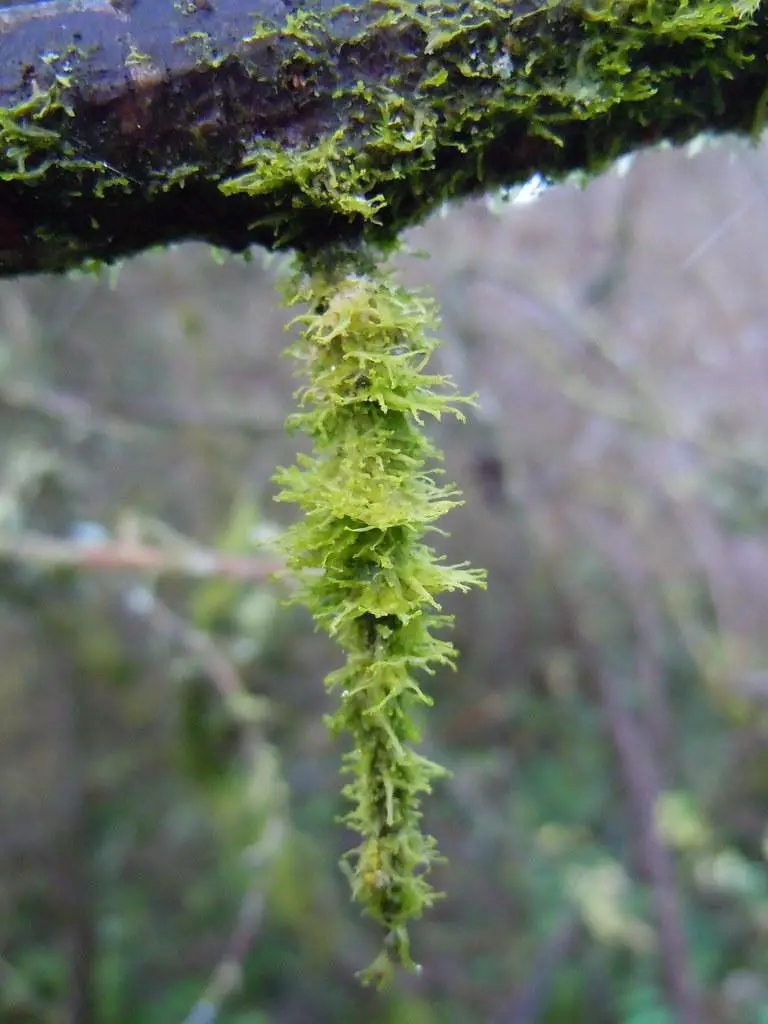

10517023294_b8da52e106_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/tim-waters/10517023294/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Metzgeria fruticulosa (O.F.Müll.) A.Evans moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Aneuraceae family. Often referred to simply as Metzgeria, this unassuming plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a unique glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s wonders.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this remarkable moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. Metzgeria fruticulosa belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta, which