
57379.jpg from: https://mushroomobserver.org/observer/show_observation/25471
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the Asterella elegans (Spreng.) Trevis., commonly known as Asterella. This delicate yet resilient member of the Aytoniaceae family belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta (liverworts) and the class Marchantiopsida. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the fascinating secrets of this unassuming moss.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Asterella elegans

Hymenophyllum_elegans_2318-627×376.jpg from: https://www.fernsoftheworld.com/fow_species/hymenophyllum-elegans-spreng/
, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted remarkably to survive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
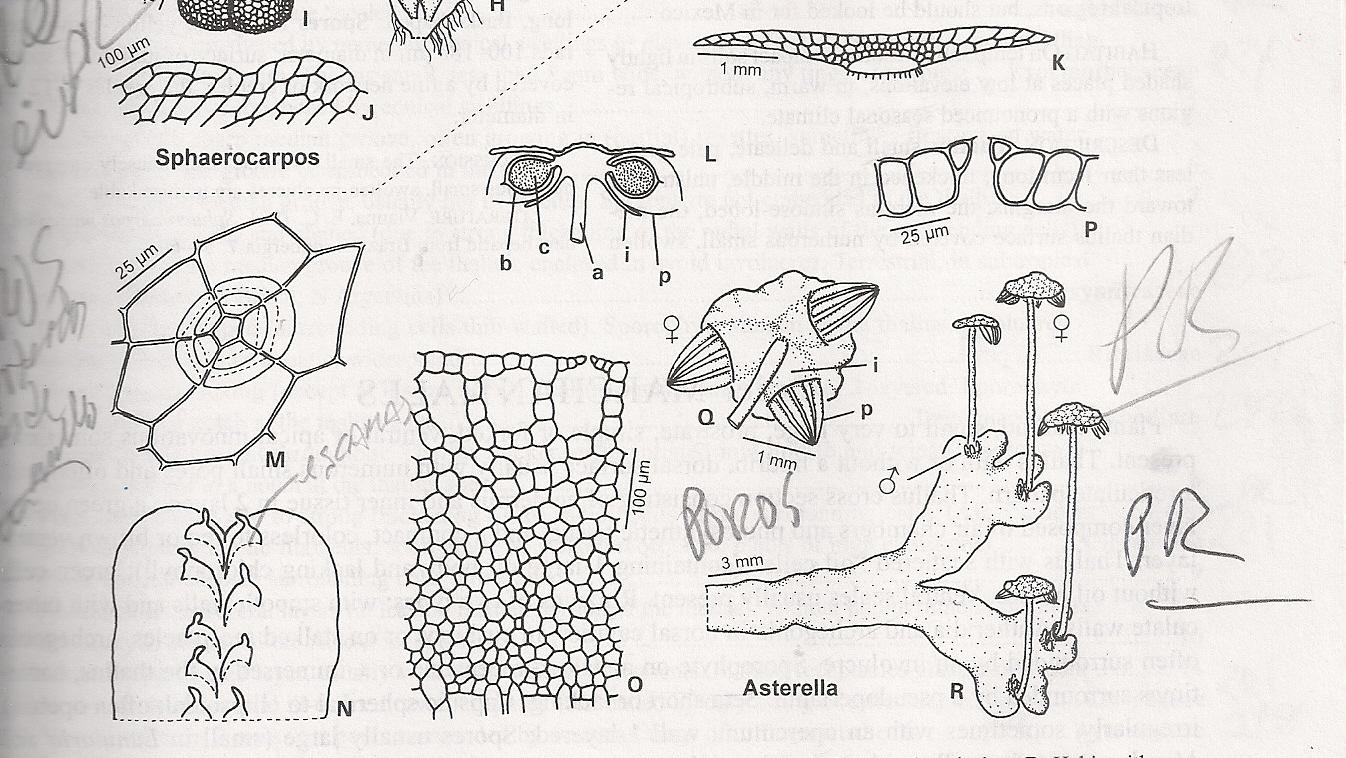
Asterella elegans is a thallose liverwort, meaning it grows in a flat, ribbon-like form. Its thallus is typically green to yellowish-green in color and can reach up to 5 cm in length. The surface of the thallus is adorned with a distinctive midrib that runs along its length, adding to its unique appearance. One of the most striking features of this moss is its umbrella-shaped reproductive structures called archegoniophores, which bear the female reproductive organs.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Asterella elegans is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. It thrives in moist and shaded environments, often found growing on soil, rocks, or decaying wood in forests, grasslands, and even urban areas. This moss is particularly fond of calcareous (limestone-rich) substrates, making it a common sight in areas with alkaline soils.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Asterella elegans plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating favorable conditions for other plants to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Asterella elegans is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up and appearing lifeless. However, when moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its incredible resilience.

