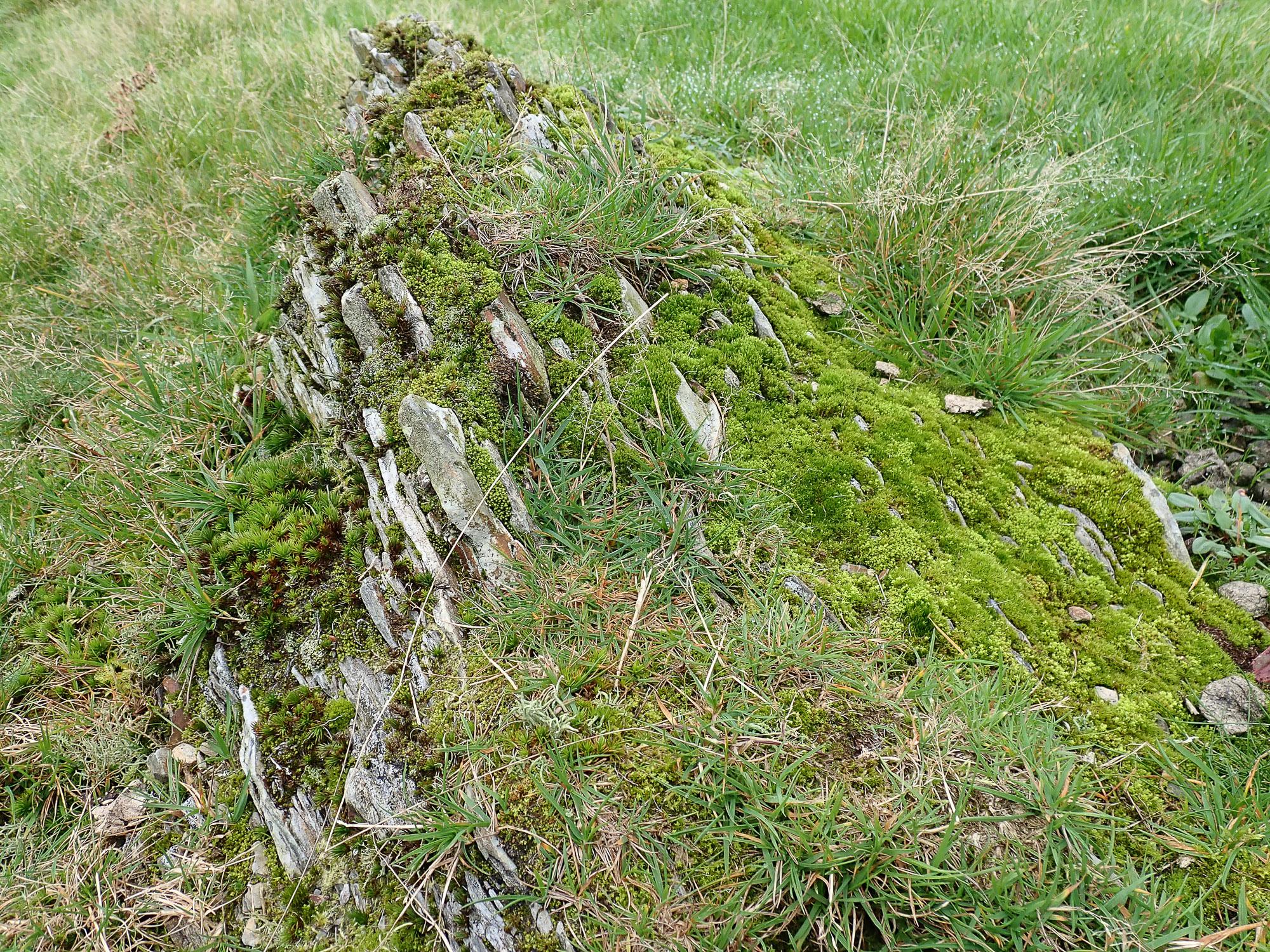

2021-10-14-10-22-49.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/leptodontium-flexifolium/
Introduction
Welcome, fellow moss enthusiasts! Today, we’re going to delve into the fascinating world of Leptodontium flexifolium (Dicks.) Hampe, a remarkable member of the Pottiaceae family, also known as Leptodontium. This unassuming yet resilient moss has captured the hearts of bryologists and nature lovers alike, and we’re about to uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty details, let’s set the stage. Leptodontium flexifolium belongs to the Bryophyta phylum, which encompasses the diverse and captivating world of mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. These tiny, non-vascular plants have been around for millions of years, playing crucial roles in various ecosystems and serving as indicators of environmental health.
