
medium.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/55331-Atrichum-selwynii
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one moss species stands out as a true marvel – the Atrichum androgynum (Müll.Hal.) A.Jaeger. Belonging to the Polytrichaceae family, this remarkable moss is also commonly known as Atrichum. Prepare to embark on an enchanting journey as we delve into the intricate details of this fascinating plant.
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Atrichum androgynum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of
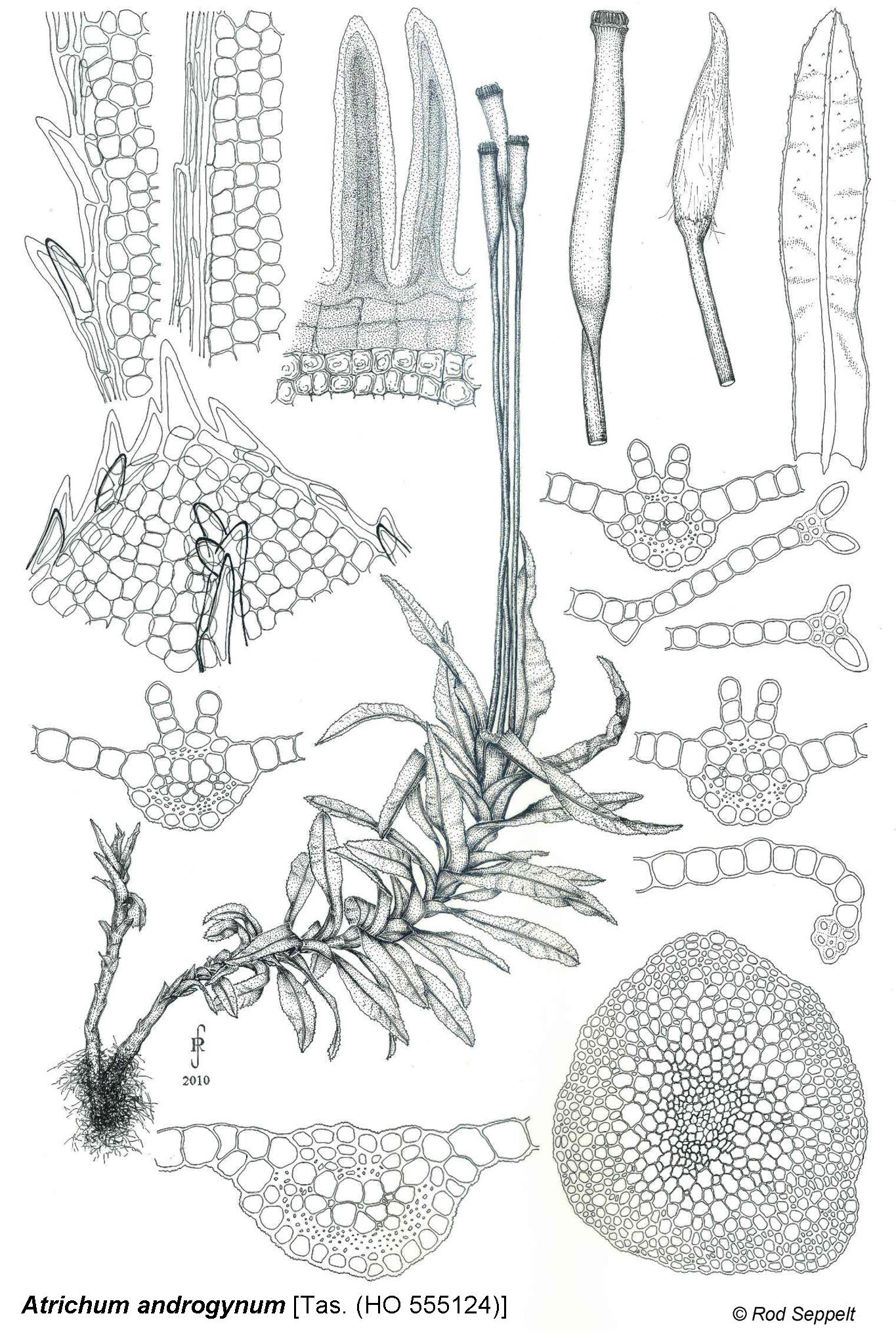
RS_Atrichum_androgynum.jpg from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/48_Polytrichaceae_images.html
bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked yet play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Atrichum androgynum is a striking moss species that can be easily identified by its distinctive features. The gametophyte