original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2688595
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that Asterella elegans

265977_10150692485620144_5966366_o-1024×768.jpg from: https://stories.rbge.org.uk/archives/27559

35968314176_6a21b7839a_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/101115103@N03/35968314176/
played a crucial role in facilitating the growth and establishment of certain coniferous tree seedlings. The moss’s ability to retain moisture and provide a suitable microclimate contributed to the successful regeneration of these economically and ecologically important tree species.
Technical Table
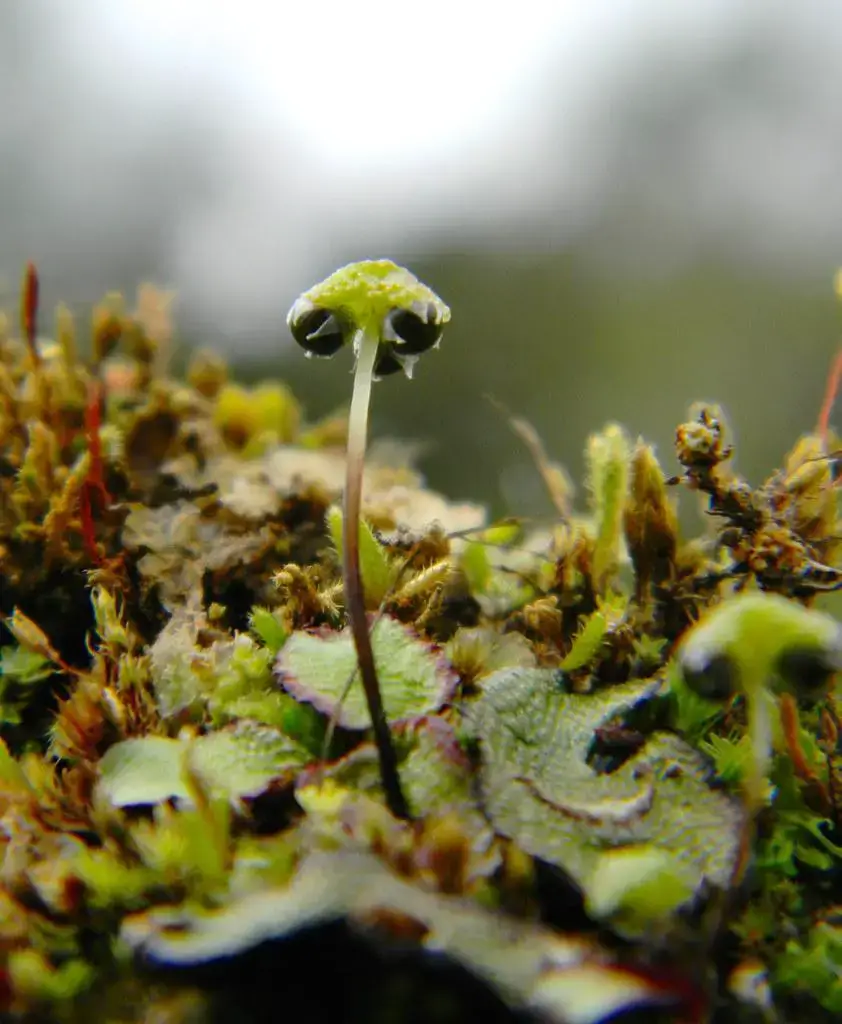

