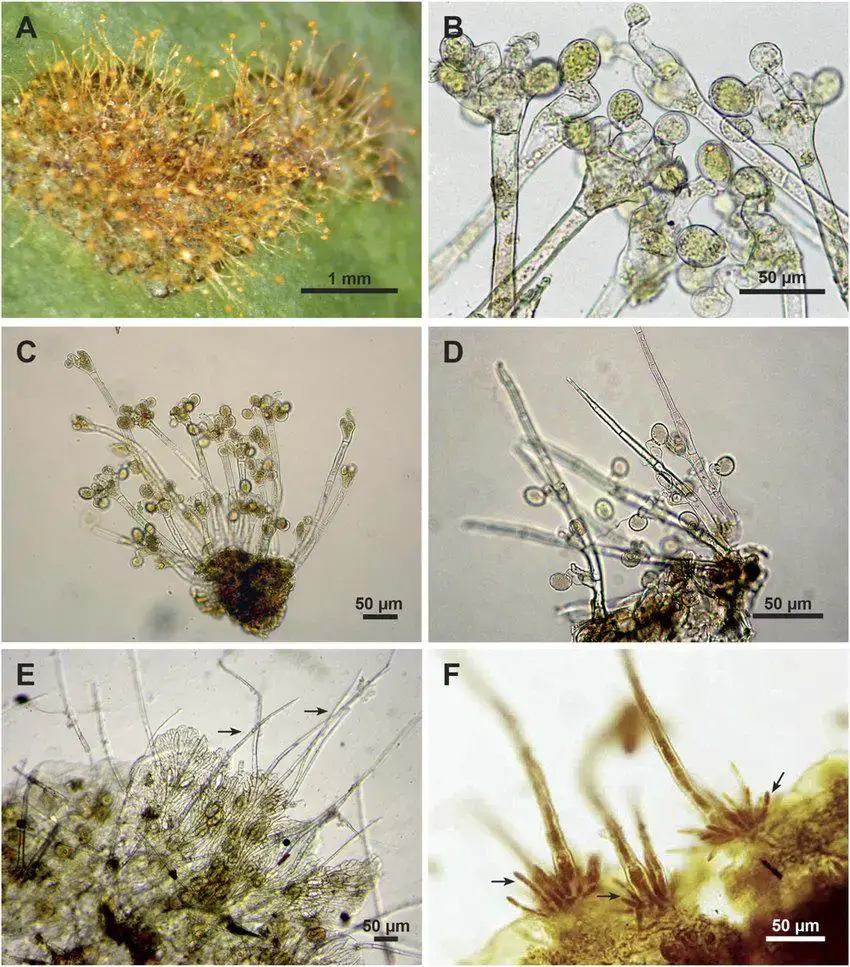

A-Typical-lesion-on-an-upper-leaf-surface-caused-by-Cephaleuros-virescens-The-erect.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-Typical-lesion-on-an-upper-leaf-surface-caused-by-Cephaleuros-virescens-The-erect_fig6_276493079
Exploring the Fascinating World of Holomitrium Moss
Introduction