stage, which is the dominant phase in the life cycle of bryophytes, consists of upright stems adorned with spirally arranged leaves. These leaves are
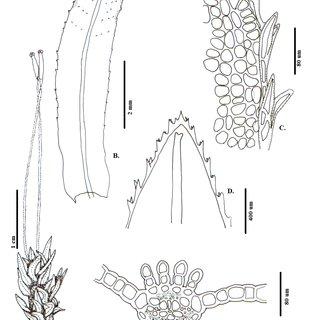
Atrichum-androgynum-MuellHal-Jaeger-A-Habito-B-E-Hoja-B-Vista-ventral-C_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/318217800_Revision_de_la_familia_Polytrichaceae_Bryophyta_para_Colombia
lanceolate in shape, with a sheathing base
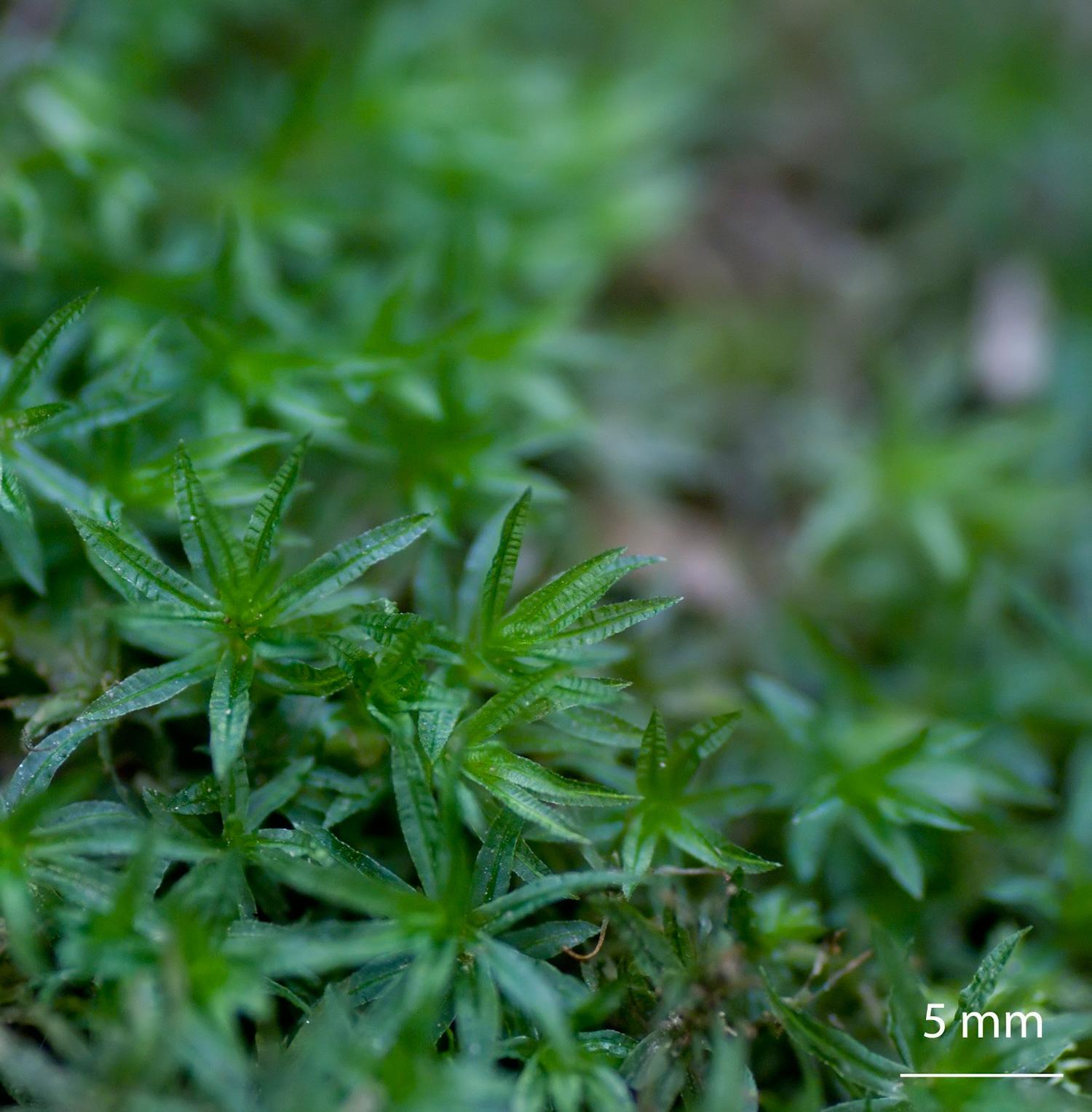

Atrichum-undulatum-moss.jpg from: https://elmusgo.blogspot.com/2012/08/atrichum-undulatum.html
and a serrated margin. One of the most remarkable characteristics of this moss is the presence of a terminal hair-like structure called the awn, which extends from the tip of each leaf.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Atrichum androgynum is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist woodlands and shaded areas to rocky outcrops and disturbed sites. This moss species is particularly adept at colonizing areas with acidic soils, making it a common sight in coniferous forests and other acidic environments.