
h-hubertus-cornelis-van-noorde-1768-1769-reimagined-by-gibon-classic-art-with-a-modern-twist-reimagined-RAYB7J.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/h-hubertus-cornelis-van-noorde-1768-1769-reimagined-by-gibon-classic-art-with-a-modern-twist-reimagined-image230482886.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Herbertus armitanus (Steph.) H.A.Mill. moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Herbertaceae family. This unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s diversity.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of this intriguing moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification.

Drinkmok-met-de-H-van-Hubertus-TH.-DSC_8931.jpg from: https://www.de-veluwenaar.nl/2019/04/24/het-legendarische-hert-hubertus-deel-144-2/drinkmok-met-de-h-van-hubertus-th-dsc_8931/
Herbertus armitanus belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta, also known as liverworts, and the class Jungermanniopsida. This classification places it within the realm of bryophytes, a group of non-vascular plants that play crucial roles in various ecosystems.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Herbertus armitanus is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the surfaces it inhabits. Its delicate, thread-like stems are adorned with tiny, overlapping leaves, creating a intricate and visually appealing pattern. The leaves themselves are deeply divided, giving the plant a feathery appearance.
One of the distinctive features of Herbertus armitanus is its unique reproductive structures. The male and female reproductive organs are borne on separate plants, a characteristic known as dioecious. The male plants produce antheridia, while the female plants develop archegoniophores, which are specialized structures that bear the archegonia (female reproductive organs).
Global Distribution and Habitat
Herbertus armitanus is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often found growing on rocks, tree bark, and decaying logs in forests and other woodland areas.
This moss prefers cool, humid conditions and is commonly found in areas with high rainfall or near streams and waterfalls. Its ability to adapt to a wide range of habitats has contributed to its widespread distribution and success as a species.

50146811272_f776e0029e_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/astrid/50146811272/
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Herbertus armitanus plays a vital role in the ecosystems it inhabits. As a pioneer species, it helps in the colonization of bare surfaces, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide a microhabitat for various invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Herbertus armitanus is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving itself when moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
Case Studies/Examples

8e3bfc6ef52b7eb243abfd23a8a4bed2.jpeg from: https://www.berggruen.com/news/the-reflective-playful-art-of-stephanie-h-shih/associations
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered a unique association between Herbertus armitanus and certain species of fungi. This symbiotic relationship, known as mycorrhizal association, enhances the moss’s ability to absorb nutrients from the surrounding environment, highlighting the intricate connections within ecosystems.

history-clifton-mill-imited-edition-p-buckley-moss.jpeg from: https://canadagoosegallery.com/product/clifton-mill/
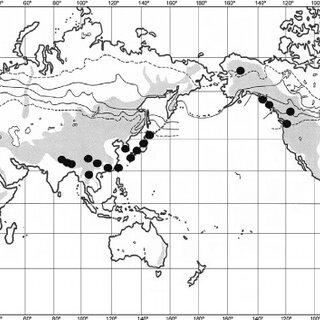
Distribution-of-Herbertus-aduncus-subsp-aduncus-based-on-examined-specimens_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Herbertus-sendtneri-from-isotype-of-H-delavayi-G-a-Habit-b-Part-of-the_fig6_255609640

abandoned-moss-covered-water-mills-and-a-small-water-canal-in-moinhos-de-rei-cabeceiras-de-basto-portugal-2DJ4339.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/abandoned-moss-covered-water-mills-and-a-small-water-canal-in-moinhos-de-rei-cabeceiras-de-basto-portugal-image389782157.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Herbertaceae |
| Genus | Herbertus |
| Species | armitanus |
| Common Name | Herbertus moss |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Shape | Deeply divided, feathery |
| Reproduction | Dioecious |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | Widespread globally |
Conclusion
The Herbertus armitanus (Steph.) H.A.Mill.
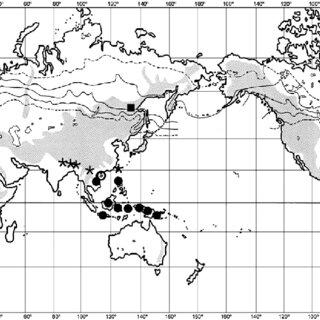
Distribution-of-Herbertus-armitanus-H-buchii-H-guangdongii-and-H-kurzii-Solid_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Distribution-of-Herbertus-aduncus-subsp-aduncus-based-on-examined-specimens_fig1_255609640
moss is a remarkable example of nature’s intricate design and resilience. Its ability to thrive in diverse environments, contribute to ecosystem health, and adapt to changing conditions make it a fascinating subject of study. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, this unassuming moss serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity that surrounds us, inviting us to delve deeper into the mysteries that lie within the realm of bryophytes.

abandoned-moss-covered-water-mills-small-canal-moinhos-de-rei-cabeceiras-basto-portugal-portuguese-nature-landscape-204707146.jpg from: https://www.dreamstime.com/abandoned-moss-covered-water-mills-small-canal-moinhos-de-rei-cabeceiras-basto-portugal-portuguese-nature-landscape-image204707146
Thought-provoking question: In a world where biodiversity is under constant threat, how can we better appreciate and protect the often overlooked yet vital members of our ecosystems, such as the Herbertus armitanus moss?

101279803-68905-800.jpg from: https://britishlistedbuildings.co.uk/101279803-former-moss-mill-preston