
plagiomnium2.jpg from: https://blogs.ubc.ca/biology321/?page_id=39
Exploring the Fascinating World of Brachymenium radiculosum Moss

169280.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4872
Introduction
Mosses are some of the most ancient and resilient plants on Earth. One particularly interesting species is

168350.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4958
Brachymenium radiculosum (Schwägr.) Hampe, a small but mighty moss in the Bryaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological importance of this fascinating bryophyte.
Background on Mosses
Before we explore B. radiculosum in depth, let’s review some key facts about mosses:
- Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta
- They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead having simple leaf-like structures
- Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds
- There are over 12,000 moss species found worldwide
Mosses play important roles in many ecosystems as pioneer species that help establish plant communities.
Morphology and Identification
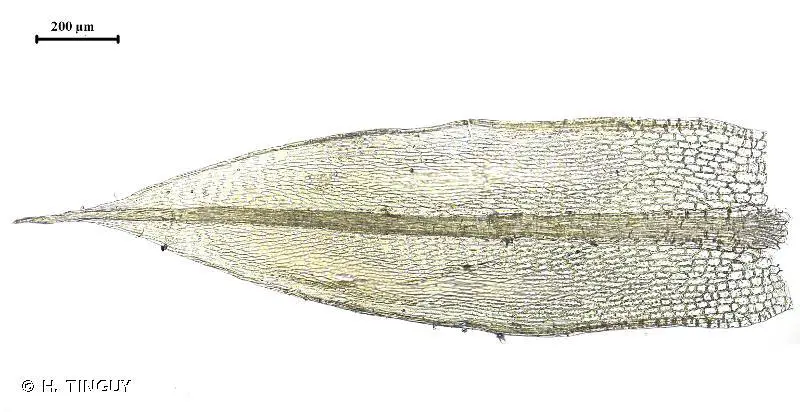
Brachymenium radiculosum is a relatively small, acrocarpous moss, typically growing in compact tufts or cushions. Its stems are short, usually under 1 cm tall. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate and have a strong midrib that extends to the leaf tip.
One identifying feature is the presence of rhizoidal gemmae

