266878.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/930633
Introduction
Welcome, fellow moss enthusiasts! Today, we’re going to delve into the fascinating world of Heterocladium dimorphum (Brid.) Schimp., a captivating member of the Heterocladiellaceae family, commonly known as Heterocladium. This unassuming moss might seem small, but it packs a punch in terms of its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty details, let’s set the stage. Bryophytes, or mosses, are a diverse group of non-vascular plants that have been around for millions of years. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers, soil stabilizers, and even indicators of environmental health.

375859.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5190
Heterocladium dimorphum is one such moss that deserves our attention and appreciation.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
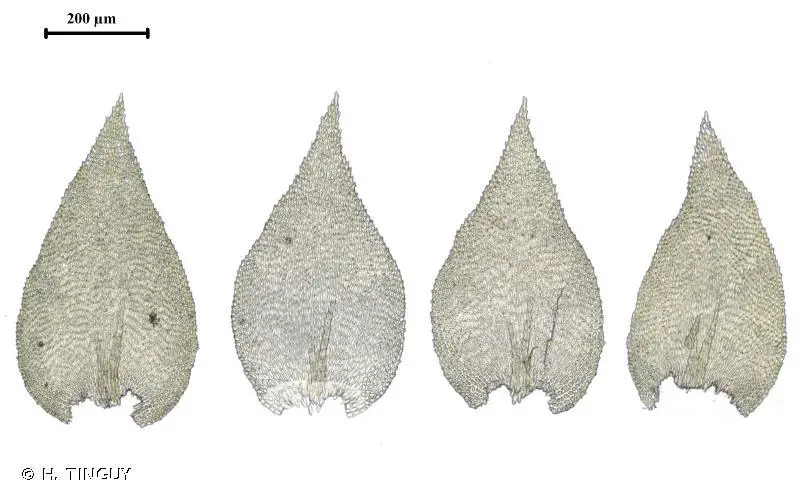
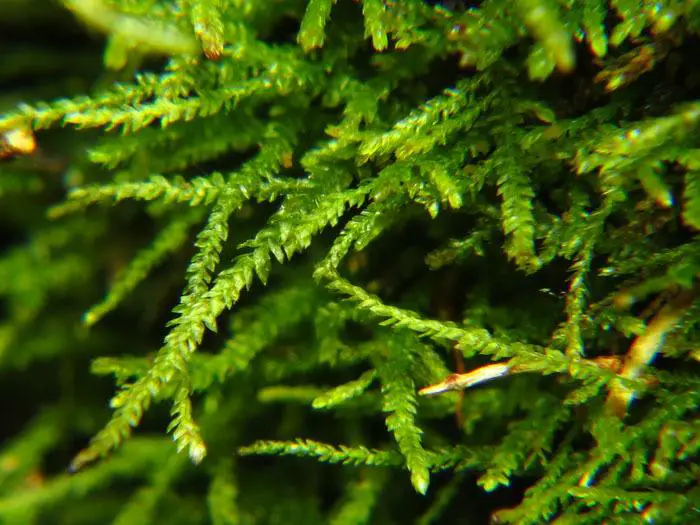
Heterocladium dimorphum is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems and branches grow horizontally. It forms dense, glossy green mats or tufts, with stems that can reach up to 10 cm in length. The leaves are

