397504.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5455?lg=en
Mitthyridium leucoloma: The Magnificent Moss of the Calymperaceae Family
Introduction
Mosses may be small, but they play a big role in ecosystems around the world. One particularly fascinating species is
Syntrichia-amphidiacea-MuellHal-RH-Zander-1-plant-2-cross-section-of-stem-3_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Syntrichia-amphidiacea-MuellHal-RH-Zander-1-plant-2-cross-section-of-stem-3_fig1_316686567
Mitthyridium leucoloma (Müll.Hal.) H.Rob., a moss in the Calymperaceae family. Also known simply as Mitthyridium, this marvelous moss is worth taking a closer look at.
Background on Mosses
Before diving into the details of M. leucoloma, let’s review some moss basics. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. Unlike other plants, they lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have leaf-like structures called phyllids. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in a wide range of habitats worldwide.
Morphology and Identification
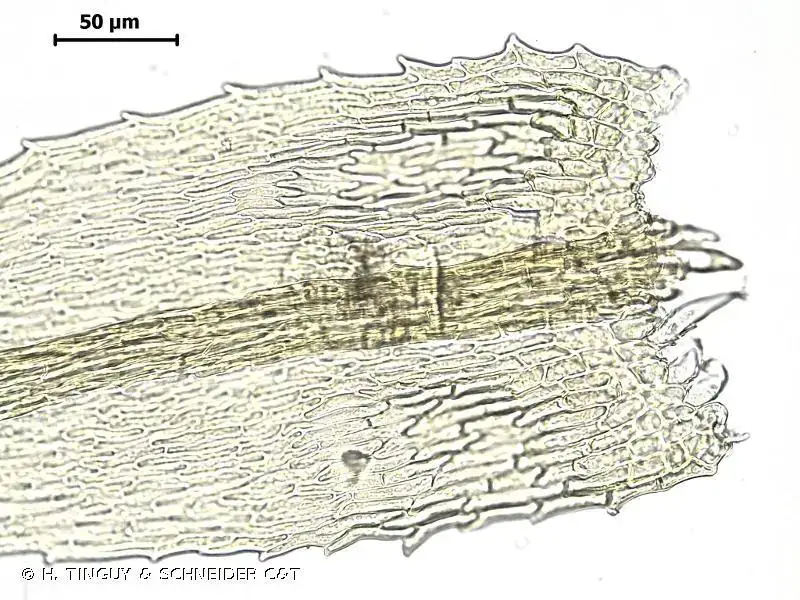
Mitthyridium leucoloma is an acrocarpous moss, meaning it has erect growth and its sporophytes develop at the tips of the main stems. Its phyllids are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and have a white, hyaline border

7037e79d418c961c5141889e083833ce.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/2355523fe7d6b11d4b7a8ac495911fd7
that helps with identification. The moss forms small cushions or tufts, typically 1-3 cm tall. Its spore capsules are cylindrical and borne on short setae (stalks).
Global Distribution and Habitat
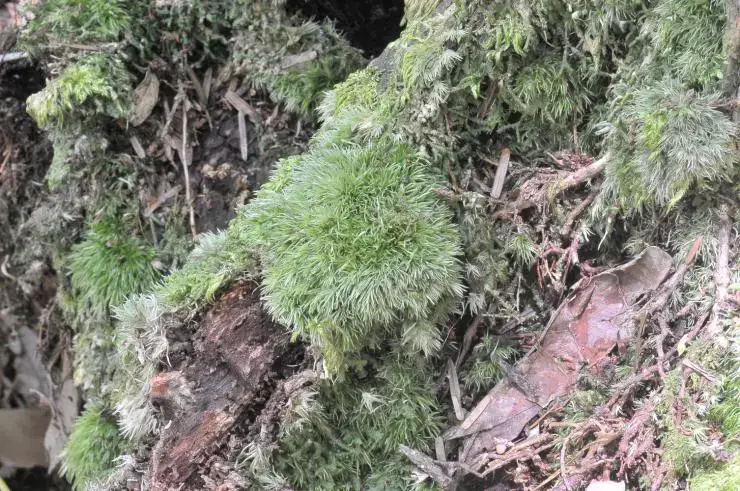
M. leucoloma has a pantropical distribution, found in tropical regions around the world including Central and South America, Africa, Asia, and the Pacific. It grows as an epiphyte on the bark of trees and shrubs in moist forests from lowlands to mountains. The moss is also sometimes found on rocks or rotting logs.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, M. leucoloma plays important roles in its ecosystem:
- Helps retain moisture and prevent erosion
- Provides habitat for micro-organisms
- Serves as a pioneer species in ecological succession
- Indicator of air quality and environmental health
The hyaline leaf borders of M. leucoloma likely aid in water retention and may deter herbivory by small insects. Its tolerance of low light levels allows it to thrive in shaded forest habitats.
Conclusion
From its unique morphology to its ecological importance, Mitthyridium leucoloma is a marvelous moss that deserves appreciation. Next time you’re in a tropical forest, take a moment to search for this small but significant species. What other mighty mosses might you discover when you start paying attention to these often-overlooked plants?