
medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/169517-Syrrhopodon-texanus
Exploring the Fascinating World of Syrrhopodon flexifolius Mitt. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Syrrhopodon flexifolius Mitt., a moss in the Calymperaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of this fascinating plant, from its unique morphology to its global distribution and ecological importance.
Background
Syrrhopodon flexifolius Mitt. is a species of moss belonging to the Bryophyta division and
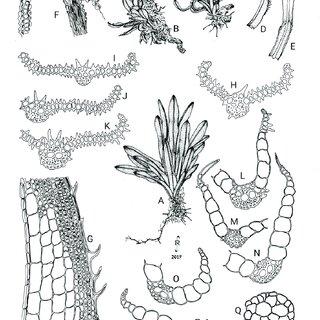
Syrrhopodon-armatus-Mitt-A-Habit-of-plant-drawn-moist-B-C-Habit-of-plants-drawn_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Syrrhopodon-armatus-Mitt-A-Habit-of-plant-drawn-moist-B-C-Habit-of-plants-drawn_fig3_371413539
Bryopsida class. The Calymperaceae family, to which it belongs, contains over 400 species found primarily in tropical regions. Syrrhopodon mosses are known for their distinctive leaf morphology and adaptations to various habitats.
Morphology and Identification
S. flexifolius
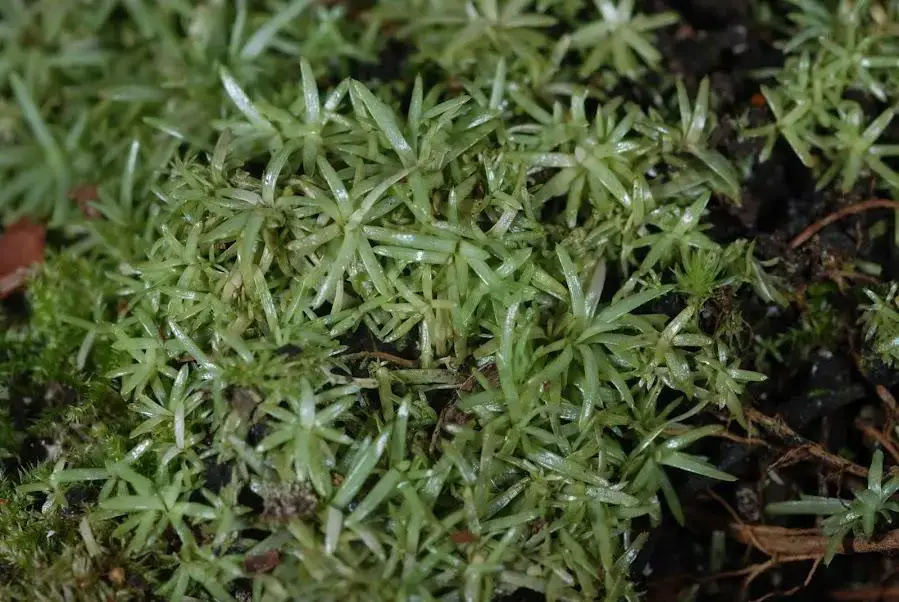

NK_Octoblepharum_albidum2.jpg from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/13_Calymper_images.html
has several key morphological features that aid in its identification:

medium.jpg from: https://enciclovida.mx/especies/136784-syrrhopodon
- Leaves: The leaves are linear-lanceolate, flexuose (wavy or bent), and have a hyaline (translucent) base that clasps the stem.
- Costa: The costa (midrib) is strong and percurrent (extending to the leaf tip).
- Leaf margins: The upper leaf margins are often serrate (toothed) and bordered by elongate cells.
- Capsules: The capsules are cylindrical and borne on a long seta (stalk).
These characteristics, along with its size (stems typically 1-3 cm long), help distinguish S. flexifolius from similar species.
Global Distribution and Habitat
S. flexifolius has a wide distribution, primarily in tropical and subtropical regions:

1dc928ba29a896ac104b26394365b498.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/9000
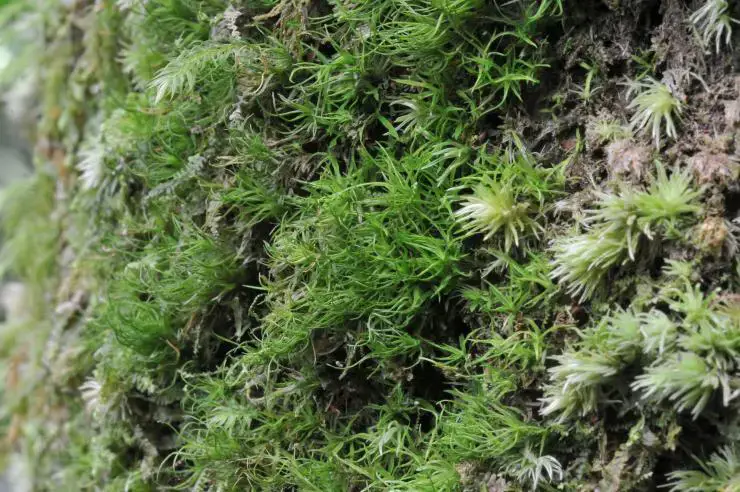

2174e69b73594fa0c620e8af5924f136.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/bf7e5eeaf8a578b6413d823dbe679935

210fd61036129d4014766d0d251836f3.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/9000/articles

Syrrhopodon-japonicus-bisL.jpg from: https://www.digital-museum.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~museum/habit/moss_habit/Syrrhopodon japonicus/Syrrhopodon_japonicus.html
| Continent/Region | Countries |
|---|---|
| Asia | China, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Vietnam |
| Africa | Madagascar, Réunion, Tanzania |
| North America | Mexico, USA (Florida) |
| South America | Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela |
| Oceania | Australia, Fiji, New Caledonia, Samoa |
This moss grows on various substrates, including tree bark, rocks, and soil, in moist forests and open habitats from lowlands to mountains.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, S. flexifolius plays important ecological roles:
- Water retention: Its dense mats help retain moisture and prevent soil erosion.
- Microhabitats: It provides shelter and microhabitats for small invertebrates.
- Nutrient cycling: It aids in nutrient cycling by trapping and breaking down organic matter.
S. flexifolius has adaptations that allow it to thrive in its habitats:
- Desiccation tolerance: It can survive periods of drought by entering a dormant state.
- Leaf structure: Its leaf morphology helps capture and retain water.
- Asexual reproduction: It can reproduce asexually via fragmentation, allowing quick colonization of new areas.
Conclusion
Syrrhopodon flexifolius Mitt. is a remarkable moss with a wide distribution and important ecological roles. Its unique morphology and adaptations showcase the diversity and resilience of bryophytes. Next time you’re in a tropical forest, keep an eye out for this small but mighty plant! What other secrets might mosses hold?