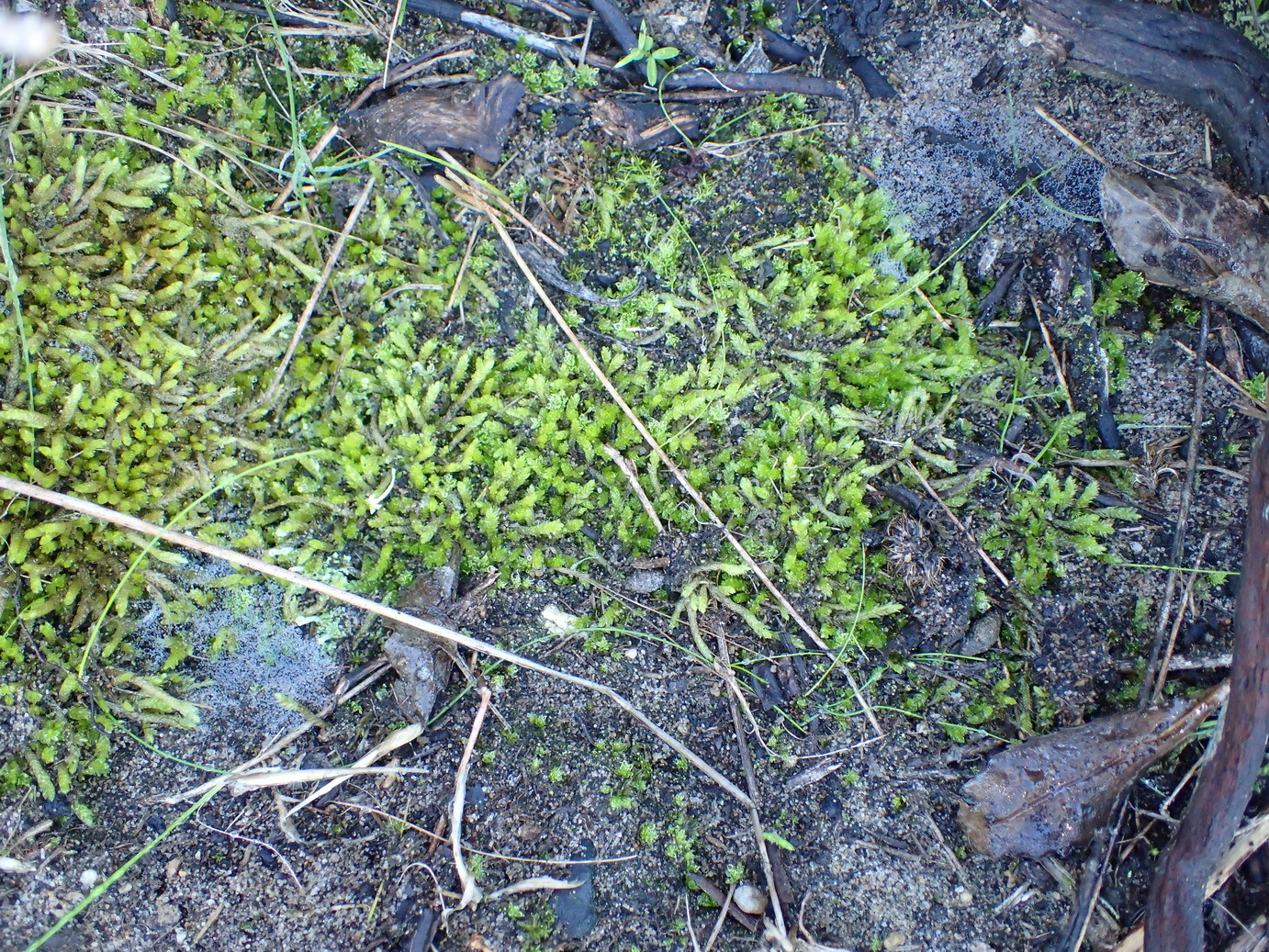

image from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one moss species stands out as a true marvel: Ectropothecium cyathothecium (Müll.Hal.) Broth., commonly known as Ectropothecium. This unassuming yet fascinating plant belongs to the Hypnaceae family and has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of this extraordinary moss, exploring its unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological significance.

