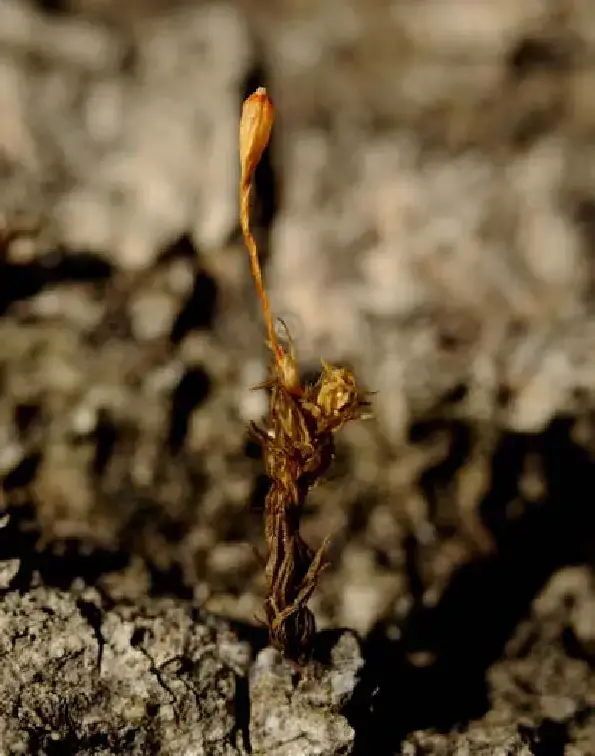

Single-shoot-of-Ulota-coarctata-P-Beauv-Hammar-photo-V-Plasek.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Single-shoot-of-Ulota-coarctata-P-Beauv-Hammar-photo-V-Plasek_fig1_303995584
Introduction
The world of bryophytes, or non-vascular plants, is a fascinating realm that often goes unnoticed by many. Among these diminutive yet remarkable organisms is the Ulota coarctata (P.Beauv.) Hammar moss, a member of the Orthotrichaceae family, commonly known as Ulota. This unassuming moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate and diverse world of bryology.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Ulota coarctata, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest and most resilient life forms on Earth. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.

Patch-of-Ulota-coarctata-P-Beauv-Hammar-on-bark-of-Quercus-petraea-in-the-forest.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Patch-of-Ulota-coarctata-P-Beauv-Hammar-on-bark-of-Quercus-petraea-in-the-forest_fig2_303995584
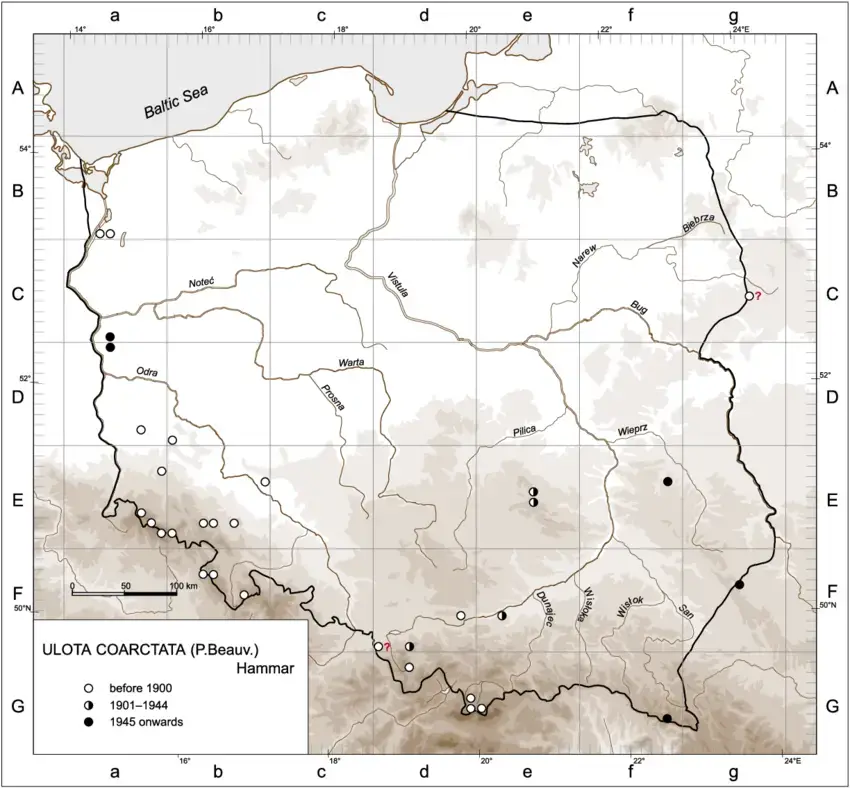
Distribution-map-for-Ulota-coarctata-P-Beauv-Hammar-in-Poland.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Distribution-map-for-Ulota-coarctata-P-Beauv-Hammar-in-Poland_fig3_303995584
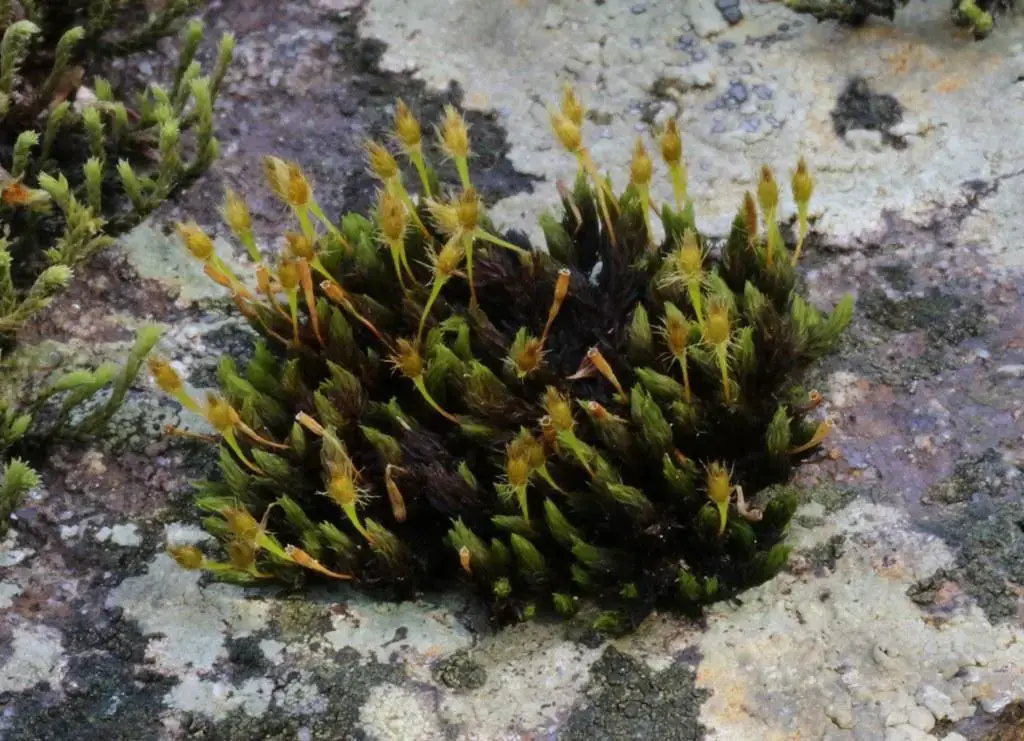

