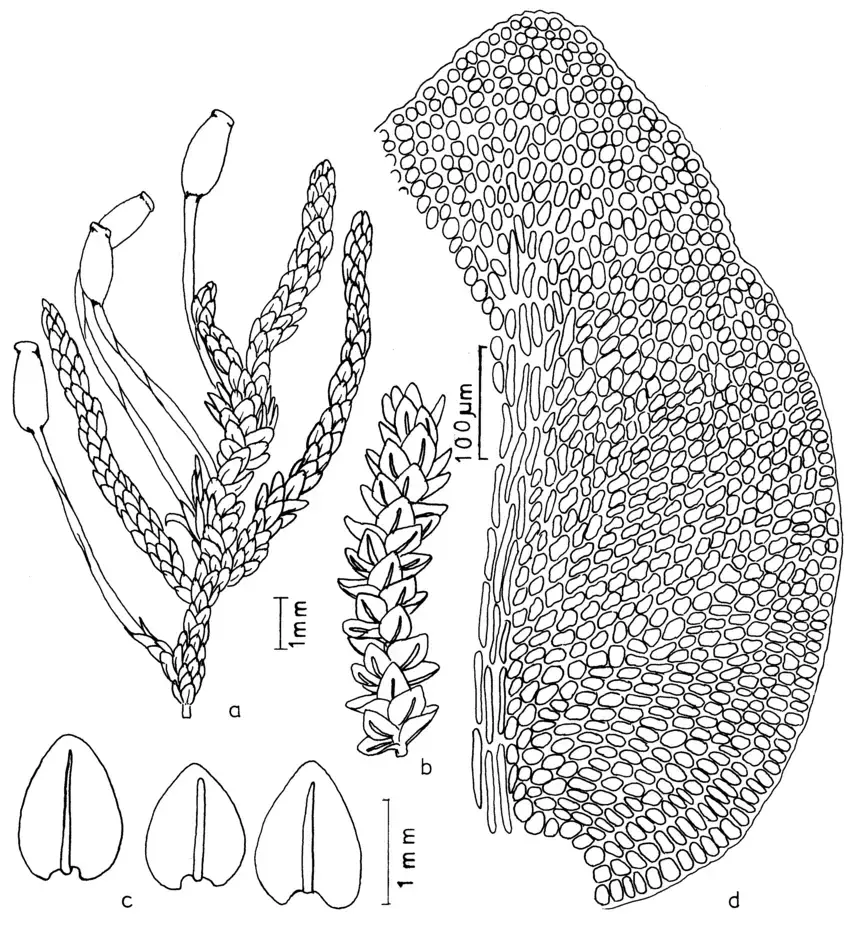
Dimerodontium-mendozense-Mitt-a-Habit-of-gametophyte-with-sporophyte-b-Habit-of.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Dimerodontium-mendozense-Mitt-a-Habit-of-gametophyte-with-sporophyte-b-Habit-of_fig3_291578034
Exploring the Fascinating World of Dimerodontium Mitt. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play a vital role in many ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting moss is

51956537051_7a3e848cf2_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/revista_de_biologia_neotropical/51956537051/
Dimerodontium Mitt., also known simply as Dimerodontium. This moss belongs to the Fabroniaceae

00ae422930c03355c1279e7d3670b688.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/5c288503a07b98ea98b8f1ea8f885b55
family and is found in various regions across the globe. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of Dimerodontium Mitt. moss and explore its unique characteristics, distribution, and ecological importance.
Background
Mosses are small, non-vascular plants that belong to the division Bryophyta. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead having simple structures that perform similar functions. Mosses reproduce through spores rather than seeds and require moisture for reproduction. There are over 12,000 species of moss worldwide.

