
19-Mitthyridium-cardotii-M-Fleisch-H-Rob-13-plant-14-portion-of-plant-15.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/19-Mitthyridium-cardotii-M-Fleisch-H-Rob-13-plant-14-portion-of-plant-15_fig2_308534623
Exploring the Fascinating World of Pterobryopsis M.Fleisch. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are some of the most ancient and resilient plants on Earth. One particularly interesting genus is Pterobryopsis M.Fleisch., commonly known as Pterobryopsis moss. This post will dive into the details of this fascinating moss, including its morphology, global distribution, ecological roles, and adaptations.
Background
Pterobryopsis M.Fleisch. is a genus of mosses in the family Pterobryaceae. The Pterobryaceae family contains around 200 species worldwide. Pterobryopsis mosses belong to the division Bryophyta and class Bryopsida. They are pleurocarpous mosses, meaning they have a creeping or hanging growth habit with sporophytes emerging from the sides of the stems.
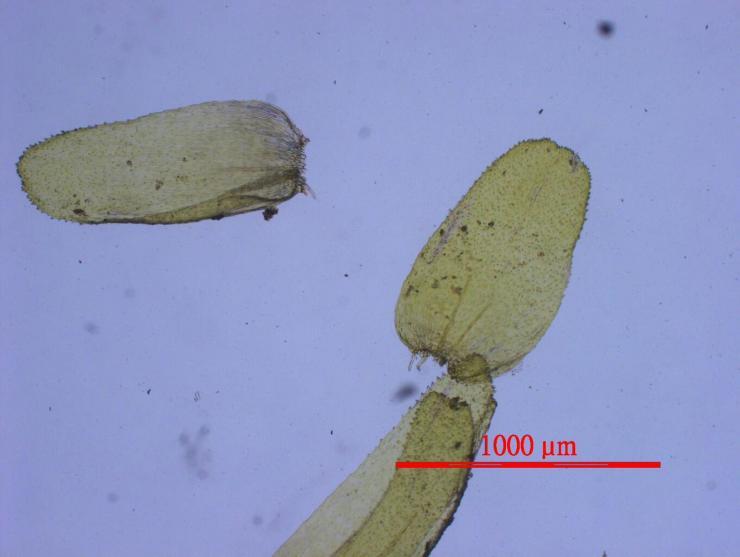
Morphology and Identification
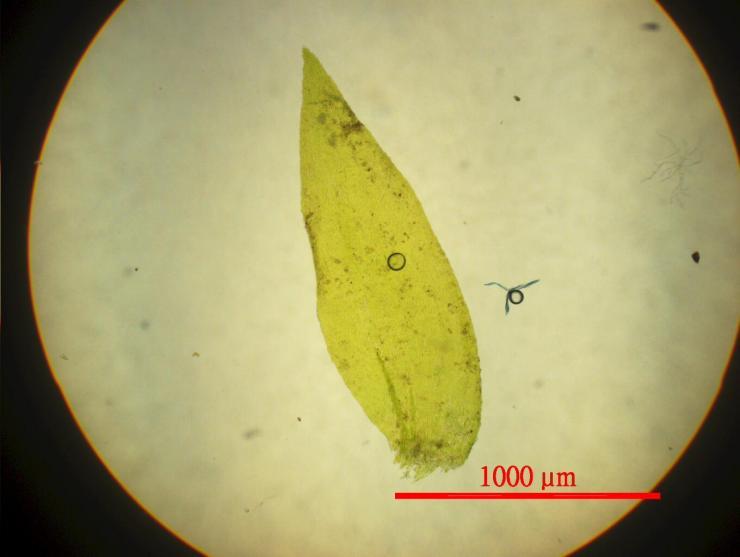
Pterobryopsis mosses have distinctive morphological features:
- Stems are creeping to pendent, irregularly branched
- Leaves are concave, ovate to oblong-lanceolate, often plicate (pleated)