encompasses liverworts, and the class Jungermanniopsida, a diverse group of leafy liverworts. This taxonomic positioning underscores the moss’s evolutionary significance and its role within the broader ecosystem.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
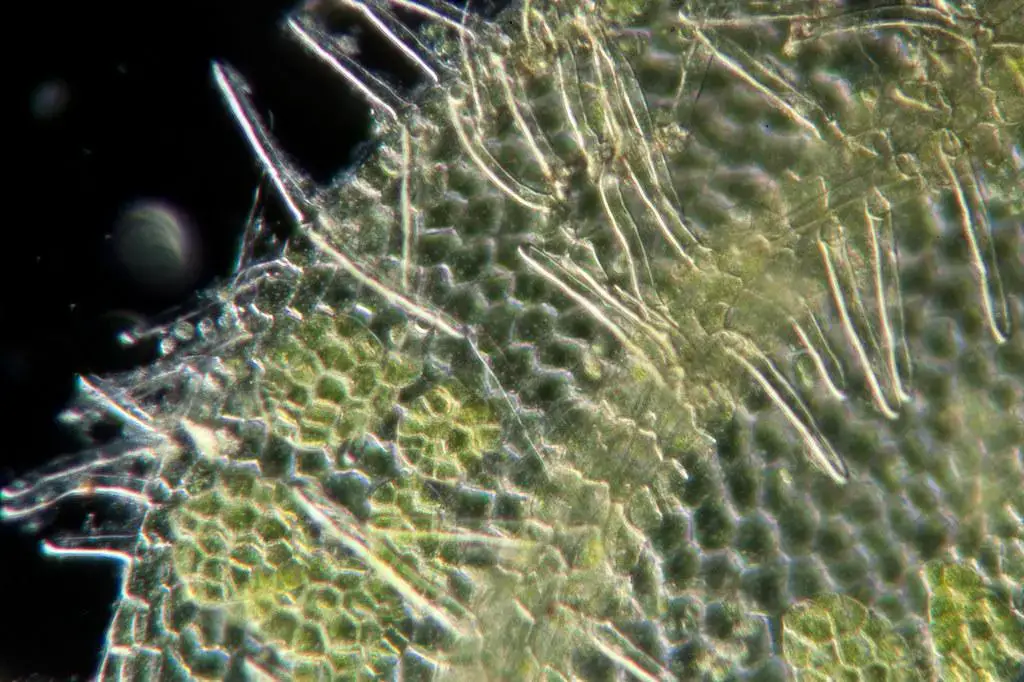
Metzgeria fruticulosa is a thalloid liverwort, meaning it lacks distinct stems and leaves. Instead, it grows in a flattened, ribbon-like form, with a distinct midrib running along its length. The thallus is typically green to bluish-green in color, with a velvety texture. One of the most distinctive features of this moss is its
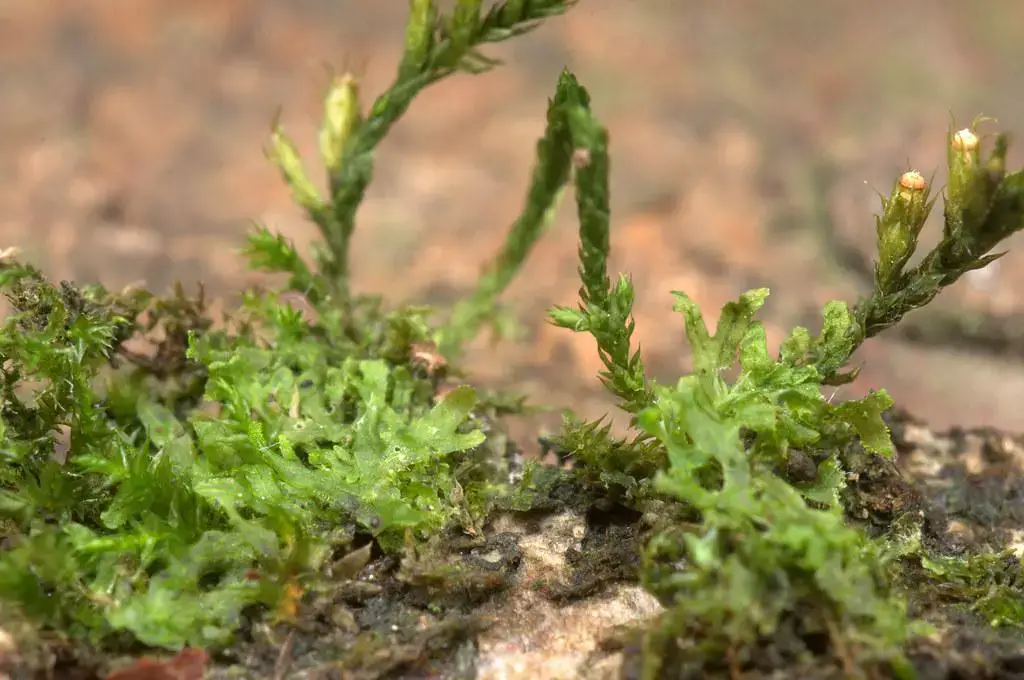

