
original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/7741803
Exploring the Fascinating World of Solenostoma lacouturei Steph. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are some of the most ancient and resilient plants on Earth, with over 12,000 species found across diverse habitats worldwide. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at one particularly interesting species: Solenostoma lacouturei Steph., a moss belonging to the Solenostomataceae family. Also known simply as
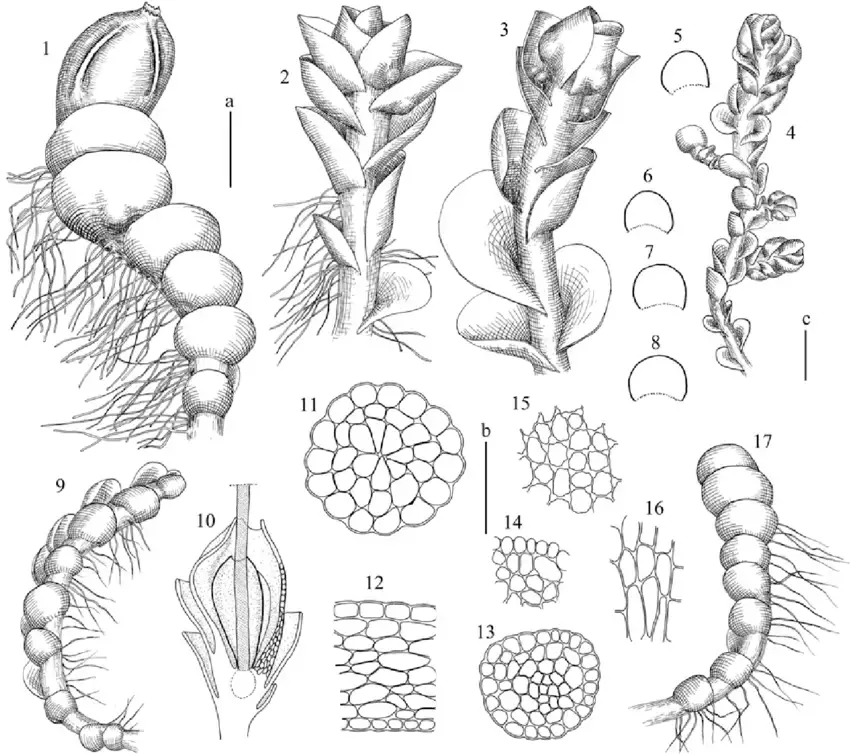
Solenostoma-pusillum-CEO-Jensen-Steph-1-branch-with-perianth-and-androecia-2-4.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Solenostoma-pusillum-CEO-Jensen-Steph-1-branch-with-perianth-and-androecia-2-4_fig8_273487708
Solenostoma, this tiny but mighty plant has some remarkable features that make it stand out in the world of bryophytes.
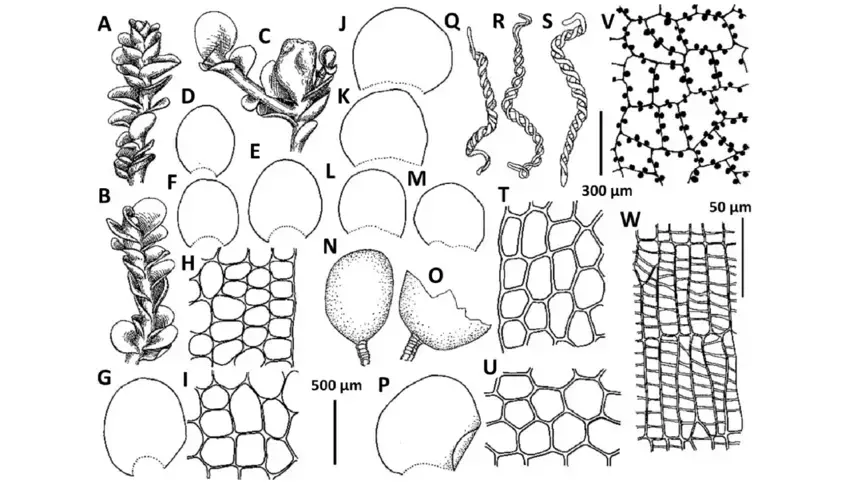
Solenostoma-pyriflorum-Steph-A-I-A-Male-branch-B-Sterile-branch-C-Female-branch.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Solenostoma-pyriflorum-Steph-A-I-A-Male-branch-B-Sterile-branch-C-Female-branch_fig17_342768325
Background on Mosses
Before diving into the specifics of S. lacouturei, let’s briefly review what mosses are. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Marchantiophyta. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead having simple leaf-like structures called phyllids. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and require water for sexual reproduction.

