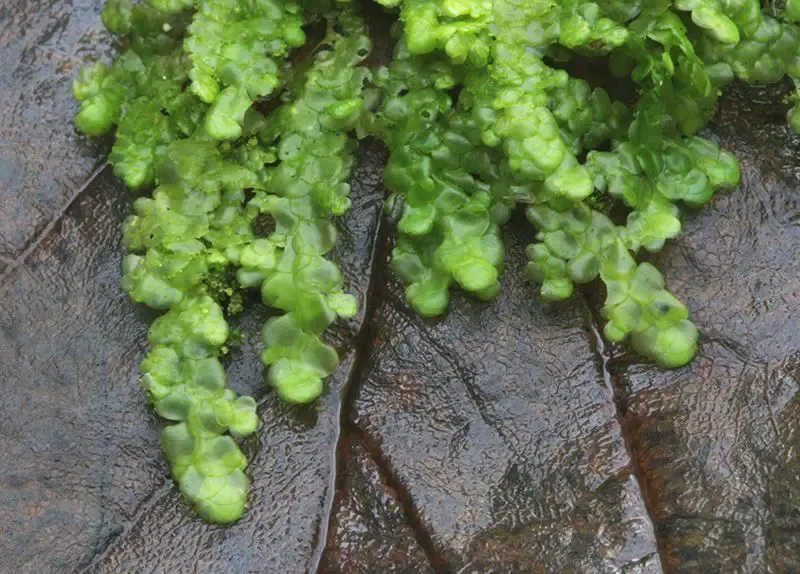

d474226b15945ba62b0ea098db18036f.jpg from: https://www.asturnatura.com/genero/radula
One of the remarkable adaptations of Radula ankefinensis is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. When conditions become dry, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves and slowing down its metabolic processes. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its incredible resilience.
Case Studies/Examples
In the lush rainforests of Madagascar, Radula ankefinensis carpets the trunks of ancient trees, creating a verdant tapestry that captivates the senses. Similarly, in the cloud forests of Costa Rica, this moss forms vibrant green cushions on the forest floor, providing a soft and inviting surface for hikers to rest upon.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Radula ankefinensis Gottsche ex Steph. |
| Family | Radulaceae |
| Order | Jungermanniopsida |
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Two rows, overlapping |
| Leaf Shape | Deeply divided, fern-like |
| Habitat | Tree bark, rocks, soil (humid forests) |
| Distribution | Tropical and subtropical regions |
Conclusion
The Radula ankefinensis moss may be small in stature, but its impact on the natural world is profound. From its intricate morphology to its vital ecological roles, this unassuming plant deserves our admiration and respect. As we continue to explore the wonders of the bryophyte world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better appreciate and protect these often overlooked yet invaluable members of our ecosystems?