3b70cf1a15e9491cf8c1e6cac433e8a1.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/d09c4cd9713aa3ed3d33a06d0ff339cf
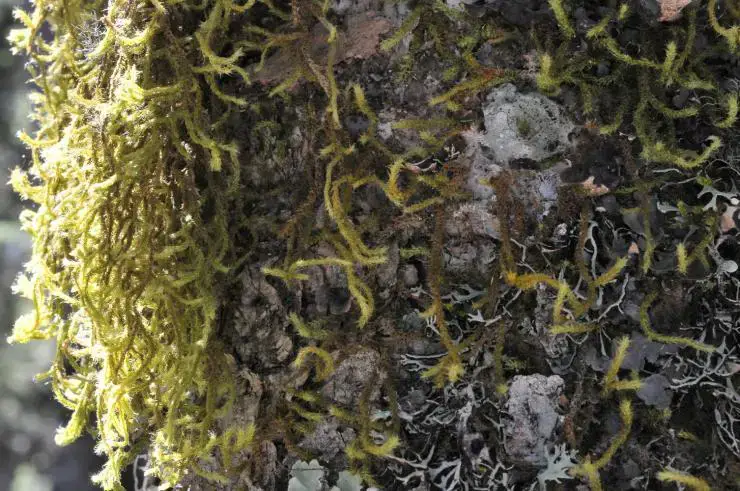
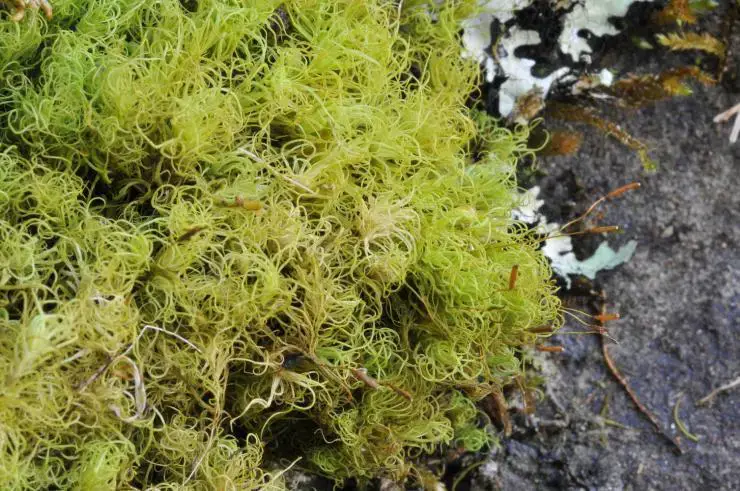
Dimerodontium Mitt. is a genus of moss in the Fabroniaceae family. The Fabroniaceae family contains about 25 genera and 450 species of mosses, primarily found in tropical and subtropical regions. Dimerodontium mosses are characterized by their small size and delicate, branching stems.
Morphology and Identification
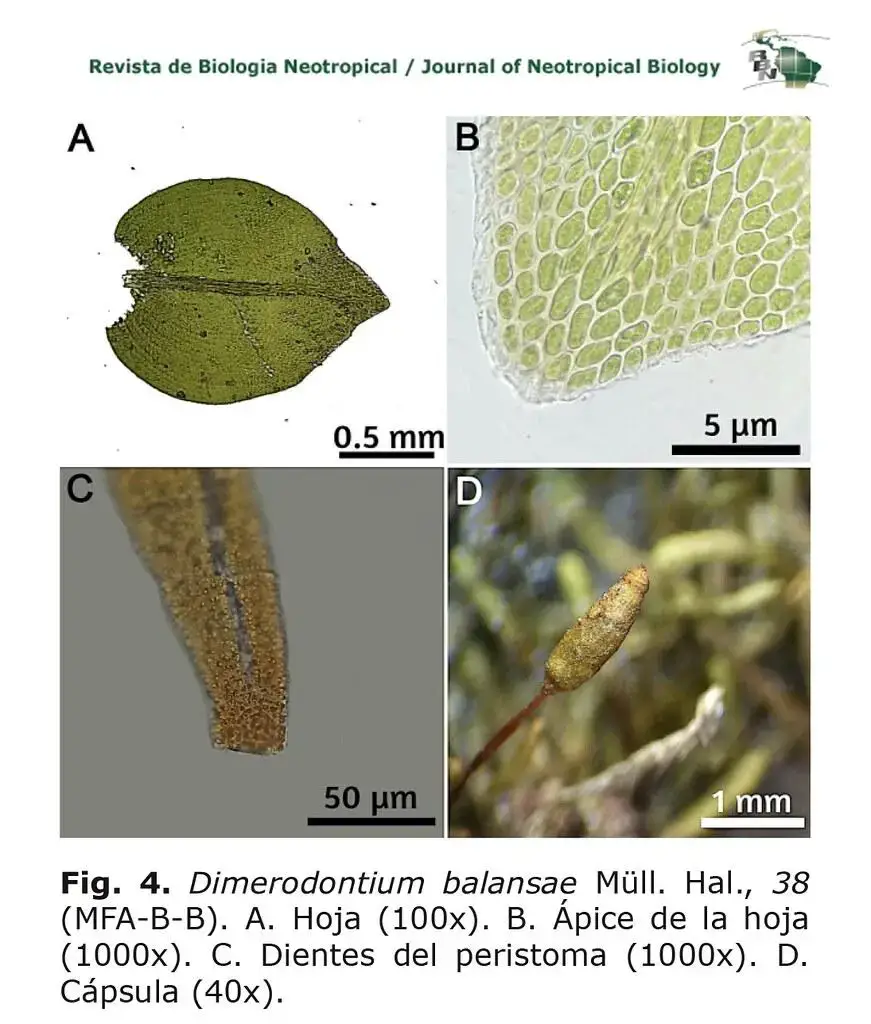
Dimerodontium Mitt. mosses are typically small, with stems reaching lengths of only a few centimeters. The stems are delicate and branching, often forming dense mats or cushions. The leaves are small, usually less than 2 mm long, and are arranged in a spiral pattern along the stem. The leaf margins are often toothed or serrated.
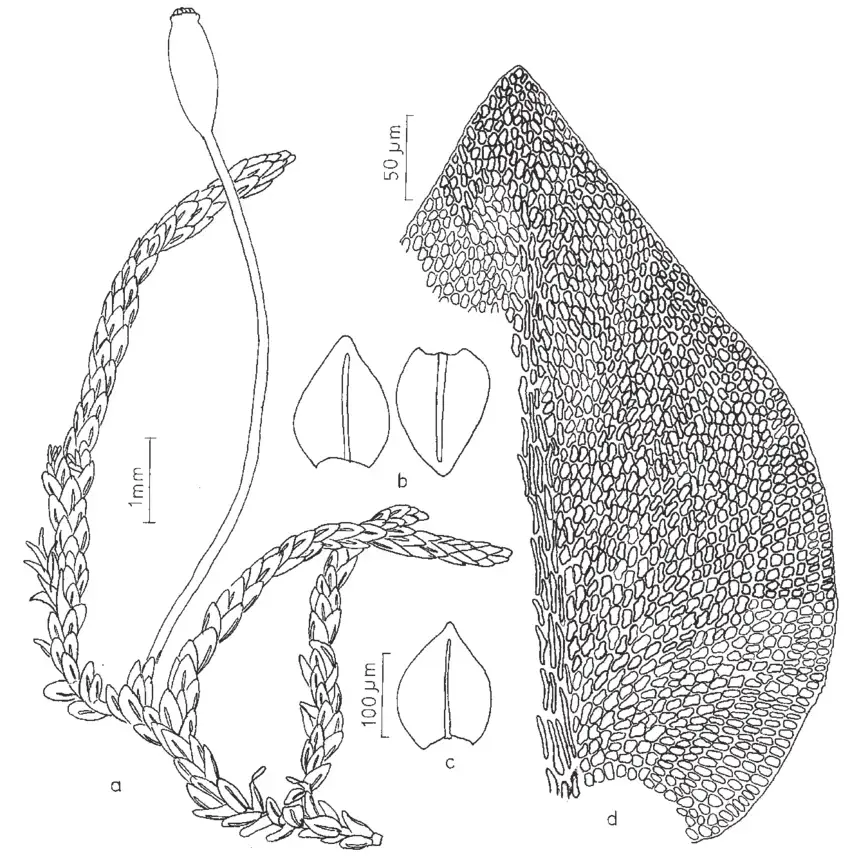
Figura-7-Dimerodontium-pellucidum-Schwaegr-Mitt-a-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-b-c.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-7-Dimerodontium-pellucidum-Schwaegr-Mitt-a-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-b-c_fig2_262547004
One key identifying feature of Dimerodontium mosses is their capsules, which are the spore-bearing structures. The capsules are erect and cylindrical, with a distinct peristome, a ring of teeth around the mouth of the capsule that aids in spore dispersal. The peristome teeth in Dimerodontium are usually paired and reflexed when dry.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Dimerodontium Mitt. mosses are found in various regions around the world, including:
- Central and South America
- Africa
- Asia
- Australia and New Zealand
These mosses typically grow on tree trunks, branches, and logs in humid forests and woodlands. They can also be found on rocks and soil in moist, shaded areas. Dimerodontium mosses prefer warm, humid climates and are most diverse in tropical and subtropical regions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Dimerodontium plays important ecological roles:
Moisture retention: Mosses absorb and retain water, helping to regulate moisture levels in their environment. This is particularly important in humid forests where Dimerodontium is found.
Nutrient cycling: Mosses trap and store nutrients from the air and water, making them available to other plants and organisms in the ecosystem.
Habitat provision: Mosses provide shelter and habitat for various small invertebrates, such as insects, spiders, and mites.

