
image from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/48126735@N03/20719304532/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Acroporium fuscoflavum (Paris) Broth., commonly known as Acroporium, stands out as a remarkable moss species. Belonging to the Sematophyllaceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this moss and uncover its secrets.

image from: https://www.semanticscholar.org/topic/Sematophyllaceae/6536687
Background
Before we explore the wonders of Acroporium, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Isopterygium-tonkinensis-Broth-Paris-YJia-SHe-A-Habit-B-Branch-C-A_fig3_331050368
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Acroporium fuscoflavum is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, creeping stems are adorned with delicate, lance-shaped leaves that form a feathery appearance. The leaves are typically fuscous (dark brown) to flavous (yellowish-green) in color, lending the moss its distinctive hue.
One of the key identifying features of
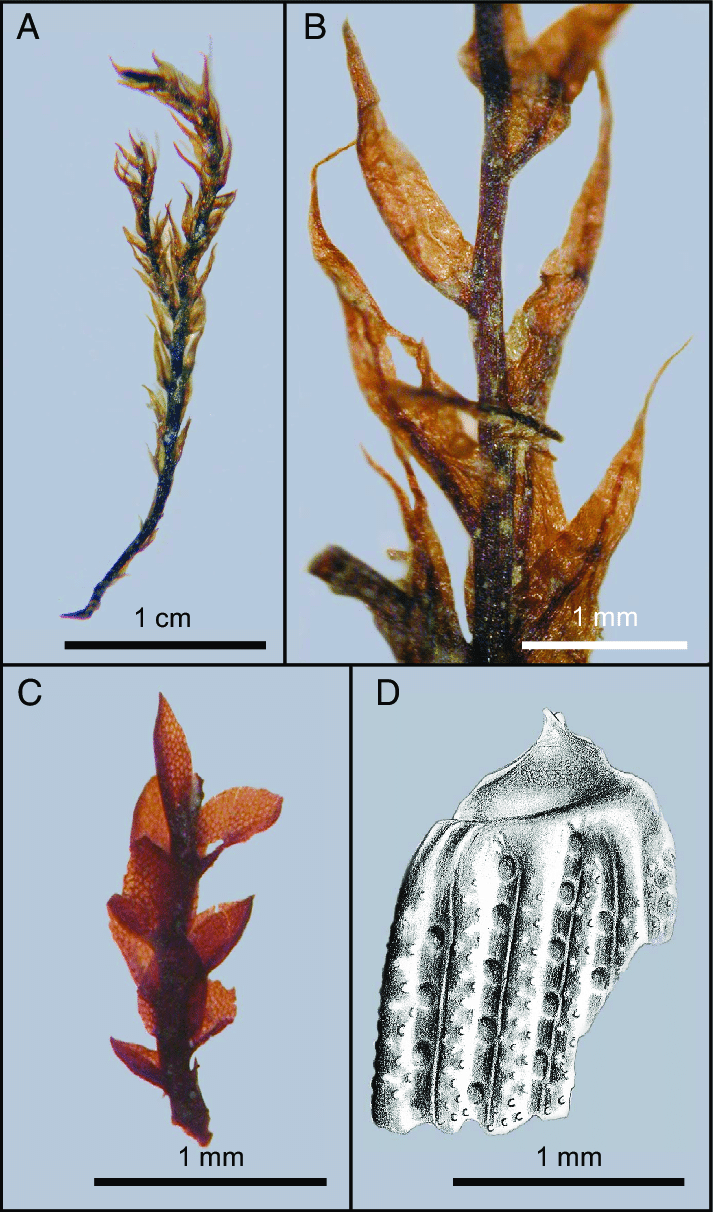
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fossil-mosses-and-a-beetle-A-Stem-and-leaves-of-the-semiaquatic-moss-Drepanocladus_fig3_23148177
Acroporium is its double costa, or midrib, which extends beyond the leaf apex. This characteristic, along with its unique leaf arrangement and capsule shape, aids in distinguishing it from other moss species.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Acroporium fuscoflavum is widely distributed across various regions, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and North America. It thrives in a range of habitats, from moist and shaded forests to rocky outcrops and even urban environments. This moss is particularly fond of growing on tree trunks, logs, and rocks, where it forms dense, velvety mats.
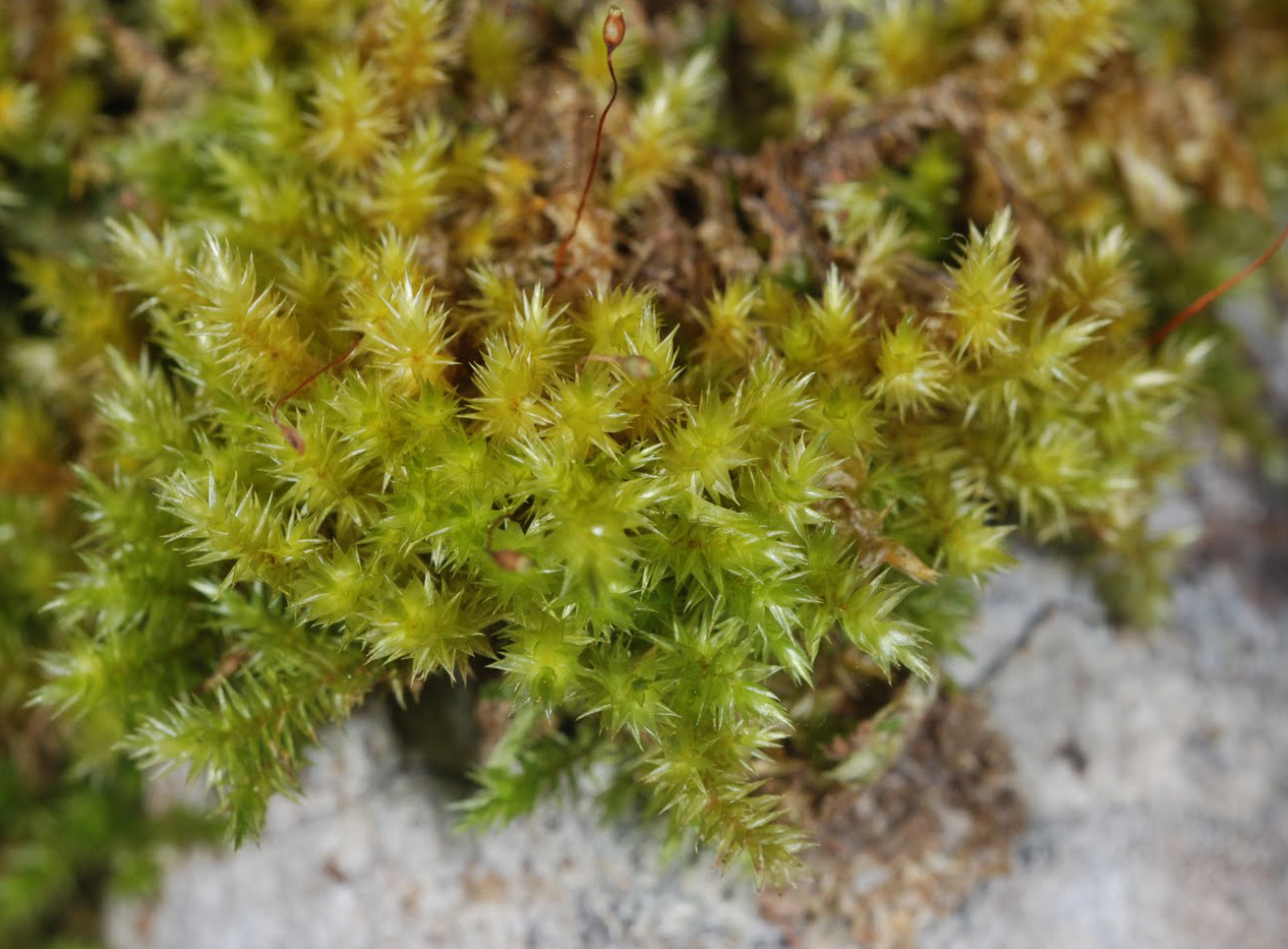

