
original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2678510
Exploring the Fascinating World of Homaliodendron stracheyanum Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Homaliodendron stracheyanum (Mitt.) M.Fleisch., also known simply as Homaliodendron

00ae422930c03355c1279e7d3670b688.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/5c288503a07b98ea98b8f1ea8f885b55
. This moss belongs to the Neckeraceae family and has some unique characteristics. Let’s dive in and learn more about this small but mighty plant!
Background on Mosses
Before we get into the specifics of H. stracheyanum, it’s helpful to understand some basics about mosses in general. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/556630-Homaliodendron-microdendron
Bryophyta. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead having structures that serve similar functions. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and require moisture for reproduction.
Morphology and Identification
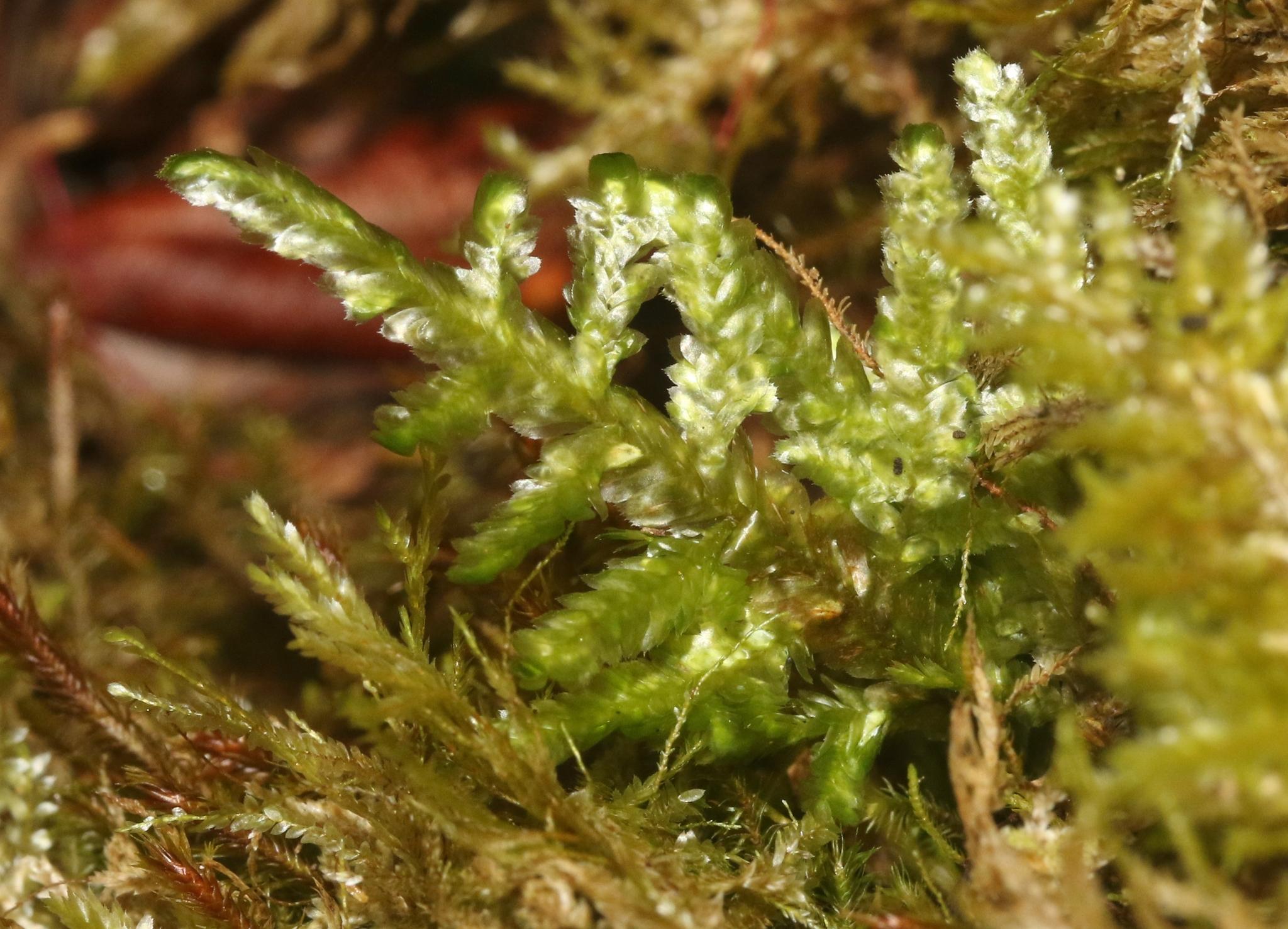
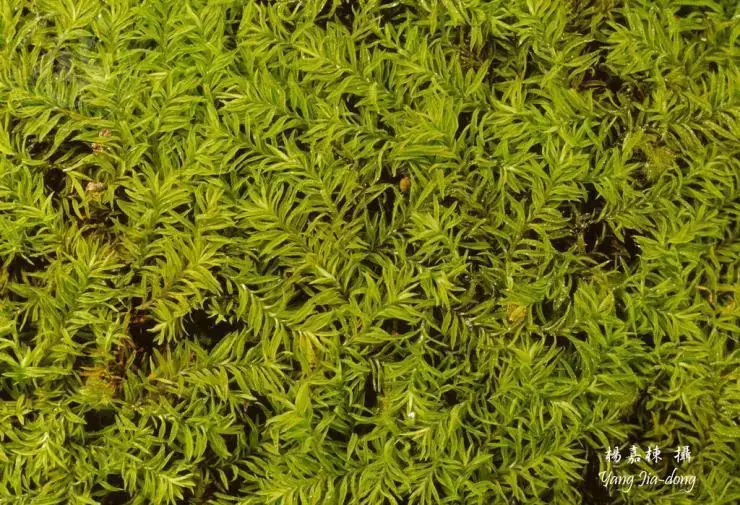
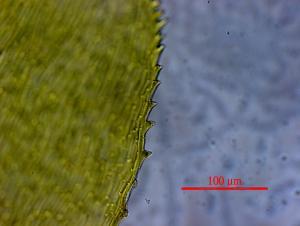
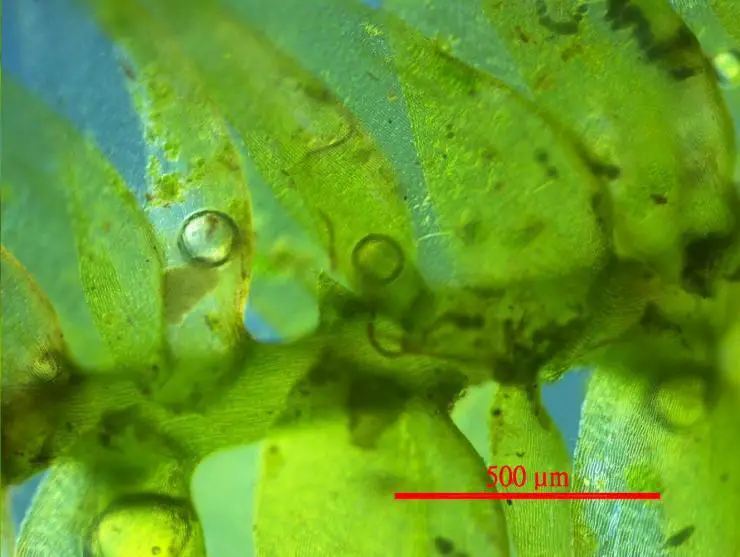
H. stracheyanum is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning it has a branching, mat-forming growth habit. Its stems can reach 3-5 cm long. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate with a rounded or cordate base. A key identifying feature is the presence of a strong, single costa (midrib) that extends 1/2 to 4/5 up the leaf. The leaf margins are entire to weakly toothed near the apex.
Global Distribution and Habitat
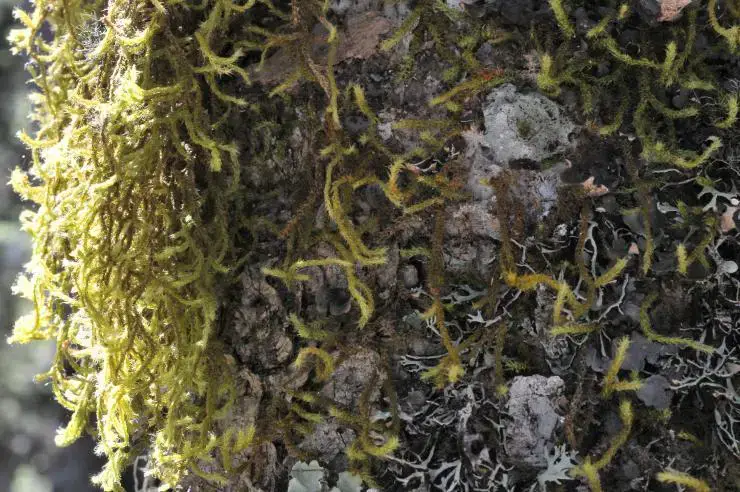
This moss has a wide distribution, being found in Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Pacific Islands. It typically grows on tree trunks and branches in humid forests from lowlands to 2000 m in elevation. In some areas, it is also found on rocks. H. stracheyanum prefers partially shaded habitats with moderate to high humidity.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, H. stracheyanum plays important roles in its ecosystem:
- Helps retain moisture and prevent erosion
- Provides habitat for micro-fauna
- Participates in nutrient cycling
- Bio-indicator of air quality
This moss has several adaptations that allow it to thrive in its environment, including:

c29e8ae203856dbb0ad57711f39a4b66.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/3e3cd9e2f829615f61e5ad5c50340a0e
- Thick cell walls to prevent desiccation
- Ability to absorb water and nutrients over its entire surface
- Production of secondary compounds that may deter herbivory
Homaliodendron stracheyanum at a Glance
62b78343d9b50e6f28b7707b266f5e6b.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/01b6e5fa4c93a37a1e5d0c57dea81875

FLQHSDLrL_(1).jpg from: https://blog.naver.com/PostView.nhn?blogId=la9496&logNo=150187905528
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Bryophyta |
Class
 062fe76a3d99abeabe1f00689b0f6142.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/941620afcf4d576ff03d5d1e1c09f139 |
Bryopsida |
| Family | Neckeraceae |
Genus
 7ce5231ecc8b0bc6696eb8cffeb247ab.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/35013 |
Homaliodendron |
Species
 61e51ec3c9b940a792bc3f9e0a907a29.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/61c0cc1dddb489ae4b135051dc513fdb |
H. stracheyanum |
| Growth Habit | Pleurocarpous, mat-forming |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Costa | Single, strong, 1/2-4/5 leaf length |
| Habitat | Tree trunks & branches, rocks; humid forests |
| Distribution | Asia, Africa, Australia, Pacific Islands |
Conclusion
H. stracheyanum is a prime example of how even tiny organisms can be fascinating and play important ecological roles. Next time you’re in a humid forest, take a closer look and see if you can spot this marvelous moss! What other overlooked organisms might be quietly working away in ecosystems near you?