t0137957f46d92a0cb3.jpg from: https://www.jidianwang.com/entry/12262795.html
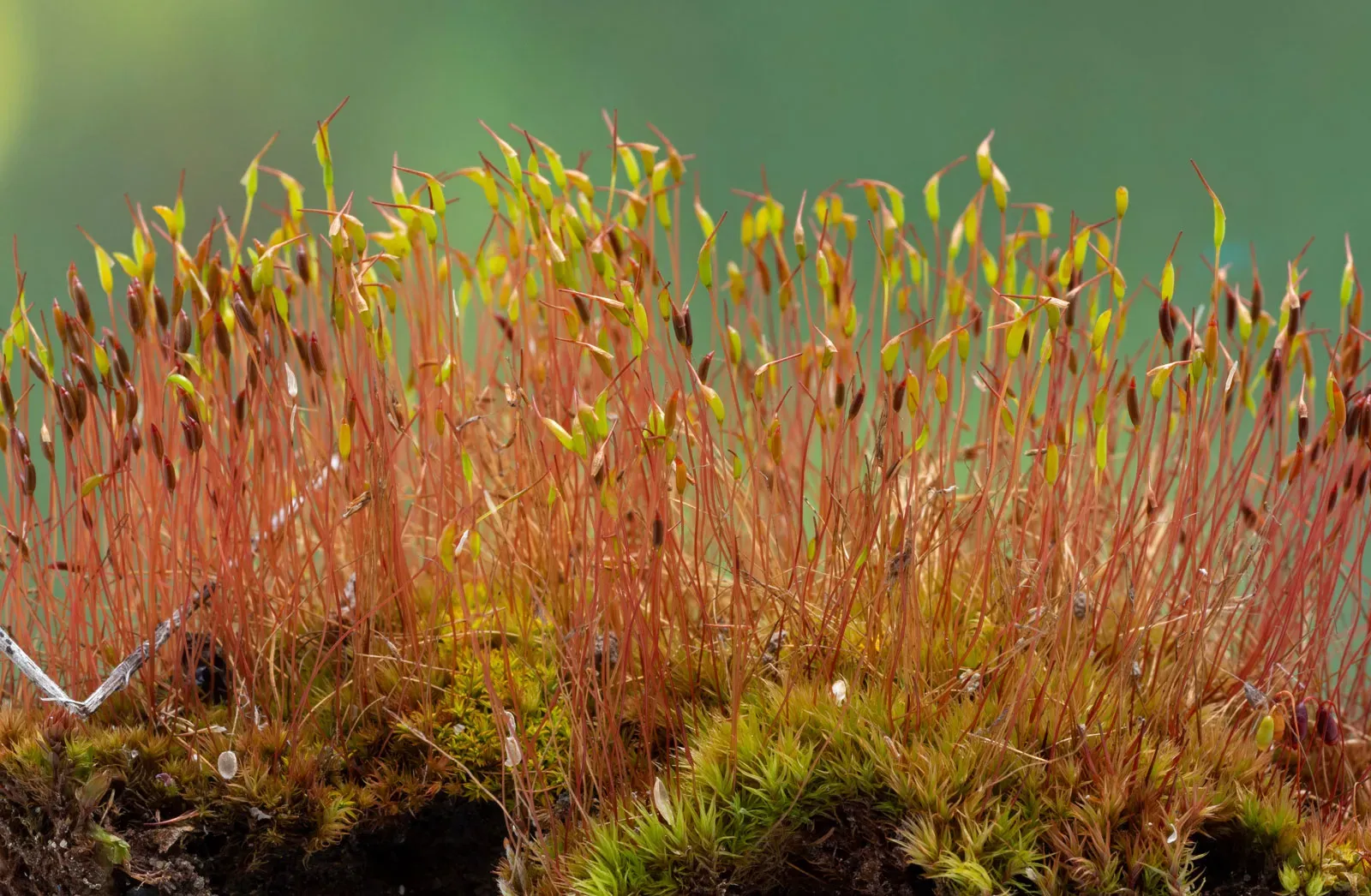

sporophyte-tortula-moss.jpg from: https://www.animalia-life.club/qa/pictures/moss-sporophyte.html
– small, spherical reproductive structures that grow from the base of the stems. Under a microscope, the leaf cells are short and hexagonal.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a wide global distribution, found on all continents except Antarctica. It commonly grows in tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas, Africa, and Asia. B. radiculosum

brachymenium_klotzschii.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/brachymenium_klotzschii.html
is able to tolerate a variety of environmental conditions.
Typical habitats for this species include:
- Tree trunks and branches
- Rotting logs and stumps
- Soil banks
- Roadside embankments
- Concrete walls and sidewalks
It frequently colonizes disturbed sites as a pioneer species. In some areas, it is considered a weed that grows on cultivated plants.

Bryum_capillare,I_MWS46505.jpg from: https://www.discoverlife.org/mp/20q?search=Bryum
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, B. radiculosum plays several important ecological roles:
- Erosion control – its dense mats help stabilize soil and prevent erosion
- Moisture retention – it absorbs and slowly releases water
2021-06-25-14-17-48.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/bryum-radiculosum/
- Habitat provision – it provides shelter and food for micro-organisms and invertebrates
- Nutrient cycling – it aids in breaking down organic matter
This moss has some notable adaptations that allow it to thrive in its habitats:
- Desiccation tolerance – it can survive periods of drying out
- Asexual reproduction via gemmae – allows rapid colonization of new sites
- Reduced cuticle – enables efficient water and nutrient uptake

210854.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5763
Conclusion
Brachymenium radiculosum may be small in stature, but it has a big impact in many ecosystems around the world. Its ability to grow in diverse habitats and environmental conditions make it an important pioneer species. Next time you see some moss growing on a tree or wall, take a closer look – it just might be this fascinating bryophyte!

Mosses.jpg from: https://knowledgeclass.blogspot.com/2013/03/mosses.html
What other mighty mosses have you encountered? Share your bryophyte experiences in the comments below.