image from: https://www.nzpcn.org.nz/flora/species/ectropothecium-sandwichense/
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Ectropothecium, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments, from arid deserts to lush rainforests.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Ectropothecium cyathothecium is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, creeping stems are adorned with delicate, ovate-lanceolate leaves that form a beautiful, feathery pattern. The leaves are typically
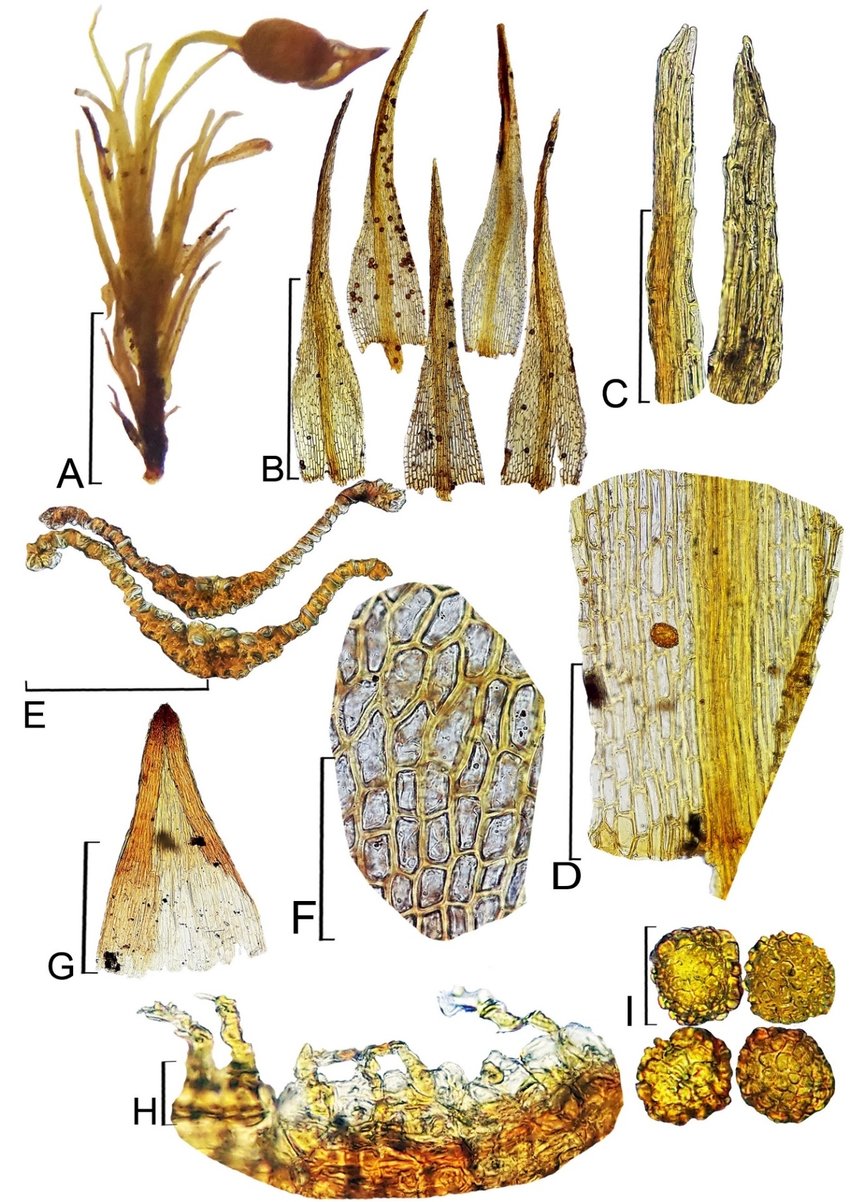
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-15-Dicranella-ulei-Muell-Hal-Broth-A-Habito-B-Filidios-C-Apices-dos_fig14_343400267
1-2 mm long and possess a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a short awn or hair-like projection.
One of the most striking features of this moss is its cyathothecium, a unique structure that gives the species its name. The cyathothecium is a cup-shaped structure that surrounds the base of the seta (the stalk that supports the capsule). This characteristic is a valuable identification tool for bryologists and moss enthusiasts alike.

