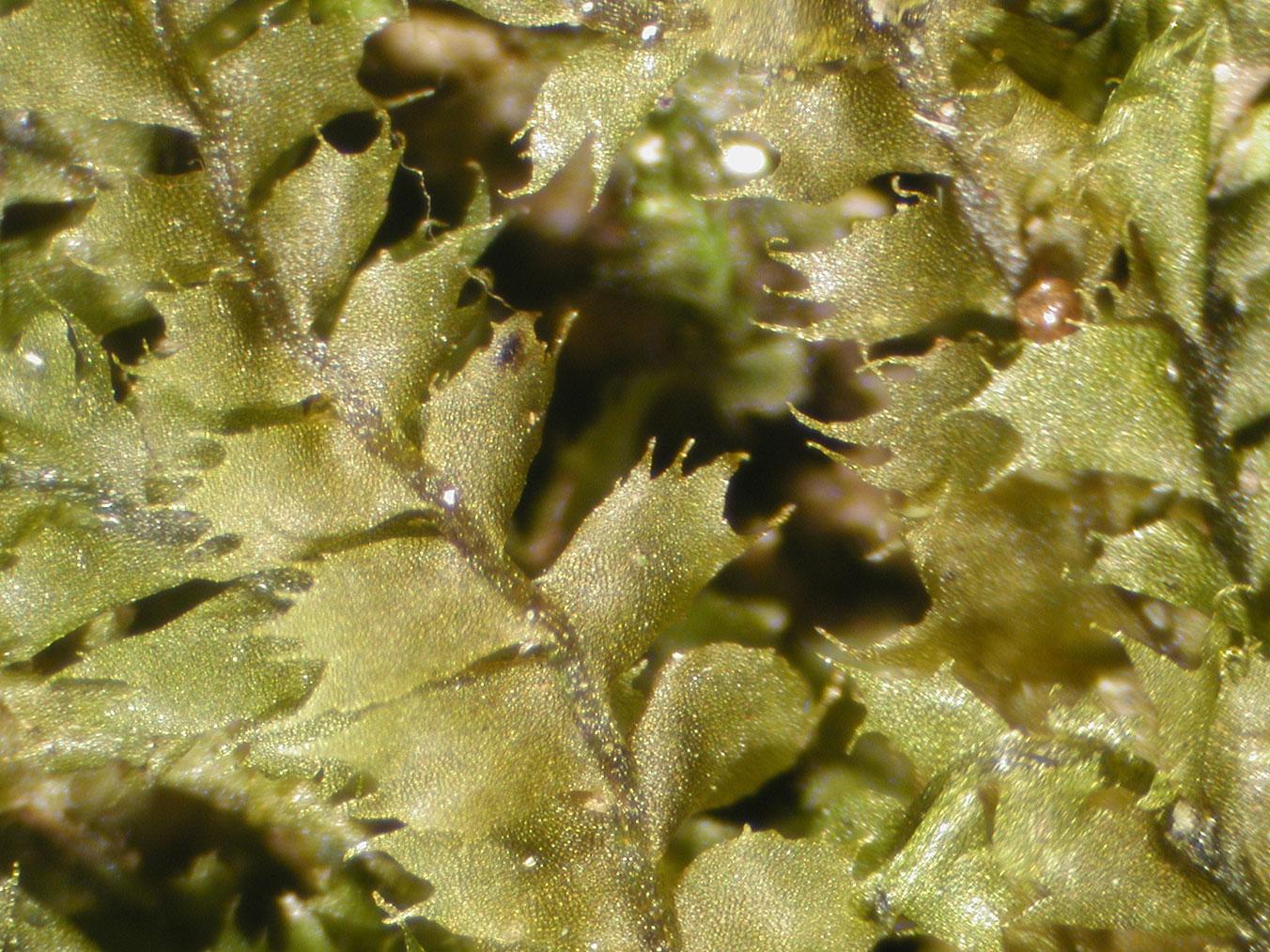
plaech_alaweb4.jpg from: https://www.southernappalachianbryophytes.org/plagiochilaechinata.html
Exploring the Fascinating World of Plagiochila filicina Herzog Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play a vital role in many ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Plagiochila filicina Herzog, a type of leafy liverwort moss in the Plagiochilaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of this fascinating plant, from its unique morphology to its global distribution and ecological importance.
Background on Plagiochila Mosses
Plagiochila is a genus of leafy liverwort mosses that includes over 1,600 species worldwide. They belong to the Marchantiophyta division and Jungermanniopsida class. Plagiochila mosses are known for their distinctive branching patterns and leaf arrangements.
Morphology and Identification of Plagiochila filicina Herzog
P. filicina has a unique appearance that sets it apart from other mosses:
- Stems are pinnately branched and can grow up to 10 cm long
- Leaves are oblong to obovate in shape and have toothed margins
- Oil bodies are numerous and segmented
- Underleaves are absent
These characteristics make P. filicina relatively easy to identify in the field for bryologists and enthusiasts.
Global Distribution and Habitat
P. filicina has a wide distribution, found in tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including:
- Central and South America
- Africa
- Southeast Asia
- Pacific Islands
This moss typically grows on tree trunks, branches, and logs in humid forests at elevations between 500-2000 meters. It prefers shaded, moist habitats with high humidity.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, P. filicina plays several important roles in its ecosystem:
- Helps retain moisture and prevent soil erosion
- Provides habitat for small invertebrates
- Contributes to nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter
P. filicina has several adaptations that allow it to thrive in its habitat:
- Pinnate branching maximizes surface area for photosynthesis
- Toothed leaf margins help capture and retain water
- Numerous oil bodies store lipids for energy and deter herbivores
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Stem | Pinnately branched, up to 10 cm long |
| Leaves | Oblong to obovate, toothed margins |
| Oil Bodies | Numerous, segmented |
| Underleaves | Absent |
Conclusion
Plagiochila filicina Herzog is a prime example of how even tiny mosses can be captivating when you take a closer look. From its intricate structure to its widespread distribution and ecological importance, this species highlights the incredible diversity within the bryophyte world. Next time you’re walking through a humid forest, take a moment to appreciate the miniature world of mosses like P. filicina living all around you. What other secrets might these small but mighty plants hold?