il_fullxfull.3551950900_cd5s.jpg from: https://www.thebryophytanursery.com/listing/1147041783/terrarium-houtsnijmos-syntrichia
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Holomitrium hodgkinsoniae var. virescens Müll.Hal., a moss in the Dicranaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of this fascinating plant.
Background
Holomitrium hodgkinsoniae var. virescens is a type of moss in the Bryophyta phylum and Bryopsida class. It was first described by German botanist Carl Müller in 1897. The species name “hodgkinsoniae” honors Elizabeth Hodgkinson, who collected the type specimen.
Morphology and Identification
H. hodgkinsoniae var. virescens forms dense tufts or cushions. The stems are erect, up to 3 cm tall
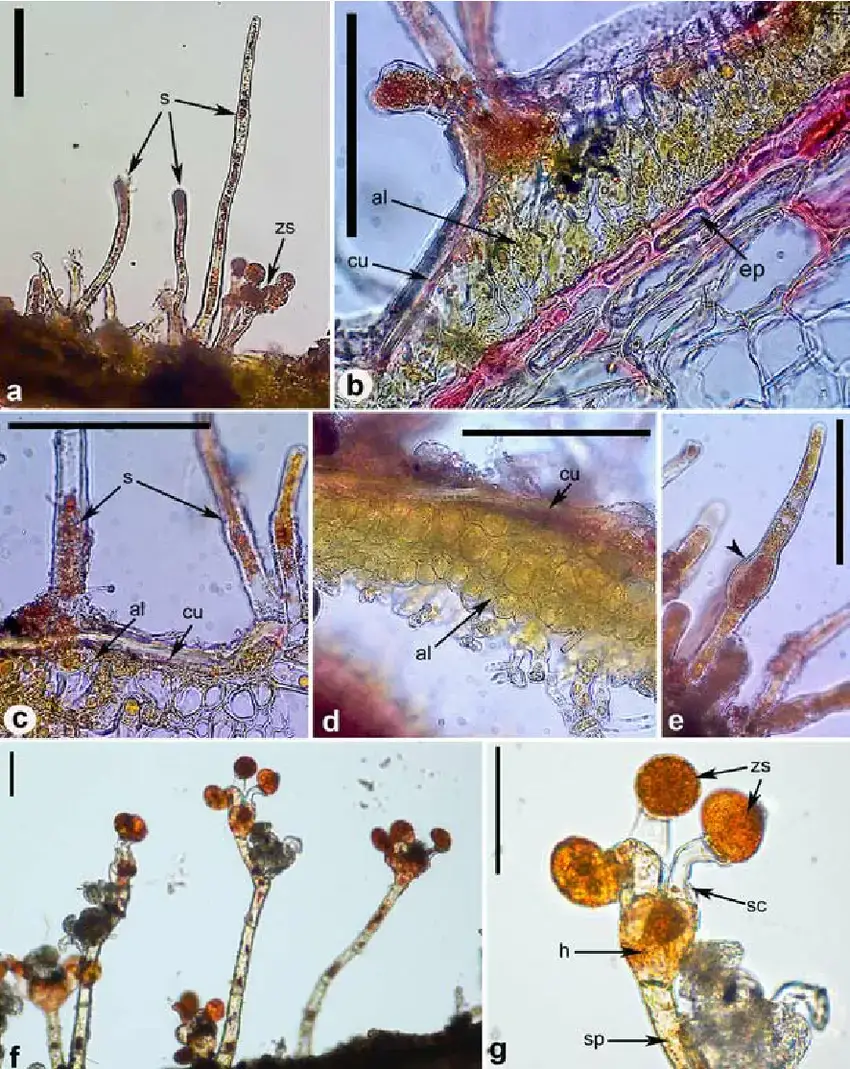