image from: https://www.nzpcn.org.nz/flora/species/ectropothecium-sandwichense/
Global Distribution and Habitat

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-7-Dicranella-harrisii-Muell-Hal-Broth-A-Habito-B-Filidios-C-Apice-do_fig7_343400267
Ectropothecium cyathothecium is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist and shaded forests to rocky outcrops and even urban environments. This moss is often found growing on tree trunks, rotting logs, and soil, forming lush, velvety mats that add a touch of green to its surroundings.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Ectropothecium plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide shelter and nesting materials for various invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-11-Orthostichopsis-tijucae-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-Pseudoparafilos-filamentosos_fig11_309232610
One of the remarkable adaptations of Ectropothecium is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. During dry spells, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In the Pacific Northwest region of North America, Ectropothecium cyathothecium is a common sight in old-growth forests, where it carpets the trunks of towering conifers. Its presence is often an indicator of a healthy, undisturbed ecosystem, making it a valuable species for conservation efforts.
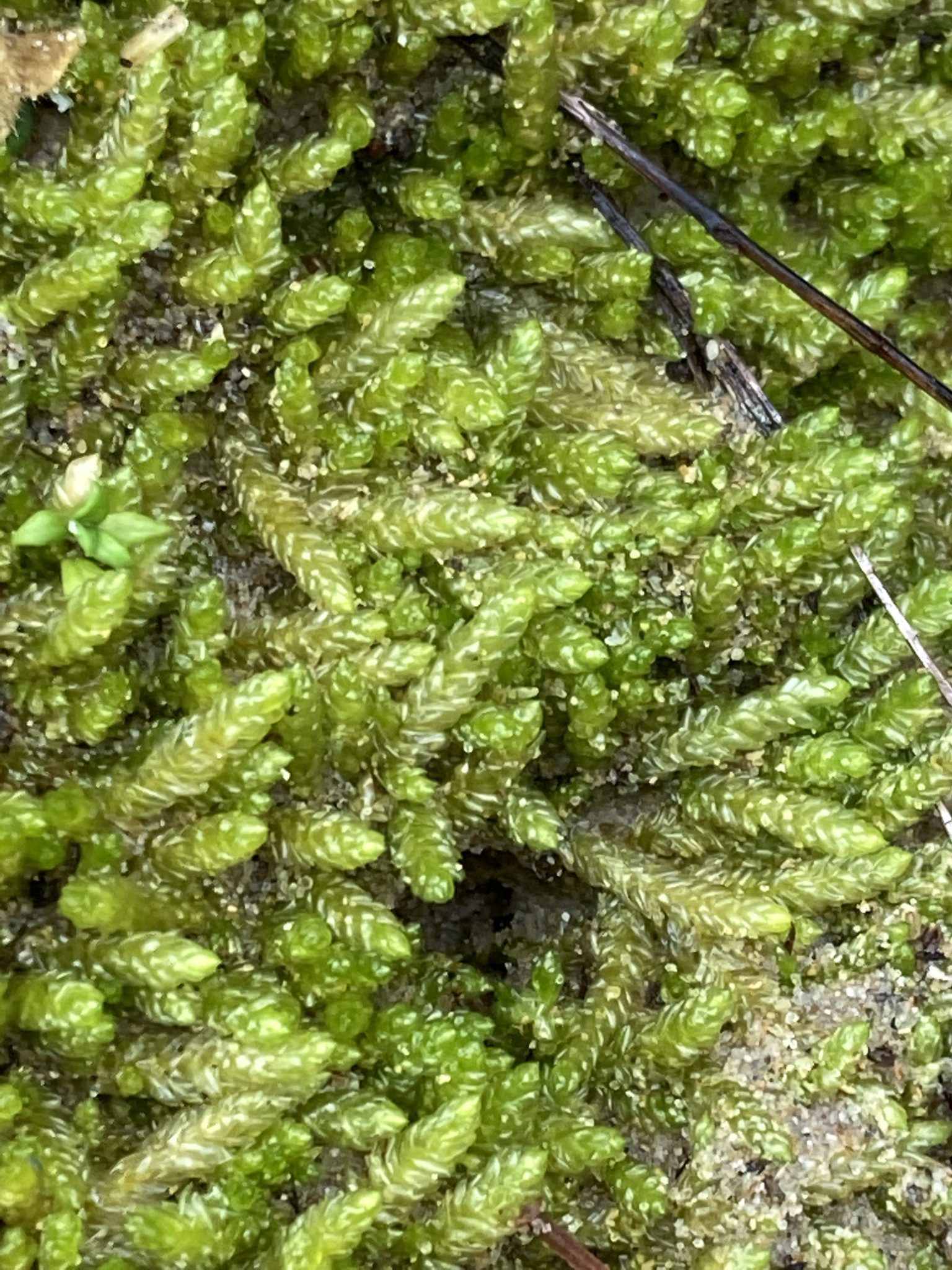

image from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552
Similarly, in the temperate forests of Europe, this moss plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of the forest floor. Its ability to retain moisture and provide a suitable microhabitat for other organisms contributes to the overall health and diversity of these ecosystems.