f8181150062c986dcc16c5958f0aae64.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/solenostoma-tetragonum–523965737891754289/
Mosses play important ecological roles, helping to regulate moisture, prevent erosion, provide habitat for microorganisms, and serve as bioindicators of environmental health. There are over 12,000 moss species, exhibiting incredible diversity in form and function.
Solenostoma lacouturei Steph. – A Closer Look
Morphology and Identification
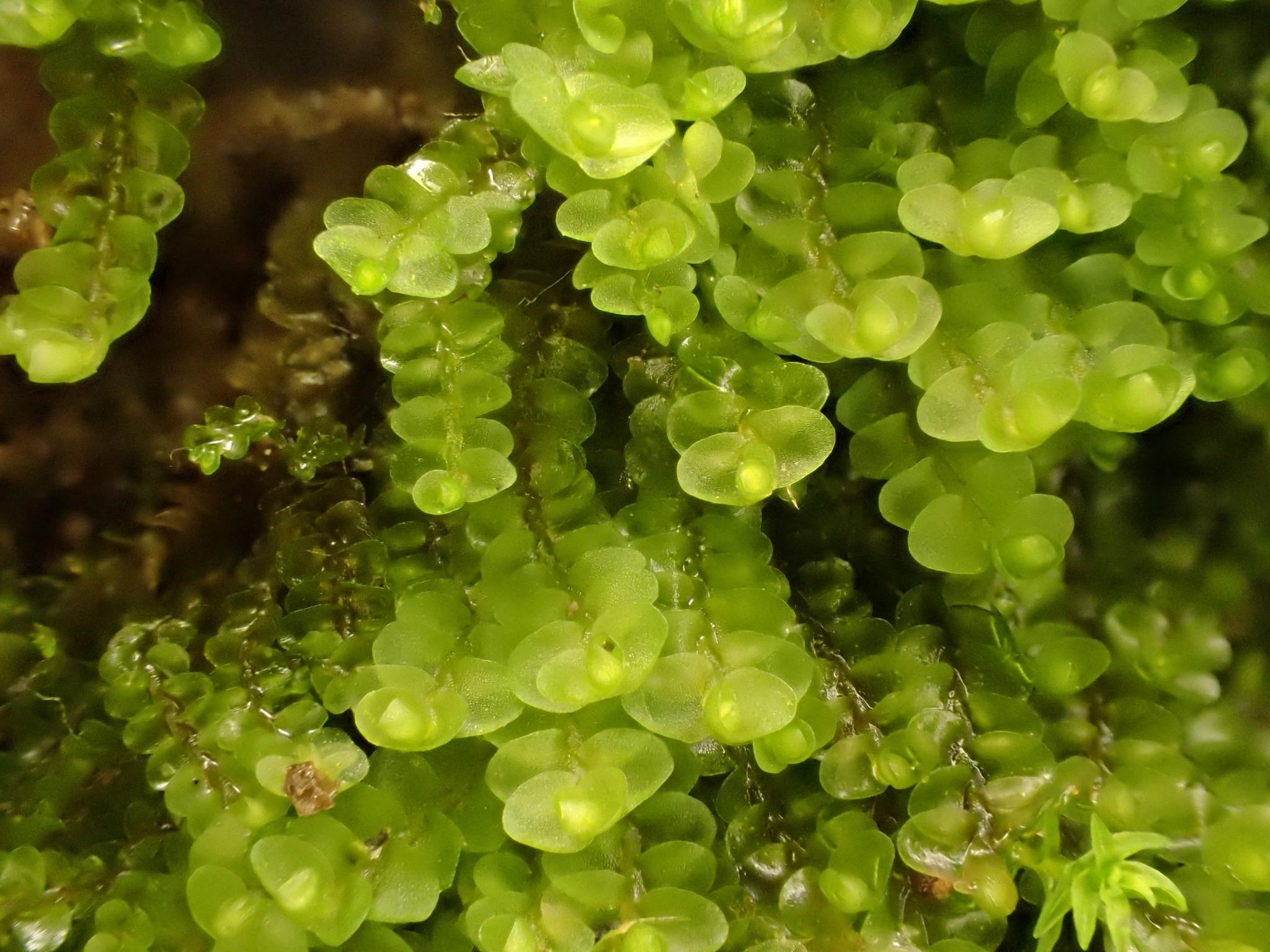
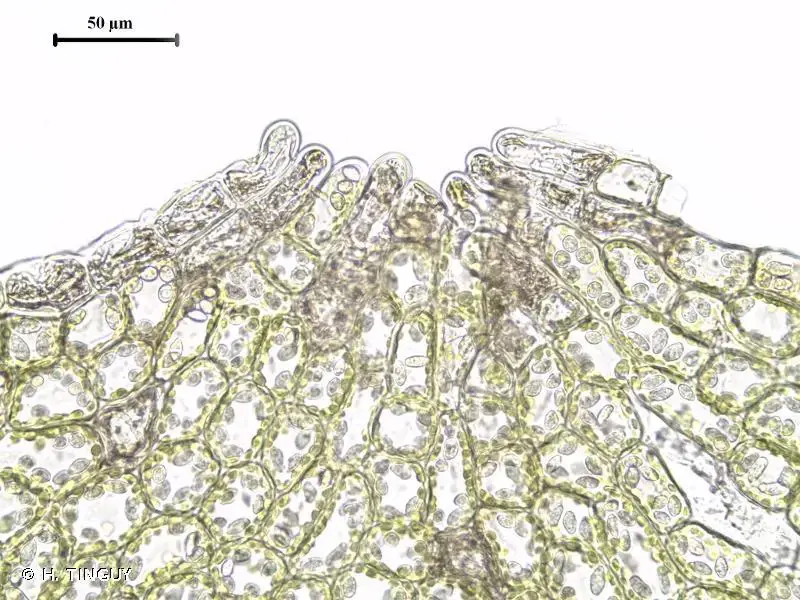
Solenostoma lacouturei is a small leafy liverwort moss in the order Jungermanniopsida. Its phyllids are succubously inserted, meaning each leaf-like