15211005679_3f18b8bf2b_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/benitofotos/15211005679
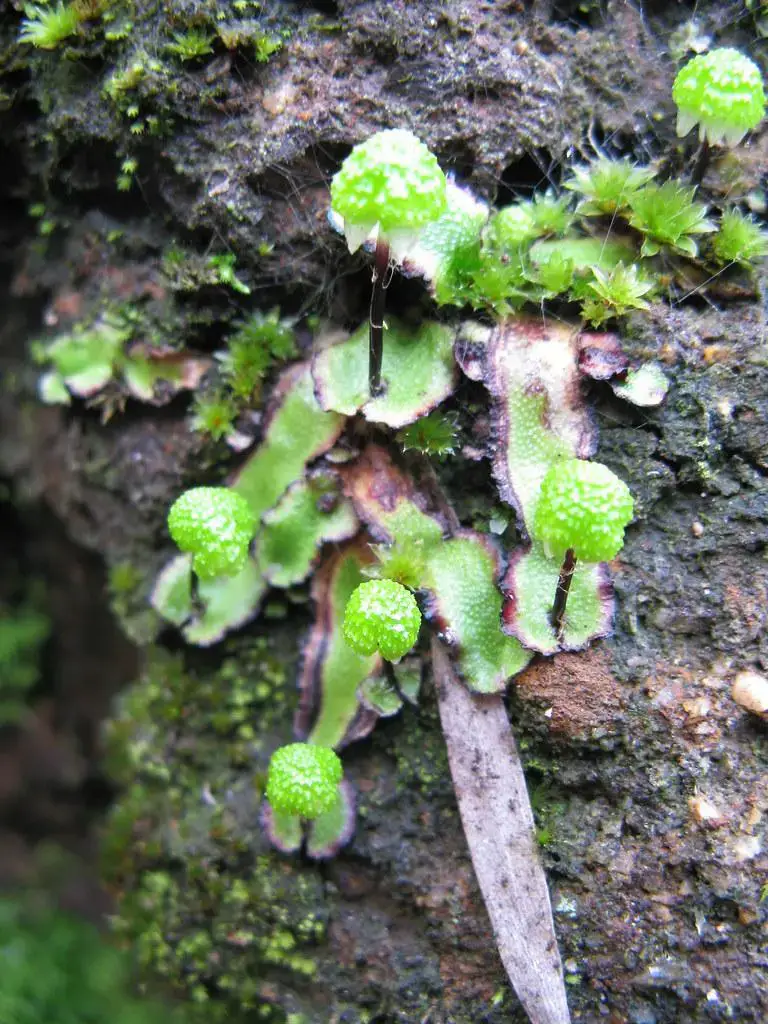

6940734141_5b39b82d96_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/kjamon/6940734141

20210511_105508.jpg from: https://osogovonature.com/2021/05/11/comandra-umbellata-subsp-elegans-spreng-piehl-syn-comandra-elegans-rochel-ex-reichenb-reichenb/
ASTERELLA%2BVENOSA.jpg from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/03/hepaticas-talosas-reboulaciaceae.html
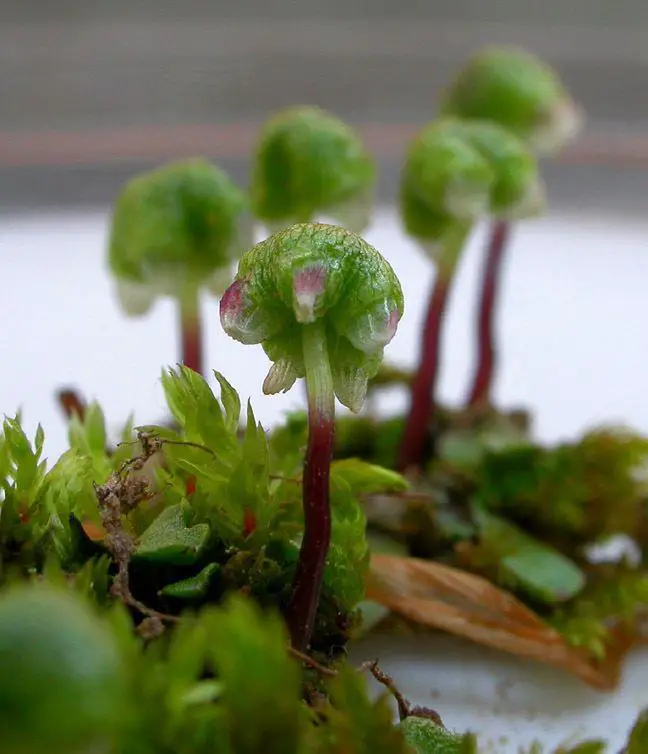

asterella-8015312b-014b-43b4-ac1a-897720aff36-resize-750.jpeg from: https://alchetron.com/Asterella
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Marchantiopsida |
| Order | Aytoniaceae |
| Genus | Asterella |
| Species | Asterella elegans (Spreng.) Trevis. |
| Thallus | Flat, ribbon-like, green to yellowish-green |
| Midrib | Distinctive midrib along the thallus length |
| Reproductive Structures | Umbrella-shaped archegoniophores |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments, calcareous substrates |
| Distribution | North America, Europe, Asia, Australia |
| Ecological Roles | Soil formation, moisture retention, microhabitat |
| Adaptations | Desiccation tolerance, dormancy |
Conclusion
Asterella elegans, a humble yet remarkable moss species, serves as a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other hidden wonders lie within the world of mosses, waiting to be discovered and cherished?