Morphology-of-Cephaleuros-virescens-a-algal-thallus-on-leaf-of-Ficus-benjamina-with.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Morphology-of-Cephaleuros-virescens-a-algal-thallus-on-leaf-of-Ficus-benjamina-with_fig2_272166878
, and sparsely branched. Leaves are lanceolate, 3-5 mm long, with a broad sheathing base. The leaf margins are entire and the costa (midrib) is strong, ending just below the apex.
Capsules are cylindrical and erect on a seta (stalk) up to 1.5 cm long. Spores are spherical and papillose, 12-16 μm in diameter
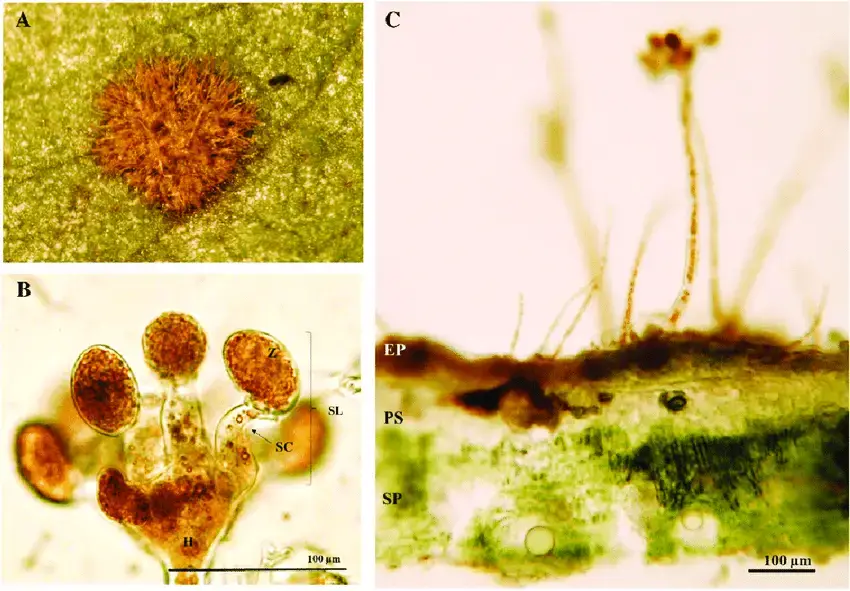
Leaf-lesions-caused-by-Cephaleuros-virescens-on-Psidium-guajava-A-Orange-alga-thalli-of.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Leaf-lesions-caused-by-Cephaleuros-virescens-on-Psidium-guajava-A-Orange-alga-thalli-of_fig3_327838250
. The calyptra (cap covering the capsule) is cucullate (hood-shaped).
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a pantropical distribution, found in tropical regions of

Coeloglossum+viride+var.+virescens+%2528Maligne+Lk%2529+%2523-12.JPG from: https://nativeorchidsofthepacificnorthwest.blogspot.com/2011/07/coeloglossum-viride-near-maligne-lake.html?m=1
Central and South America, Africa, and Asia. It grows as an epiphyte on tree trunks and branches in humid montane forests, typically between 1000-3000 m elevation.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, H. hodgkinsoniae var. virescens plays important roles in its forest ecosystems:
- Captures and retains moisture
- Provides habitat for micro-organisms and invertebrates
- Contributes to nutrient cycling
- Helps stabilize soils and prevent erosion
Its cushion life form is an adaptation to capture water from fog and retain moisture in the often cool, misty environments where it lives. The thick-walled cells help the moss withstand periodic drying.

76918.jpg from: https://mushroomobserver.org/observations/33150

Coeloglossum+viride+var.+virescens+%2528Canmore%2529+%252319.JPG from: https://nativeorchidsofthepacificnorthwest.blogspot.com/2014/08/coeloglossum-viride-var-virescens.html

Morphology-of-Cephaleuros-virescens-a-algal-thallus-on-leaf-of-Ficus-benjamina-with_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Lesions-caused-by-Cephaleuros-virescens-on-different-hosts-a-velvety-algal-lesions_fig1_272166878

2020-12-31-16-35-25.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/scleropodium-cespitans/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Stem height | Up to 3 cm |
| Leaf shape | Lanceolate |
| Leaf length | 3-5 mm |
| Leaf margin | Entire |
| Capsule shape | Cylindrical |
| Seta length | Up to 1.5 cm |
| Spore diameter | 12-16 μm |
| Calyptra shape | Cucullate |
Conclusion
Holomitrium hodgkinsoniae var. virescens is a prime example of how even tiny, inconspicuous organisms like mosses lead fascinating lives and play outsized roles in the world’s ecosystems. Next time you’re in a tropical montane forest, take a closer look at the trees – you just might spot this marvelous moss! What other overlooked wonders of nature have caught your eye?
Macrocoma-abyssinica-MuellHal-Vitt-var-abyssinica-A-G-A-Branch-leaf-B-Stem.ppm from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Macrocoma-abyssinica-MuellHal-Vitt-var-abyssinica-A-G-A-Branch-leaf-B-Stem_fig1_317595504