10108203314_d1bdda0d3a_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/cladoniophile/10108203314/
forked branching pattern, which resembles the antlers of a deer.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss has a widespread distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often growing on the bark of trees, rocks, or soil in forests and woodlands. Metzgeria fruticulosa is particularly abundant in temperate regions, where it plays a crucial role in the ecosystem.
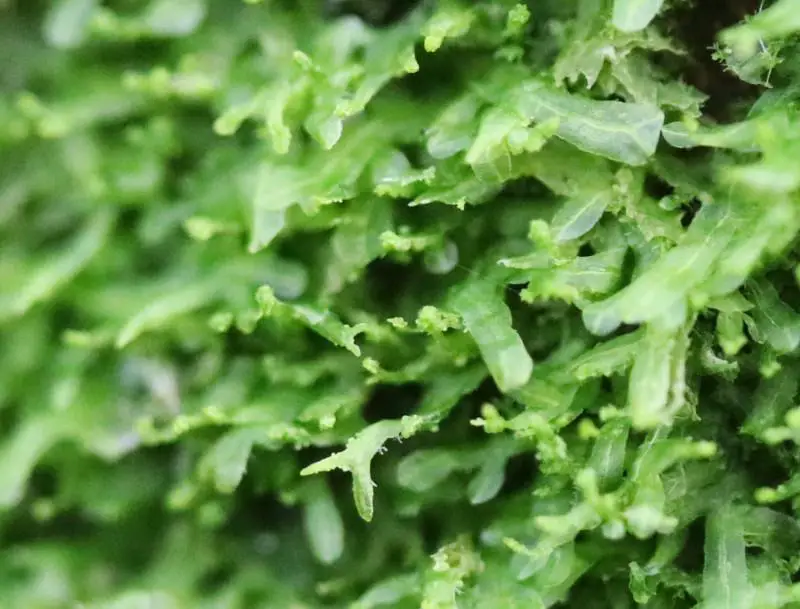

60689397.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/258839756
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its unassuming appearance, Metzgeria fruticulosa is a vital component of many ecosystems. It serves as a pioneer species, colonizing bare surfaces and paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss acts as a habitat for various microorganisms and invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of its environment.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Metzgeria fruticulosa is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. This versatility ensures its survival and propagation in a wide range of conditions, making it a resilient and adaptable species.
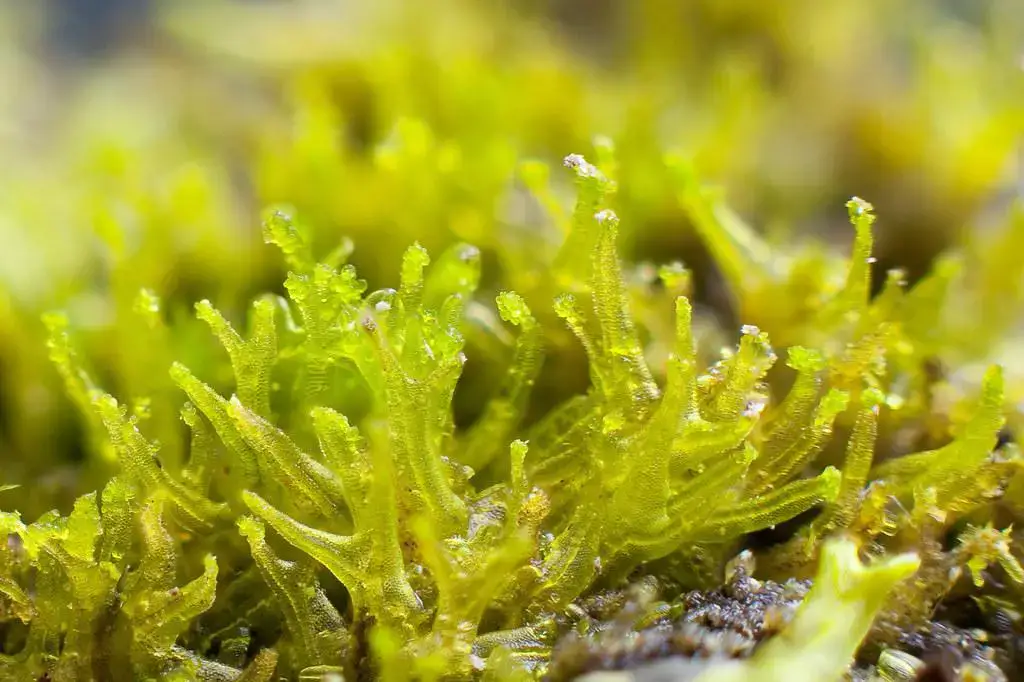