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite their diminutive size, Atrichum androgynum and other bryophytes play vital roles in their respective ecosystems. They act as pioneers, colonizing bare or disturbed areas and facilitating the establishment of other plant species. Additionally, these mosses contribute to
Figura-2-A-G-Prospodium-appendiculatum-sobre-Tecoma-stans-A-espermogonio-B-C_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Distribucion-geografica-departamental-de-Atrichum-androgynum-Notoligotrichum_fig4_318217800
soil formation and water retention, creating favorable conditions for various organisms to thrive.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Atrichum androgynum is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, only to revive and resume growth when moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to survive in challenging environments and contributes to its widespread distribution.
Case Studies/Examples
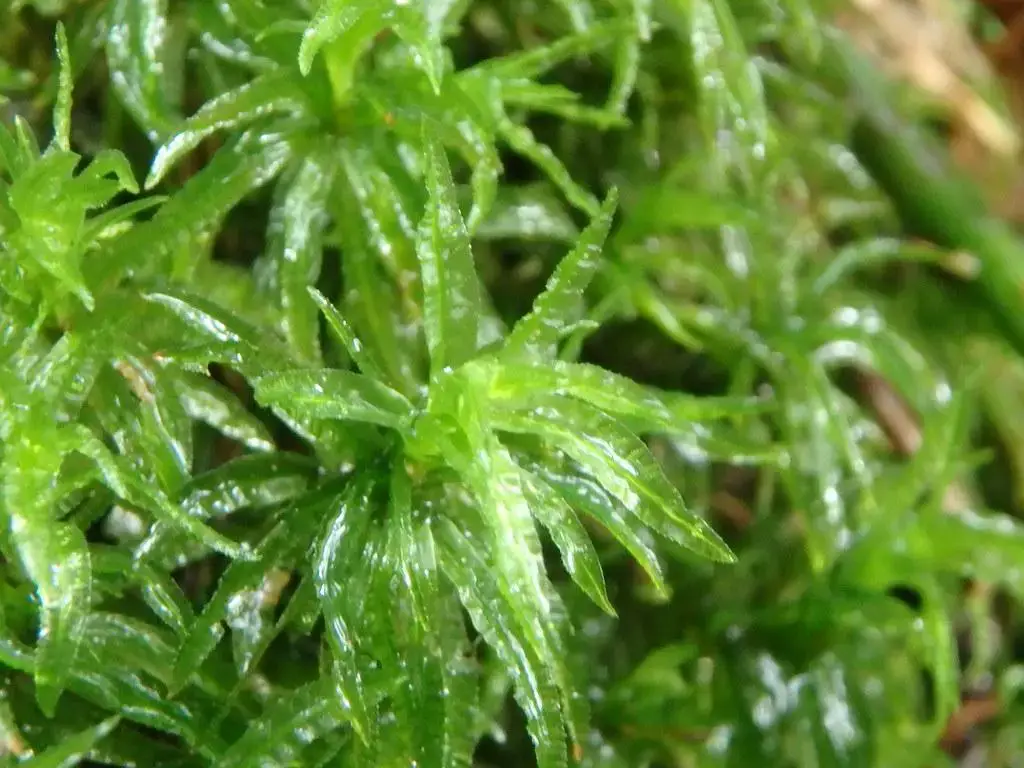

49874548211_308a148237_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/98938839@N07/49874548211/
In a recent study conducted in a temperate deciduous forest, researchers observed the crucial role played by Atrichum androgynum in facilitating the establishment of tree seedlings. The moss’s dense mats provided a suitable microhabitat, retaining moisture and protecting the delicate seedlings from desiccation and erosion.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Polytrichopsida |
| Order | Polytrichales
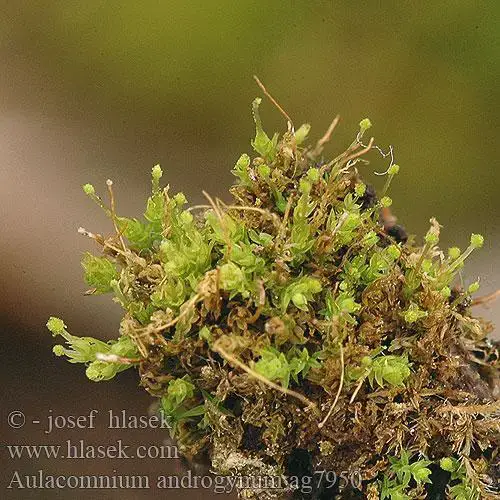 aulacomnium_androgynum_ag7950.jpg from: https://hlasek.com/aulacomnium_androgynum_ag7950.html  largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236596564_The_sexual_reproduction_and_phenology_of_Atrichum_androgynum_Mull_Hal_AJaeger |