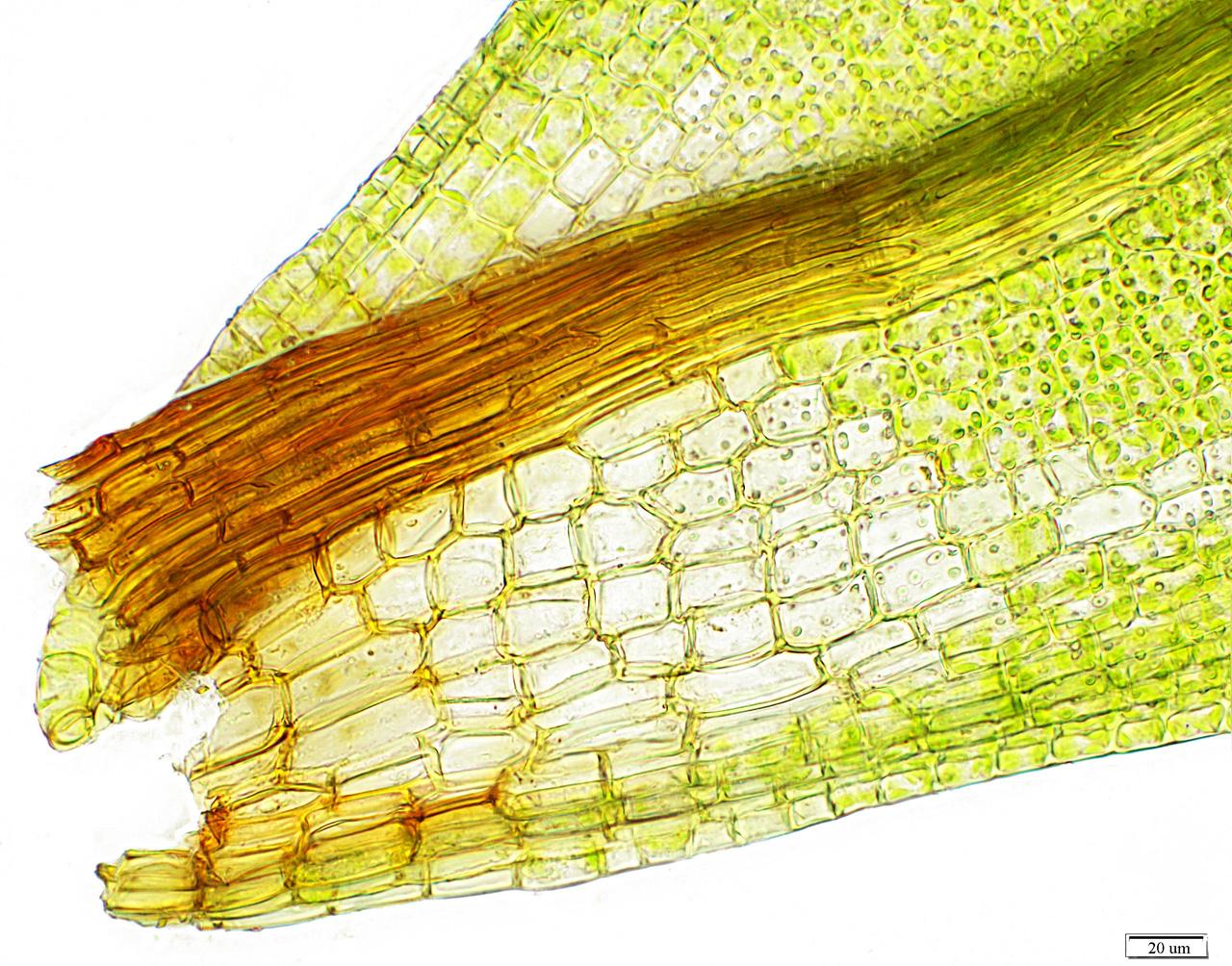

l_flexifolium5.jpg from: https://admissions.wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/leptodontium_flexifolium.html
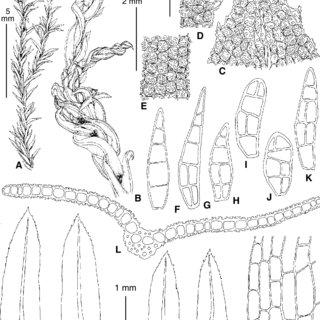
A-O-Leptodontium-flexifolium-Dicks-Hampe-from-Ingushetia-A-Bersanova-29IV2004_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-O-Leptodontium-flexifolium-Dicks-Hampe-from-Ingushetia-A-Bersanova-29IV2004_fig1_275607615
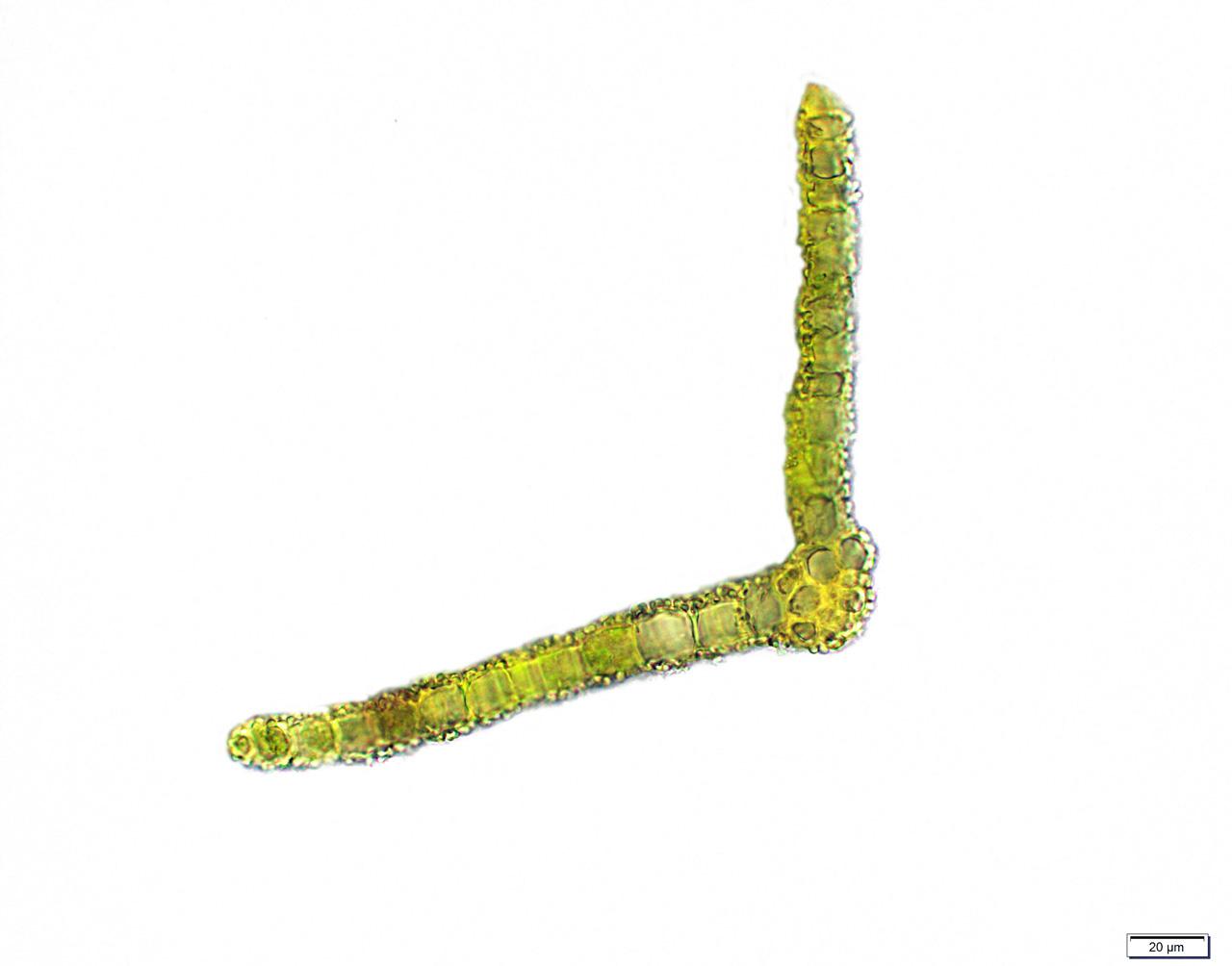

l_flexifolium13.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/leptodontium_flexifolium.html
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Leptodontium flexifolium is a true chameleon in the moss world. Its flexifolium (flexible-leaved) name is a nod to its ability to adapt to different environmental conditions. This moss can range in color from vibrant greens to rich browns, depending on its habitat and moisture levels. Its slender stems and delicate leaves form intricate carpets, often adorning rocks, tree bark, and soil.
One of the key identifying features of Leptodontium flexifolium is its distinctive leaf shape. The leaves are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and acuminate (tapering to a slender point), with a prominent midrib running along their length. Under a microscope, you’ll notice the intricate patterns of the leaf cells, which can aid in accurate identification.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Leptodontium flexifolium is a true globetrotter, found on every continent except Antarctica. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, from temperate forests to alpine regions, and even in urban environments. This moss is particularly fond of acidic substrates, such as rocks, tree bark, and soil, where it can form dense mats or cushions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Leptodontium flexifolium plays a vital role in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Its ability to absorb and retain moisture also contributes to the regulation of water cycles in its environment.
One of the most remarkable adaptations of Leptodontium flexifolium is its tolerance for desiccation. During dry periods, this moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its incredible resilience.
Case Studies/Examples
In the Pacific Northwest of North America, Leptodontium flexifolium is a common sight on the bark of coniferous trees, such as Douglas fir and western red cedar. Its presence is often an indicator of healthy forest ecosystems, as it thrives in areas with clean air and moderate moisture levels.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Leptodontium |
| Species | flexifolium |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous (upright) |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, acuminate |
| Leaf Cells | Elongated, smooth |
| Habitat | Acidic substrates, rocks, tree bark, soil |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan (found worldwide except Antarctica) |
Conclusion
Leptodontium flexifolium is a true marvel of the moss world, showcasing incredible adaptability, resilience, and ecological significance. From its intricate morphology to its global distribution and vital roles, this unassuming moss has captured our hearts and minds. As we bid farewell to this fascinating species, we’re left with a thought-provoking question: What other wonders lie hidden in the world of mosses, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?