Technical Table

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Linbergia-sinensis-Muell-Hal-Broth-1-Habit-of-plant-Wet-2-A-portion-of-plant_fig1_341098152
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Hypnaceae |
| Genus | Ectropothecium
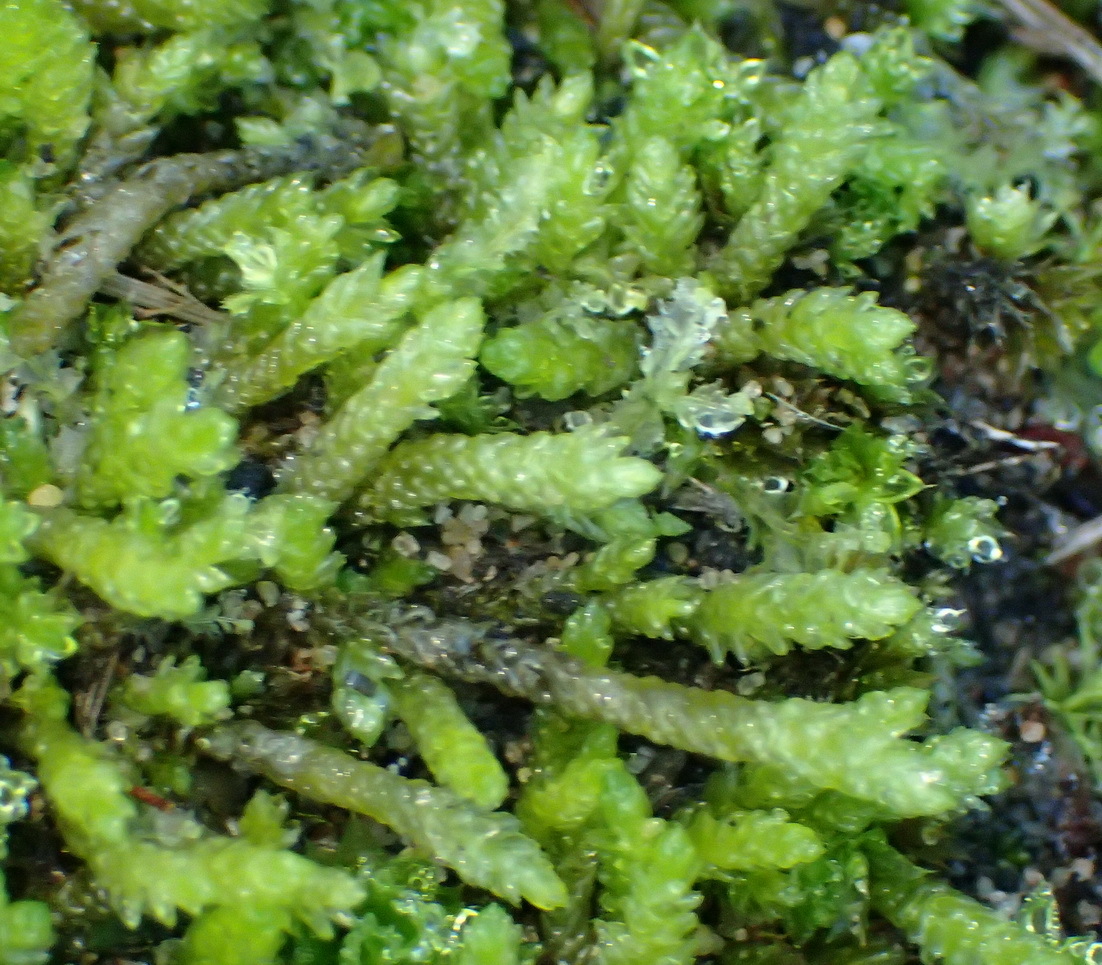 image from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552 |
| Species | E. cyathothecium (Müll.Hal.) Broth.