Family
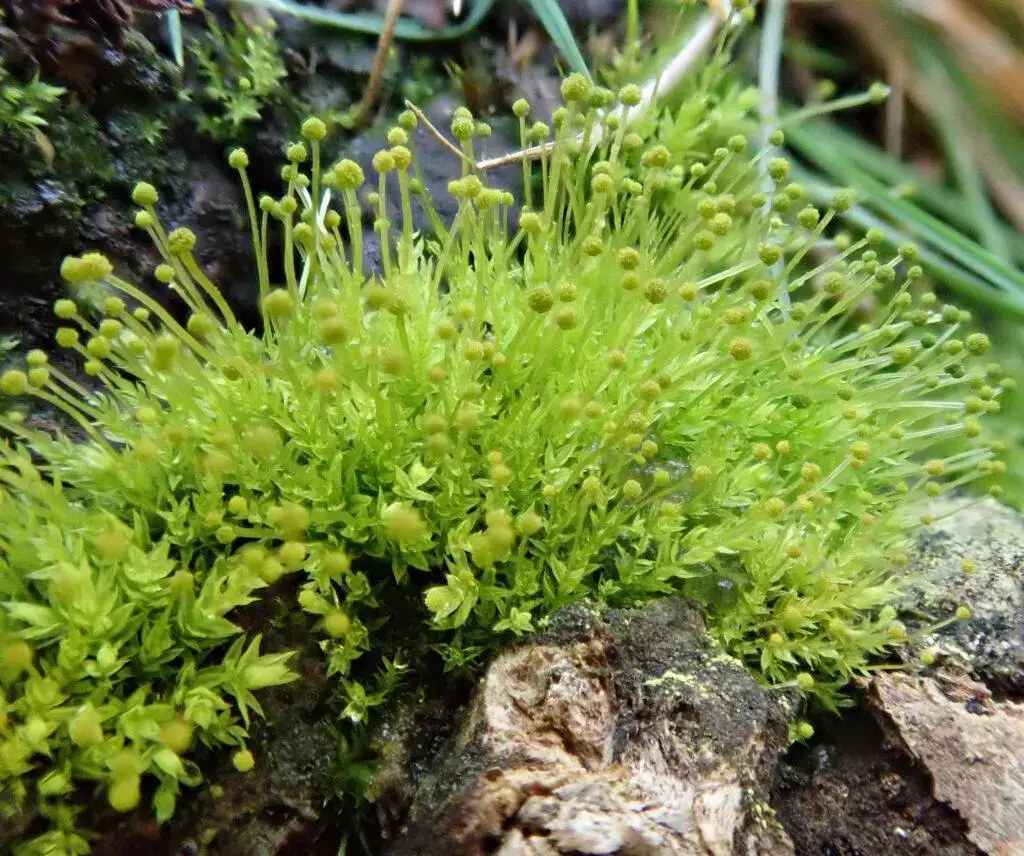 2019-10-27-15-23-39-1024×856.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/aulacomnium-androgynum/ |
Polytrichaceae |
| Genus | Atrichum |
| Species | Atrichum androgynum (Müll.Hal.) A.Jaeger
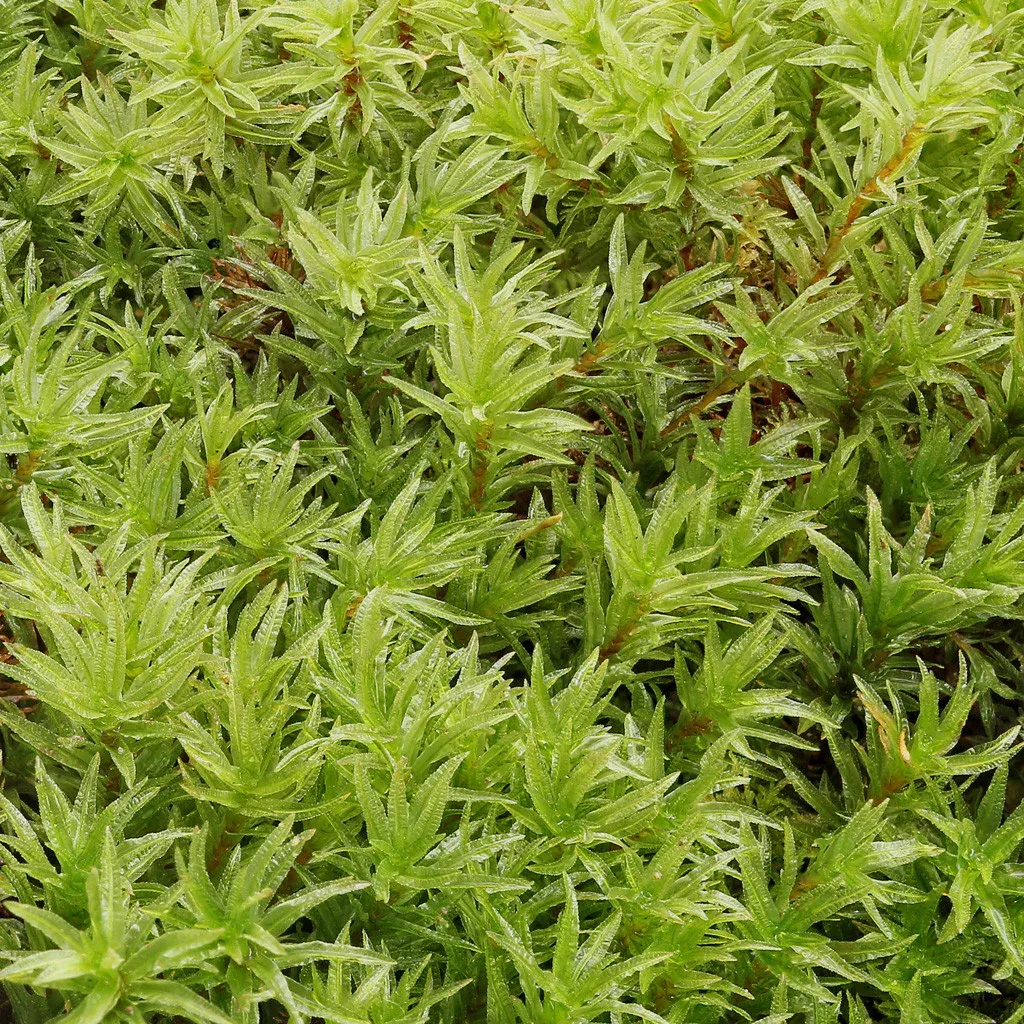 02_ID_005.jpg from: https://www.mountainmoss.com/products/atrichum-undulatum |
Conclusion
The Atrichum androgynum (Müll.Hal.) A.Jaeger moss, with its intricate morphology, global distribution, and ecological significance, is a true testament to the wonders of the bryophyte world. As we continue to unravel the secrets of these ancient plants, we are reminded of the intricate web of life that surrounds us and the importance of preserving and appreciating even the smallest of organisms. Perhaps the next time you encounter a lush carpet of moss, you’ll pause and reflect on the remarkable journey of Atrichum androgynum and its bryophyte kin.