6870178579_ce933c8caa_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/stephenbuchan/6870178579/
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that Metzgeria fruticulosa played a crucial role in maintaining the moisture levels of its surrounding environment. The moss’s ability to absorb and retain water helped create a microclimate that supported the growth of other plant species, highlighting its importance in ecosystem dynamics.
Technical Table
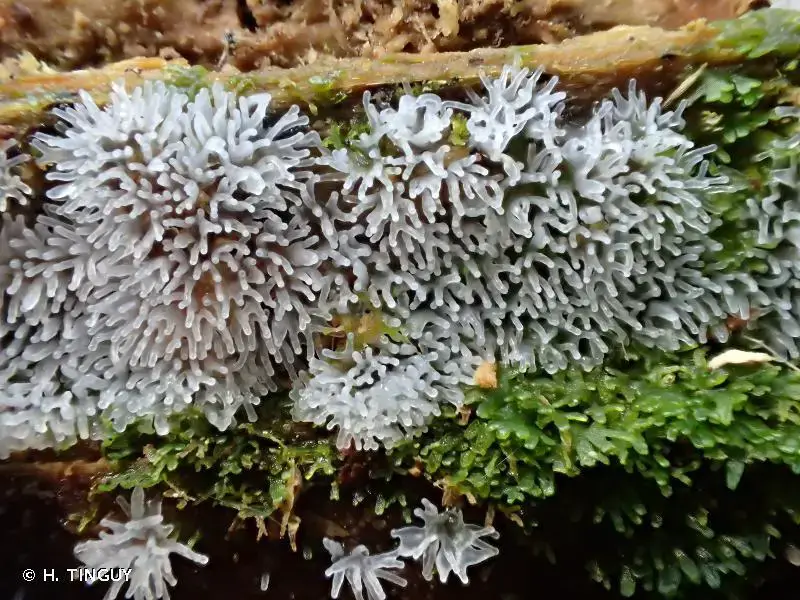

199268.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/50475/tab/taxo
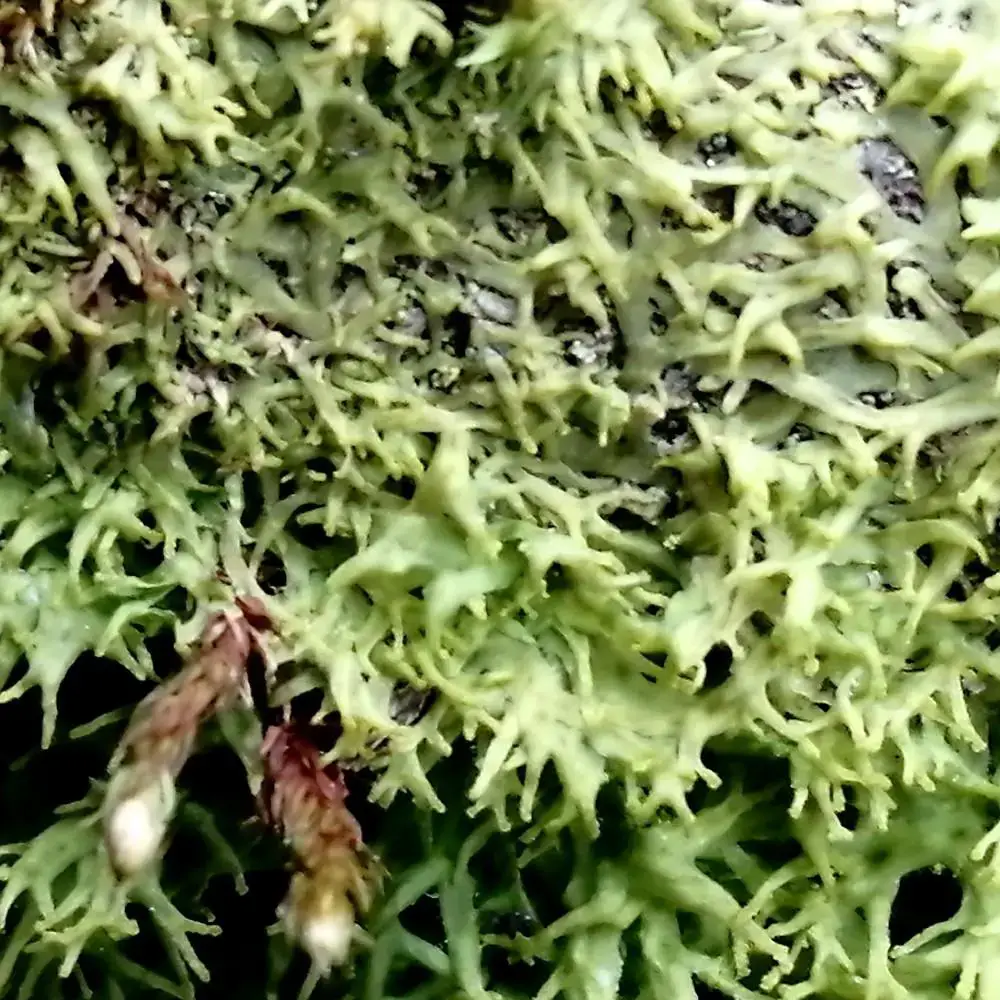