28720031423_29ab4a5197_z.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/kochibii/albums/72157672145243572/
- Costa (midrib) is single and strong, extending 1/2 to 3/4 the leaf length
- Leaf cells are linear, smooth or weakly prorulose
- Capsules are immersed to exserted on short setae
Pterobryopsis can be distinguished from related genera by its single costa, concave and often plicate leaves, and linear leaf cells. However, microscopic examination is usually needed for definitive identification to species.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Pterobryopsis has a primarily tropical and subtropical distribution. Species are found in:
- Central and South America
largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/359712696_The_complete_mitochondrial_genome_of_the_moss_Neckeropsis_nitidula_Mitt_M_Fleisch
- Africa
- Southern Asia
- Northern Australia
- Pacific Islands
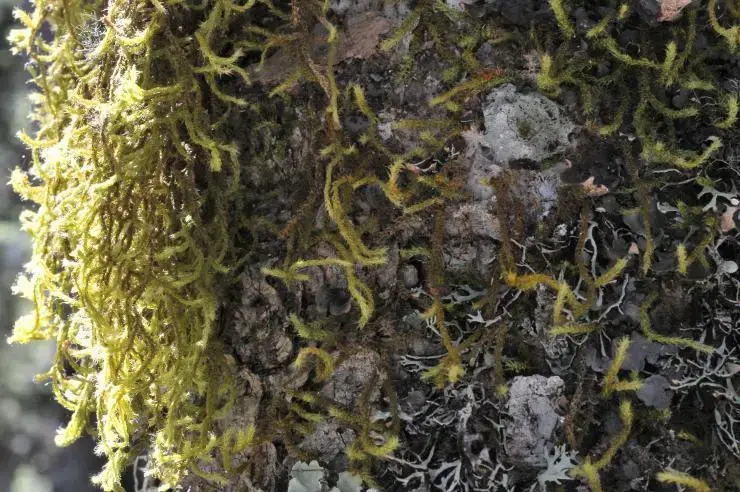
They typically grow as epiphytes on tree trunks and branches in humid forests

874ac4d960d122c6eff5f661ea5deea5.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/01b6e5fa4c93a37a1e5d0c57dea81875
. Some species also grow on rocks or rarely on soil. Pterobryopsis mosses prefer shaded, moist habitats from lowlands to montane elevations.
1119bdc908a153854307430eec7a89ab.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/bee7a4eea7b4e8b55eb04f8f158c8f8a
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
As epiphytes, Pterobryopsis mosses play important roles in forest ecosystems:
- Provide habitat and shelter for invertebrates
- Capture and retain

00ae422930c03355c1279e7d3670b688.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/5c288503a07b98ea98b8f1ea8f885b55
moisture and nutrients

062fe76a3d99abeabe1f00689b0f6142.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/941620afcf4d576ff03d5d1e1c09f139
- Contribute to nutrient cycling
- Increase structural complexity and biodiversity in forest canopies
Pterobryopsis mosses have several adaptations for the epiphytic lifestyle:
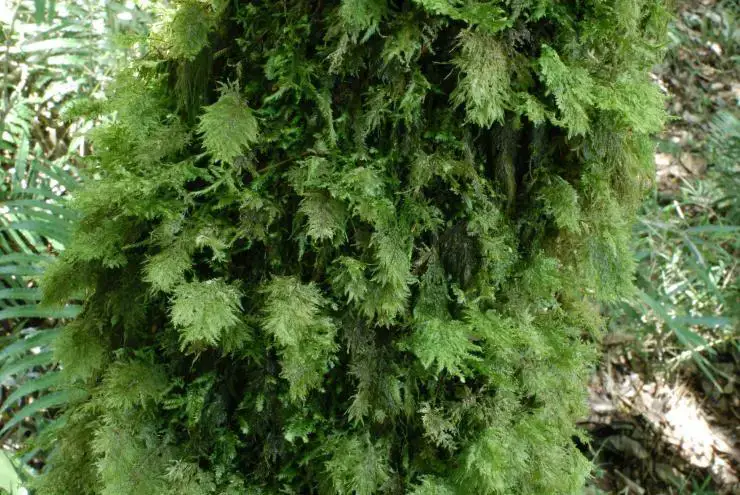

5622e6df2ce9f1051a576c6c516b9db2.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/d3c69fc27fdd03291ec8fc9aa7341fc5
- Concave leaves help capture and funnel water down the stems
- Thick cell walls and costa provide structural support
- Rhizoids anchor the mosses to bark substrates
- Desiccation tolerance allows survival during dry periods
Conclusion
Pterobryopsis is a fascinating genus of tropical mosses with unique morphology and ecological roles. From humid lowland forests to misty mountain slopes, these unassuming plants form an integral part of the epiphyte communities that make tropical forests so diverse and complex. Next time you’re in a tropical forest, take a closer look at the mossy branches overhead – you might just spot a patch of plicate Pterobryopsis leaves! What other secrets of the bryophyte world remain to be uncovered?