structure overlaps the next in a shingle-like manner. The phyllids are orbicular to ovate in shape with an obtuse to rounded apex.
Identifying S. lacouturei requires microscopic examination of its cellular structure. Key features include:
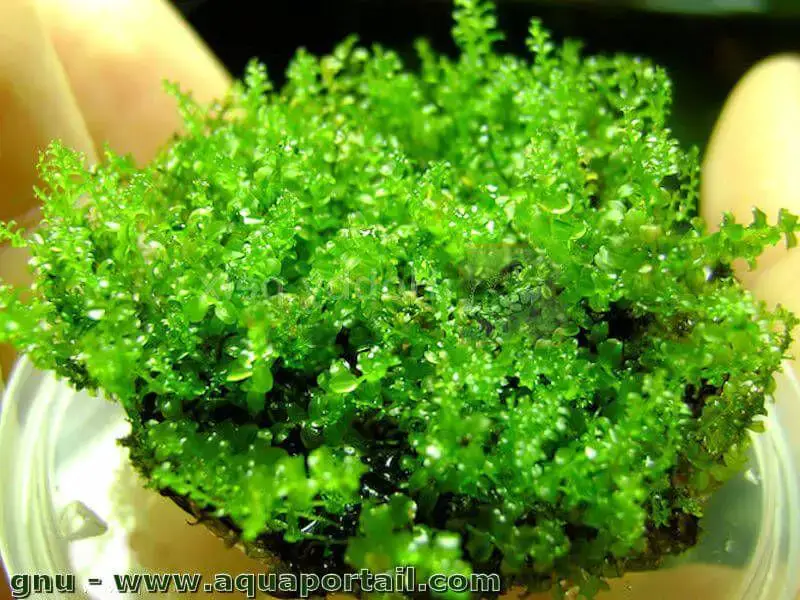

solenostoma-tetragonum.jpg from: http://www.aquaportail.com/fiche-plante-3140-solenostoma-tetragonum.html
- Oilbodies that are granular and few per cell
- Rhizoids with branched terminal ends
- Lack of underleaves (amphigastria)
- Presence of perianths that are dorsiventrally compressed and truncate at the mouth
Global Distribution and Habitat
S. lacouturei has a scattered global distribution, with records from:
- Europe