842948.jpg from: https://www.bio-forum.pl/messages/3280/842946.html
dimorphic, meaning they come in two distinct shapes – the stem leaves are ovate-lanceolate, while the branch leaves are smaller and more narrowly lanceolate. This dimorphism is a key identifying feature of this moss.
Global Distribution and Habitat
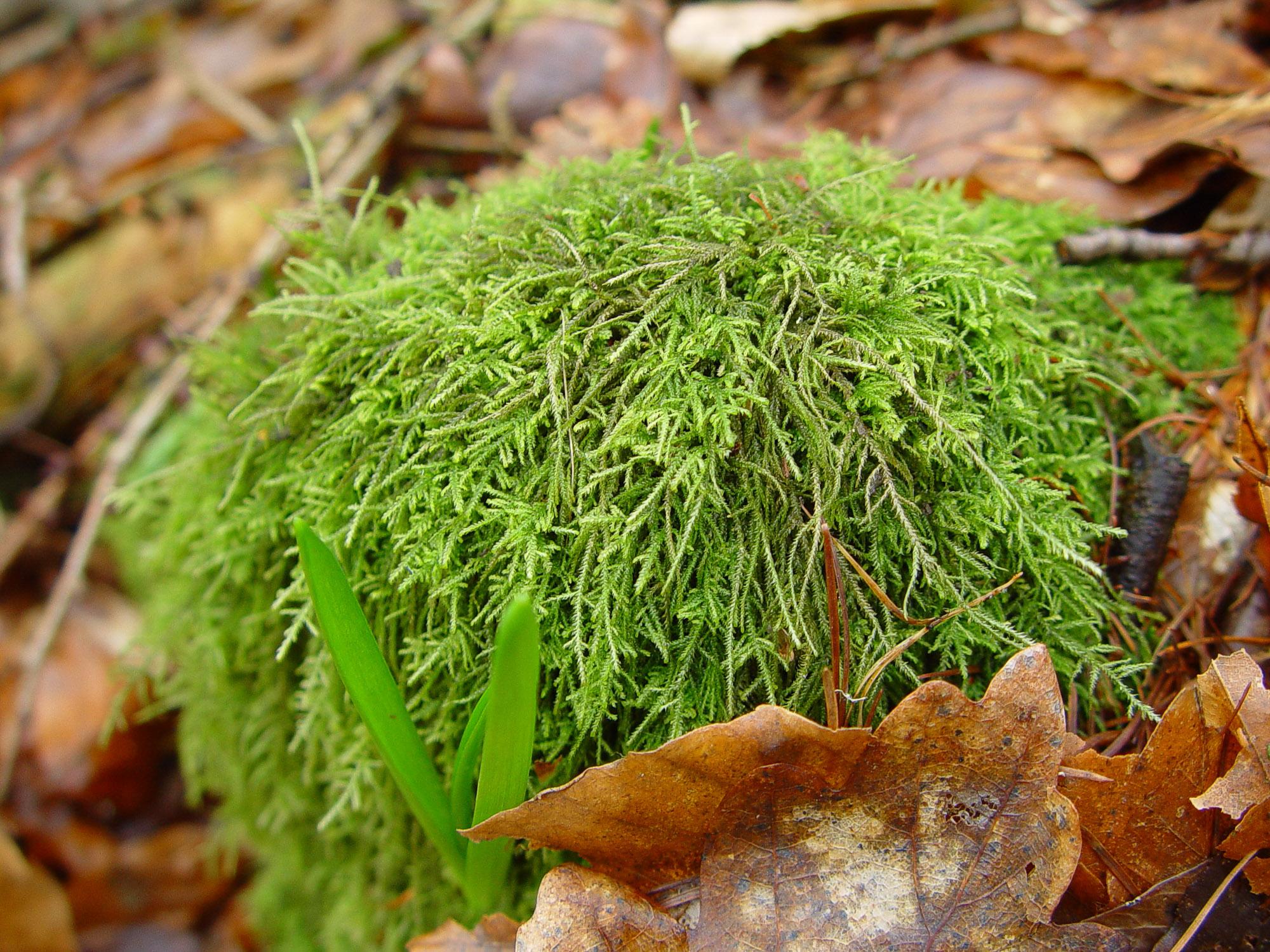
This moss has a widespread distribution, found across Europe, Asia, North America, and even parts of South America. It thrives in cool, moist environments, often growing on rotting logs, stumps, and the bases of trees in coniferous or mixed forests.

Heterocladium-heteropterum-207.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/heterocladium-heteropterum/
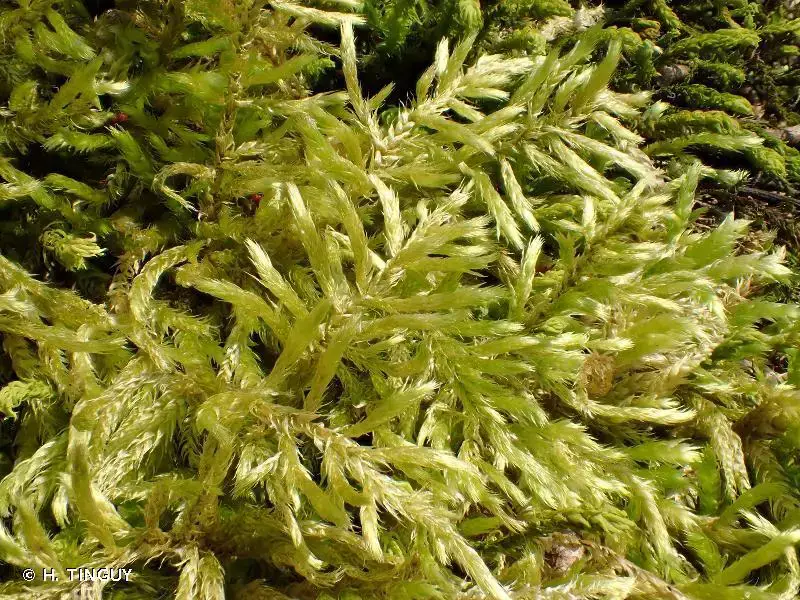

263620.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/434456
Heterocladium dimorphum is a true lover of shade and moisture, making it a common sight in damp, shaded woodlands.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like many mosses, Heterocladium dimorphum plays a vital role in its ecosystem. Its dense mats help retain moisture and prevent soil erosion, creating a microhabitat for other tiny organisms. Additionally, this moss is known for its ability to absorb and retain heavy metals, making it a potential biomonitor for environmental pollution.

Bryum-caespiticium-7.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-bryum-caespiticium/
One of the fascinating adaptations of Heterocladium dimorphum is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. While it produces spores through its reproductive structures, it can also propagate vegetatively through fragmentation, allowing it to colonize new areas efficiently.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest, researchers found that Heterocladium dimorphum played a crucial role in maintaining the moisture levels and nutrient cycling in old-growth forests. Its presence was closely linked to the overall health and biodiversity of these ecosystems.
Technical Table

2020-08-29-11-58-02.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/heterocladium-flaccidum/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Heterocladiellaceae |
| Genus | Heterocladium |
| Species | dimorphum |
Conclusion
Heterocladium dimorphum might be small, but its impact on the natural world is anything but insignificant. From its unique morphology to its ecological roles, this moss is a true marvel of nature. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, let’s ponder this thought-provoking question: How many other hidden gems like Heterocladium dimorphum are waiting to be discovered and celebrated?