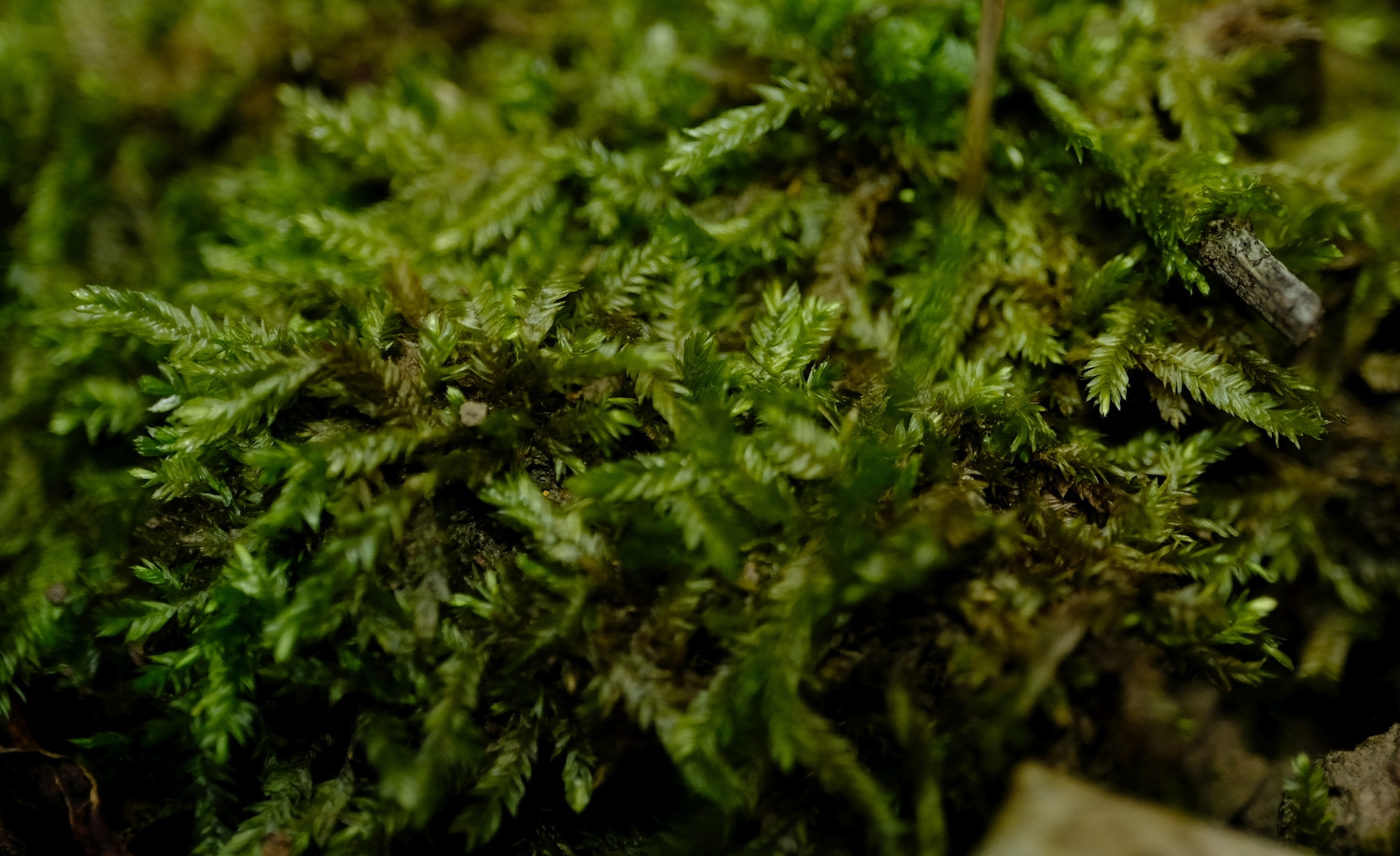 image from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552 |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Size | 1-2 mm |
| Distinctive Feature | Cup-shaped cyathothecium |