- Asia
299386.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/718837?lg=en
- Africa
- North America
- South America
This moss typically grows on damp, acidic substrates like soil, rocks, decaying wood, and tree bases in shaded forests and along streams. It is often found in montane habitats.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
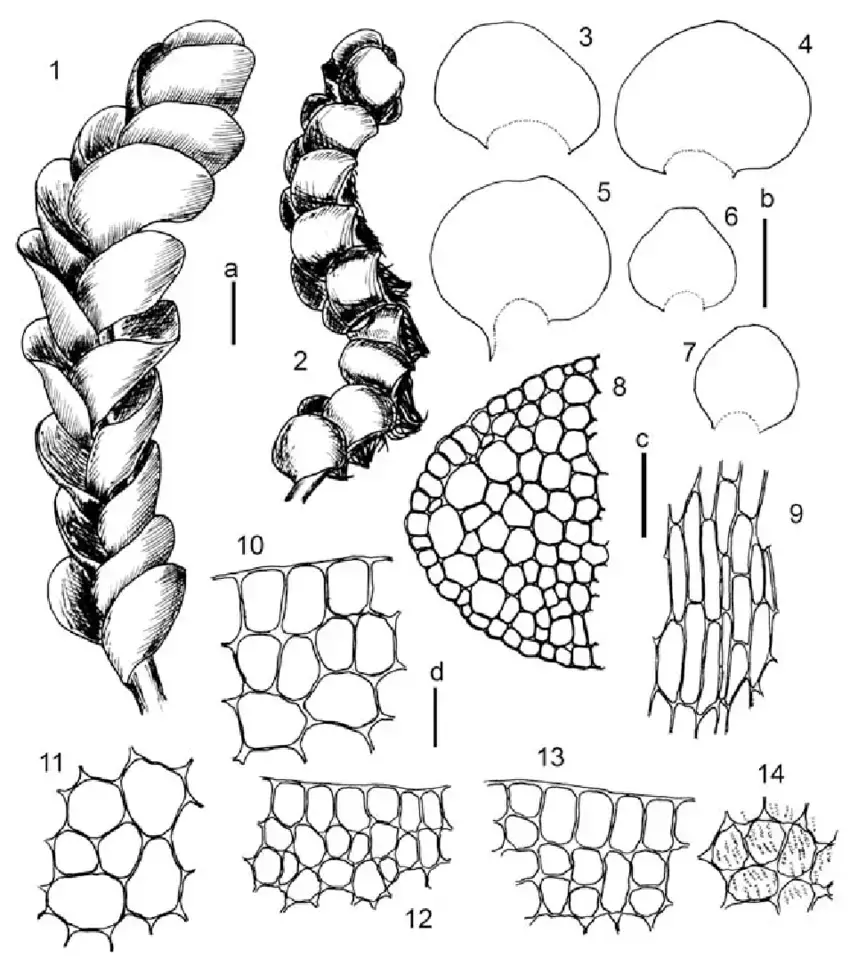
Solenostoma-fusiforme-Steph-R-M-Schust-1-2-plant-habit-3-7-leaves-8-stem.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Solenostoma-fusiforme-Steph-R-M-Schust-1-2-plant-habit-3-7-leaves-8-stem_fig1_282721225
Like other mosses,
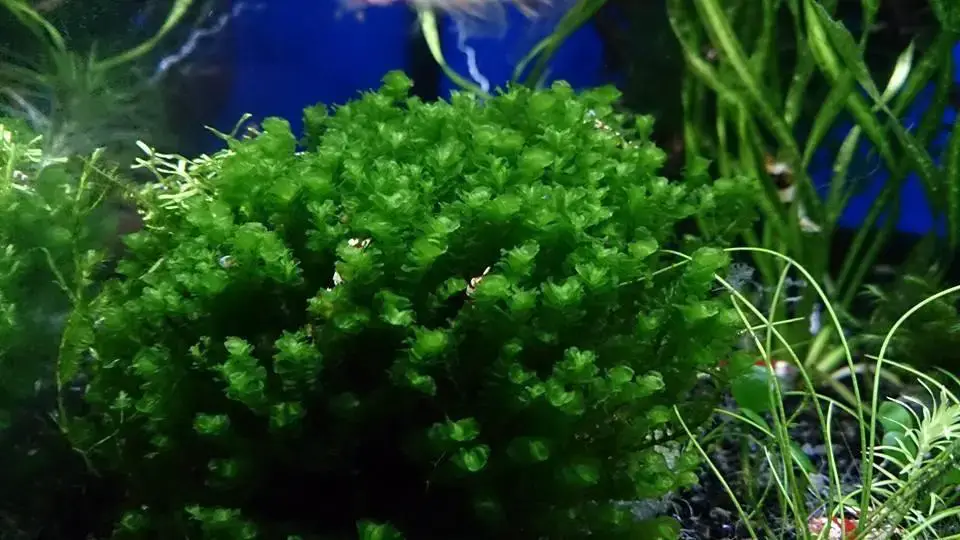