17941970781_2cdf5d2fff_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/26803925@N05/17941970781/
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Ulota coarctata

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/170059-Ulota-coarctata
is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and costate (with a prominent midrib), often curling when dry. The calyptrae (caps covering the developing sporophytes) are hairy, a distinctive feature that aids in identification. The capsules (spore-bearing structures) are immersed within the perichaetial leaves, giving the moss a unique appearance.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Ulota coarctata is widely distributed across various regions, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of Africa. It thrives in a range of habitats, from tree bark and rocks to soil and decaying wood. This moss is often found in temperate and boreal forests, where it plays a vital role in the ecosystem’s nutrient cycling and moisture retention.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like many bryophytes, Ulota coarctata exhibits remarkable adaptations that enable it to survive in harsh environments. Its ability to desiccate and revive upon rehydration is a testament to its resilience. Additionally, this moss contributes to the formation of biological soil crusts, which help stabilize soil and prevent erosion.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found that Ulota coarctata

ulota-coarctata.jpeg from: https://projets.cbnmc.fr/bryophytes/especes-remarquables
played a crucial role in the epiphytic (tree-dwelling) bryophyte communities. Its presence on tree bark provided microhabitats for other bryophyte species, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the forest ecosystem.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Orthotrichales |
| Family | Orthotrichaceae
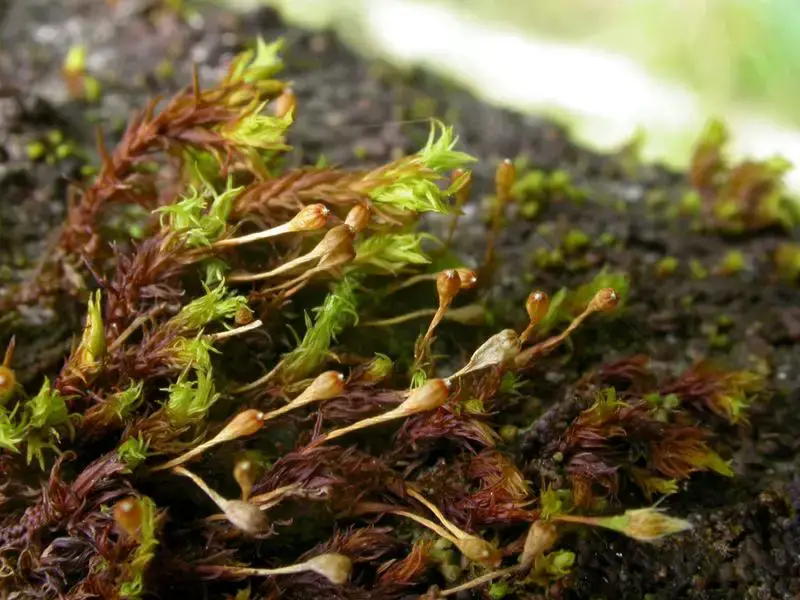 24134_1629_4.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/ulota-coarctata-1629 |
| Genus | Ulota |
Species
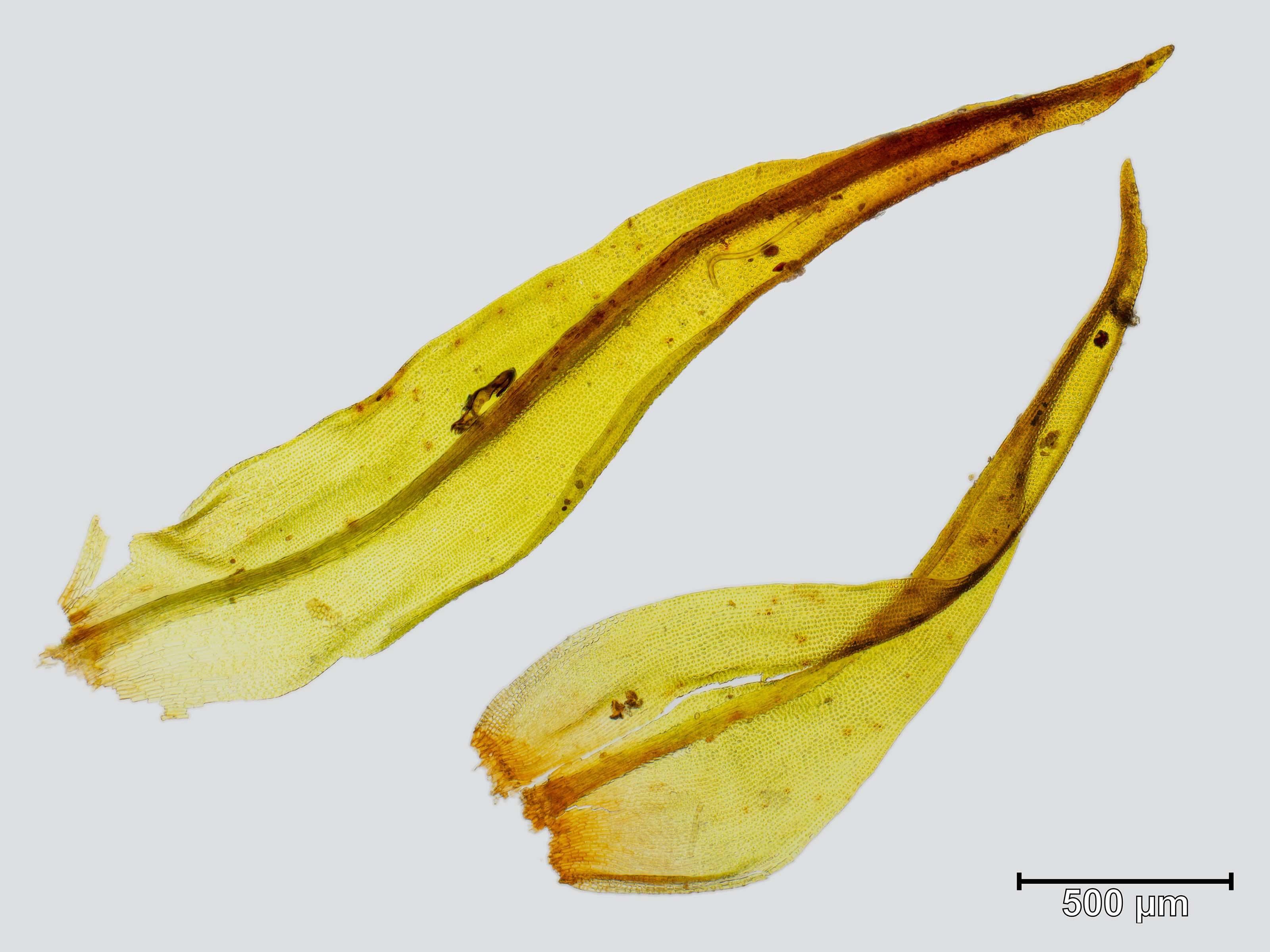 ulota_coarctata_blatt.jpeg from: https://www.korseby.net/outer/flora/bryophyta/orthotrichaceae/ |
Ulota coarctata (P.Beauv.) Hammar |
Conclusion
The Ulota coarctata (P.Beauv.) Hammar moss, a member of the Orthotrichaceae family, may be small in stature, but its significance in the natural world is undeniable. From its unique morphological features to its ecological roles and adaptations, this unassuming bryophyte serves as a reminder of the intricate beauty and resilience found in nature’s smallest inhabitants. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of life on our planet, perhaps we can find inspiration in the humble
Ulota-coarctata.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/ulota-coarctata/

0ee379dd891f41ae93e3a20487f17caa.JPG from: https://portal.wiktrop.org/group/animation_communication_wikwio/observation/show/348350
Ulota coarctata, a moss that has persisted and thrived through eons of environmental change.
Ponder this: In a world where we often overlook the smallest of creatures, what lessons can we learn from the resilience and adaptability of bryophytes like Ulota coarctata?