25267072.jpg from: https://observations.be/photos/25267072/

240px-Metzgeria_fruticulosa_(a%2C_144707-474823)_2301.JPG from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Metzgeria_fruticulosa

46589531.jpg from: https://observation.org/photos/46589531/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Metzgeriales |
| Family | Aneuraceae |
| Genus | Metzgeria |
| Species | fruticulosa |
| Growth Form | Thalloid liverwort |
| Branching Pattern | Forked |
| Color | Green to bluish-green |
| Texture | Velvety |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | Widespread, except Antarctica |
Conclusion
The Metzgeria fruticulosa (O.F.Müll.) A.Evans moss, a member of the Aneuraceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its unique morphology, widespread distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, this unassuming moss serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and resilience that exists within the natural world.
12237877596_374319f84c_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/stephenbuchan/12237877596/
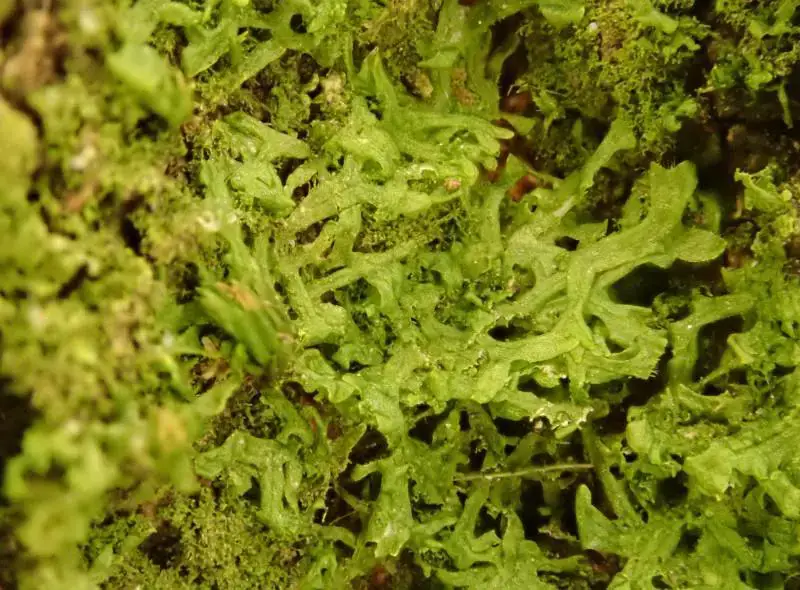

46082995.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/232867832?_popup=1
Ponder this: In a world where every organism plays a vital role, how can we better appreciate and protect the often overlooked wonders that surround us?