post-150-0-31428500-1418943521_thumb.jpg from: https://www.shrimpspot.com/topic/2192-solenostoma-tetragonum-crown-moss/
Solenostoma lacouturei plays important roles in its ecosystem:
- Helps retain moisture and slow water loss from soil
- Stabilizes soil and prevents erosion
- Provides microhabitat for invertebrates and other organisms
- Serves as a bioindicator of air and water quality
This tiny moss has several adaptations that allow it to thrive:
- Poikilohydry – ability to tolerate desiccation and rehydrate quickly
- Clonal growth via fragmentation
- Spore dispersal by water
- Associations with beneficial fungi (mycorrhizae)
Conclusion
Solenostoma lacouturei Steph. may be small, but this mighty moss is a fascinating example of bryophyte diversity. From its distinctive morphology to its important ecological functions,
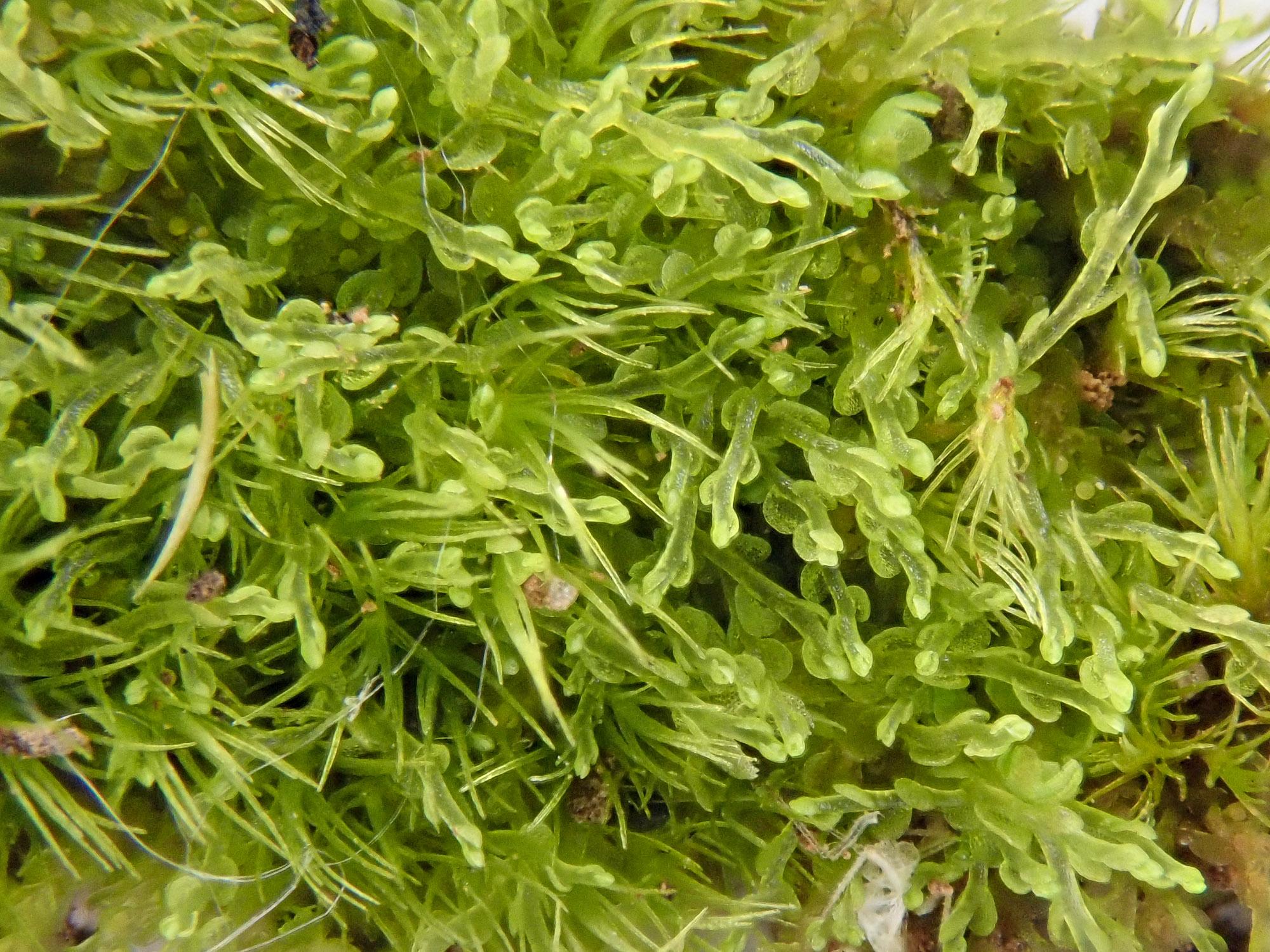

2021-09-26-12-32-37.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/solenostoma-gracillimum/
S. lacouturei highlights how these ancient plants continue to thrive in the modern world.
The next time you’re out in nature, take a closer look – you might just spot some Solenostoma growing inconspicuously underfoot! These unassuming mosses have an important story to tell about the complexity and resilience of life on Earth.
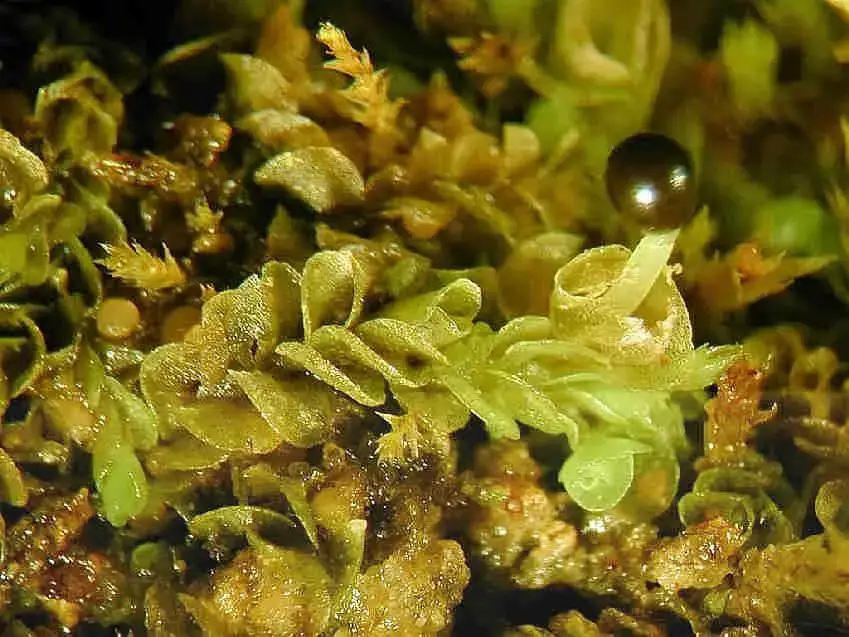

Solenostoma_hyalinum.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Solenostoma_hyalinum.html