moss-bathroom-mat-3655.jpg from: https://odditymall.com/natural-moss-bathroom-mat
Dimerodontium mosses have several adaptations that allow them to thrive in their environments:
Figura-3-Dimerodontium-pellucidum-Schwaegr-Mitt-a-aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-com.ppm from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-3-Dimerodontium-pellucidum-Schwaegr-Mitt-a-aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-com_fig5_237363226
- Poikilohydry: Like other mosses, Dimerodontium can tolerate desiccation and quickly rehydrate when water becomes available.

Golden_Thread_Moss_Moniteau_Co_4-12-15.jpg from: https://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/mosses
- Branching stems: The delicate, branching stems of Dimerodontium allow them to form dense mats, which help retain moisture and protect against desiccation.
- Spore dispersal: The paired, reflexed peristome teeth in Dimerodontium capsules aid in efficient spore dispersal, allowing the mosses to colonize new areas.

4c2951bea3af6a9338013bdee77a4559.jpg from: http://www.pinterest.com/pin/222646775302380722/
Conclusion
Dimerodontium Mitt. moss may be small, but it plays a significant role in the ecosystems where it is found. From moisture retention and nutrient cycling to providing habitat for small invertebrates, these fascinating plants are an essential component of humid forests and woodlands worldwide. Next time you’re in a suitable habitat, take a closer look and see if you can spot some Dimerodontium moss – you might be surprised by the intricate beauty of these tiny plants!

2686847280_574703eb77_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/warrenski/2686847280/