image from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/01_Semat.html
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Isopterygium-tonkinensis-Broth-Paris-YJia-SHe-A-Habit-B-Branch-C-A_fig3_331050368
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Acroporium plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating a suitable environment for other plants and organisms to flourish. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Acroporium is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to conserve moisture. Once favorable conditions return, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and adaptability.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that Acroporium fuscoflavum played a crucial role in maintaining the biodiversity of epiphytic (tree-dwelling) bryophyte communities. The moss’s ability to colonize a wide range of tree species and its tolerance to varying environmental conditions made it a valuable contributor to the overall ecosystem health.

image from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=omHfixpx_6c
Technical Table
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Acroporium-hyalinum-var-turgidum-A-Habit-of-stem-B-Sporophyte-C-D-Leaves-E-Leaf_fig4_329961872

image from: http://www.flickr.com/photos/zpyder/3665519279/
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Acroporium-hyalinum-var-hamulatum-A-Habit-of-stem-B-Habit-of-branch-C-D-Leaves-E_fig3_329961872
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Sematophyllaceae |
| Genus | Acroporium |
| Species | fuscoflavum |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spirally arranged |
| Leaf Shape | Lance-shaped |
| Leaf Color | Fuscous to flavous |
| Distinctive Feature | Double costa extending beyond leaf apex |