image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/12-Entodontopsis-setschwanica-Broth-W-R-Buck-et-R-R-Ireland-1-sporophytic_fig1_308534623
Exploring the Fascinating World of Pseudoleskea setschwanica Broth. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Pseudoleskea setschwanica Broth., a moss in the Pseudoleskeaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of this fascinating bryophyte, from its morphology to its ecological importance. Get ready to discover the hidden world of

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/12-Entodontopsis-setschwanica-Broth-W-R-Buck-et-R-R-Ireland-1-sporophytic_fig1_308534623
Pseudoleskea!
Background on Mosses
Before we focus on P. setschwanica specifically, let’s review some background on mosses in general. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead having structures that serve similar functions. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and require moisture for sexual reproduction. There are over

image from: https://subjectweb.forest.gov.tw/species/mosses/mosses/192.htm
12,000 species of moss found all around the world, from the Arctic to the tropics.
Morphology and Identification
Pseudoleskea setschwanica is a relatively small moss, typically growing in dense mats or cushions. Its stems are irregularly branched and covered in small, ovate leaves. The leaves have a short, double costa (midrib) and are usually around 0.5-1 mm long. Capsules are rare but cylindrical and borne on short setae when present.

image from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/156427-Pseudoleskea
Distinguishing P. setschwanica
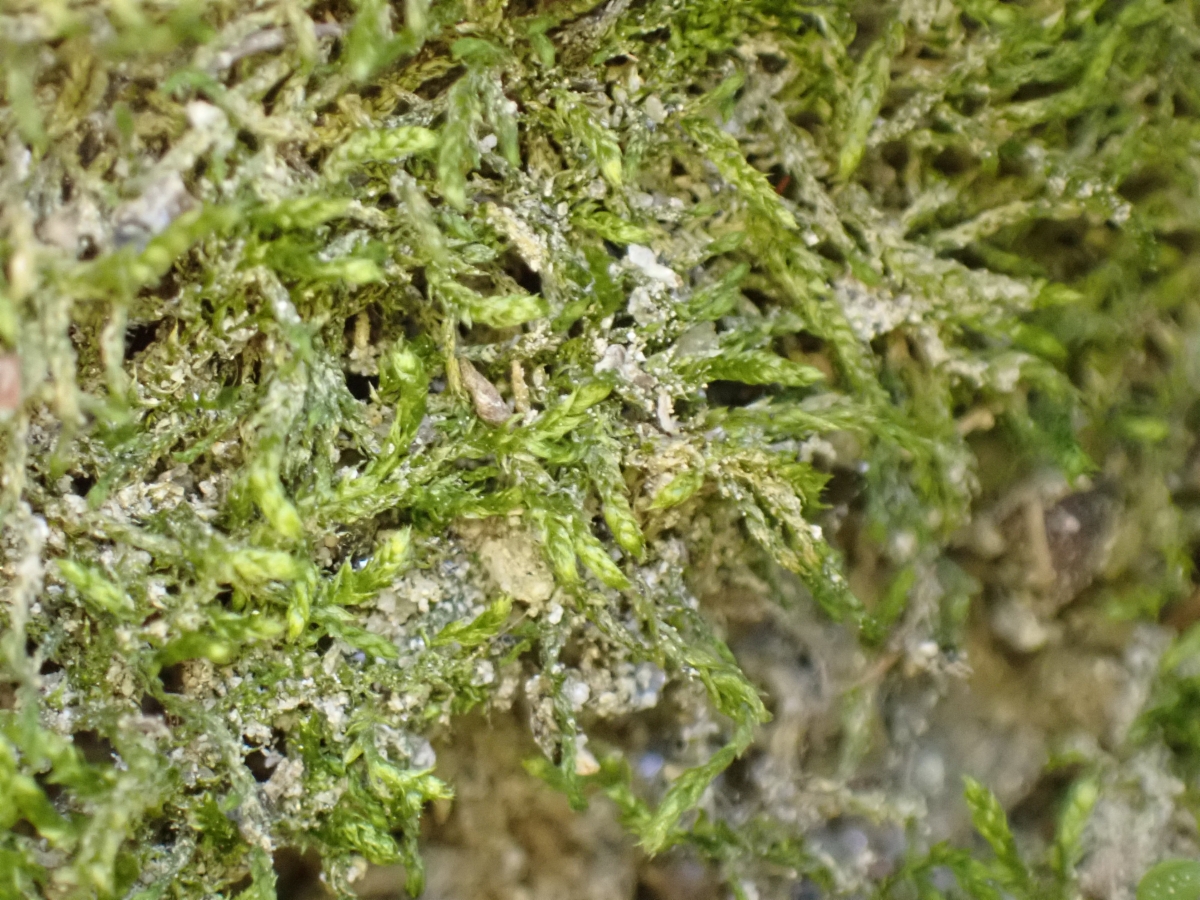

image from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=14098
from similar species can be tricky and often requires microscopic examination. Key identifying features include:
- Ovate, concave leaves with short, forked costae
- Irregular branching pattern
- Small, cylindrical capsules (when present)
Global Distribution and Habitat
P. setschwanica has a wide distribution, being found across much of Asia, Europe, and North America

image from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552
. It typically grows on rock or bark in montane forests and subalpine zones. In North America, it ranges from
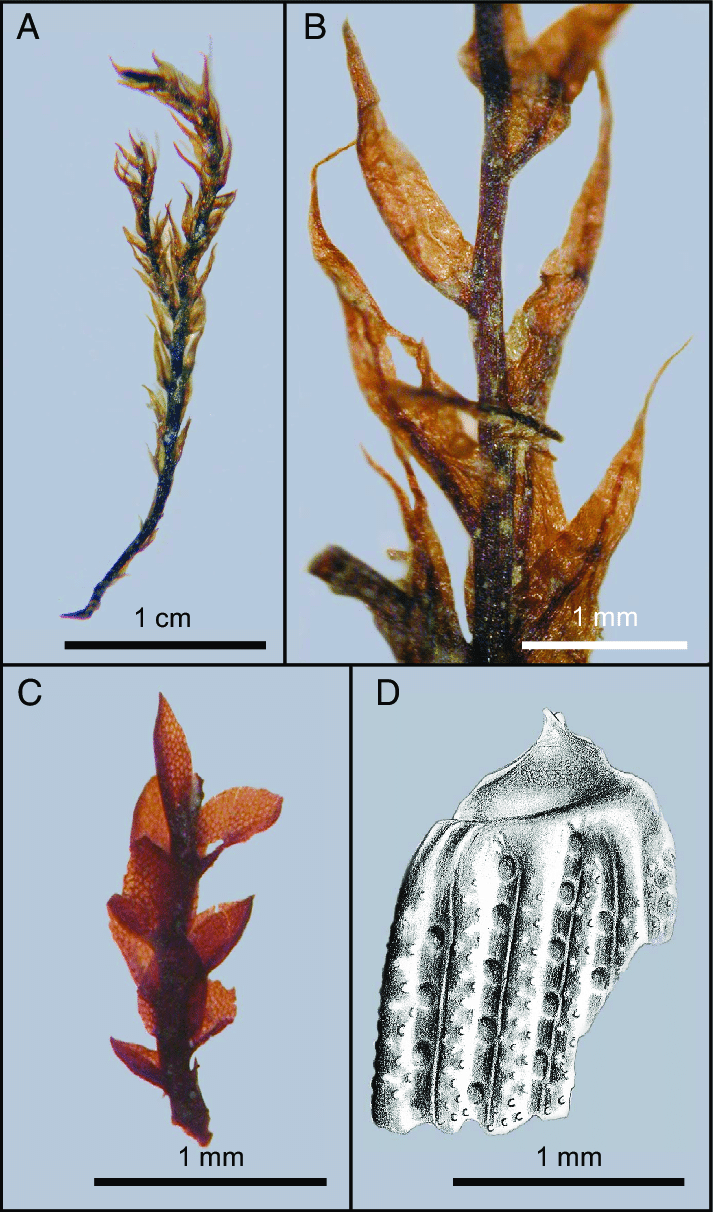
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fossil-mosses-and-a-beetle-A-Stem-and-leaves-of-the-semiaquatic-moss-Drepanocladus_fig3_23148177
Alaska to Newfoundland south to the mountains of California, Arizona, and New Mexico

image from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5248
.
This moss is able to tolerate cold temperatures and high elevations, often growing in exposed sites above treeline. It is a component of cliff and boulder plant communities in subalpine and alpine zones.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, P. setschwanica plays important roles in its ecosystem:
- Helps retain moisture and prevent erosion
- Provides habitat for micro-organisms
- Regulates nutrient cycling
- Acts as a pioneer species in succession
Its small size and dense growth form help it conserve moisture in exposed, rocky habitats. The ability to dry out and rehydrate allows it to survive harsh conditions.
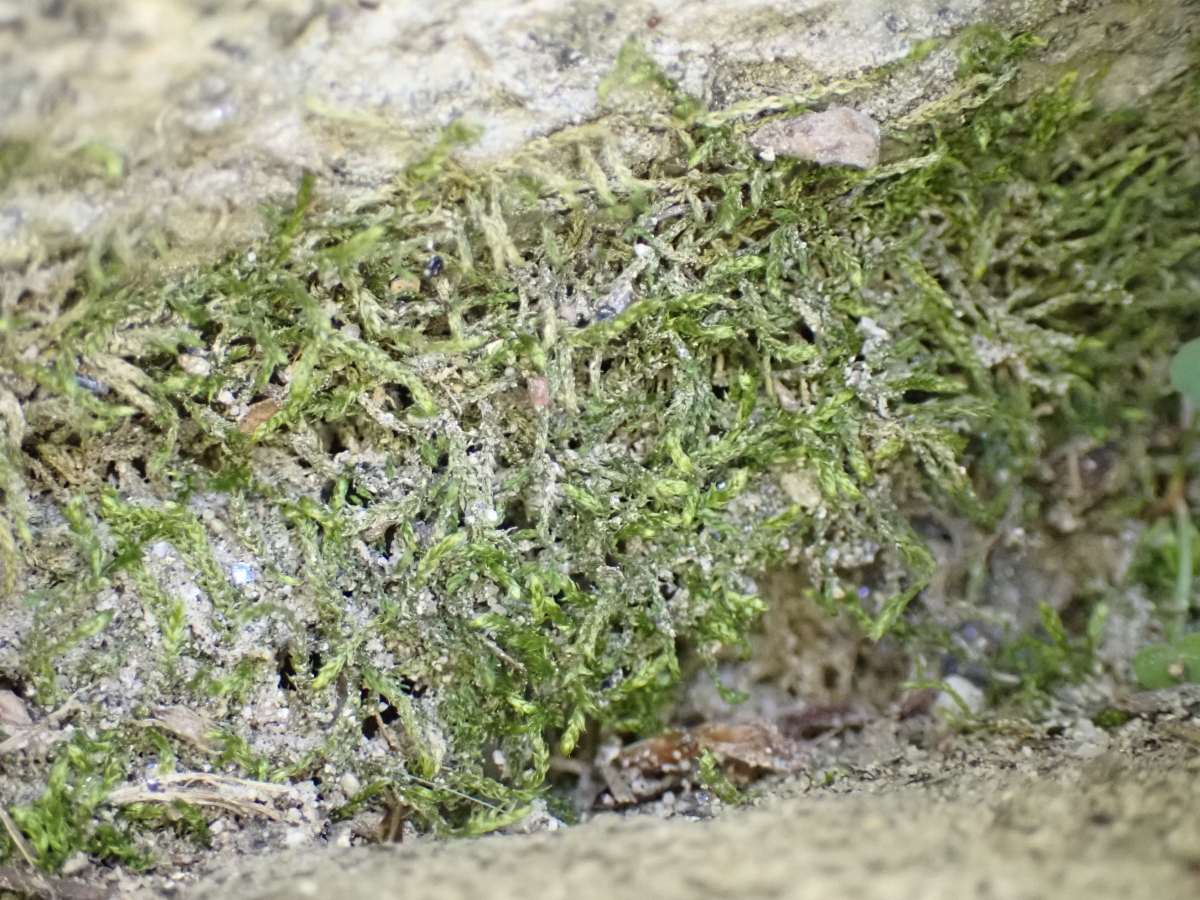

image from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=14098
Conclusion

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/12-Entodontopsis-setschwanica-Broth-W-R-Buck-et-R-R-Ireland-1-sporophytic_fig1_335110680
The diminutive Pseudoleskea setschwanica may not be the most glamorous plant, but it is a fascinating and ecologically valuable species. From the Himalayas to the Rockies, this mighty moss makes its home in some of the world’s harshest environments. Next time you’re hiking in the mountains, take a closer look at the rocks and see if you can spot this bryological wonder!