Exploring the Realm of Trematodon: A Closer Look at Trematodon longicollis Michx.
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!

Trematodon_longicollis,I_TQBH8334.jpg from: https://www.discoverlife.org/mp/20q?search=Bruchiaceae
Introduction
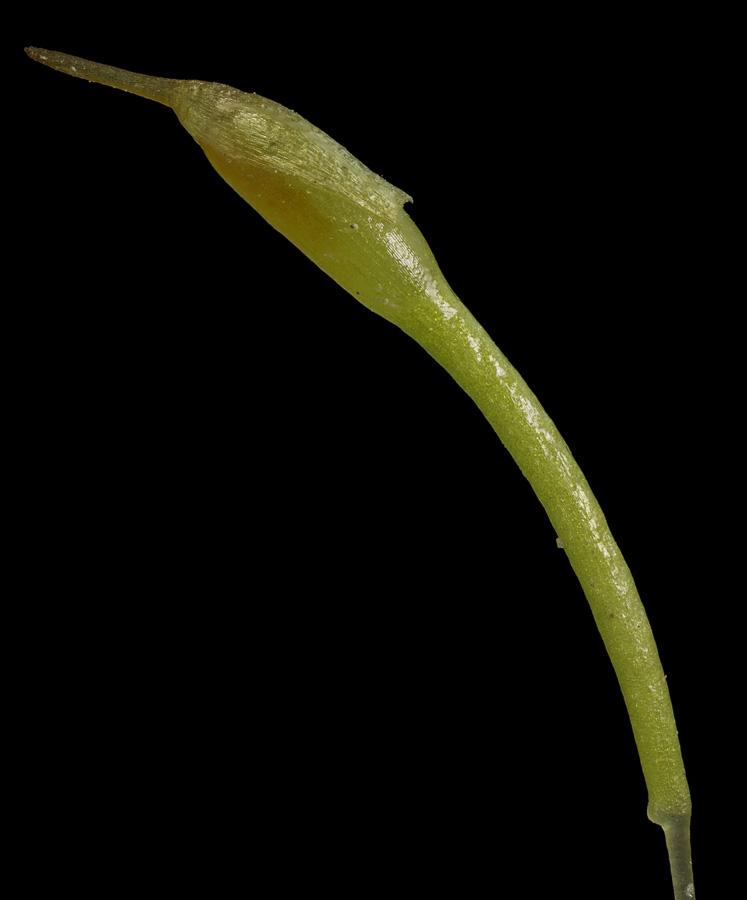

NFA-Bryos-Trematodon-longicollis-00962.jpg from: https://northernforestatlas.org/atlas-image-category/trematodon-longicollis-uncommon-species/
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Trematodon longicollis Michx. moss stands out as a remarkable species within the Bruchiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Trematodon, this unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Trematodon longicollis Michx., it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
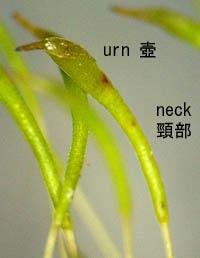
Trematodon longicollis Michx. is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are narrow, lance-shaped, and often twisted when dry, giving the plant a distinctive appearance. One of its most striking features is the long, slender seta (stalk) that supports the capsule, which is cylindrical and slightly curved.

a69b7eab60e25713148bc020c85e2139.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/33758
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss species has a widespread distribution, occurring across various regions of North America, Europe, and Asia. It thrives in a variety of habitats, including moist soil, rotting logs, and disturbed areas such as roadside banks and ditches.
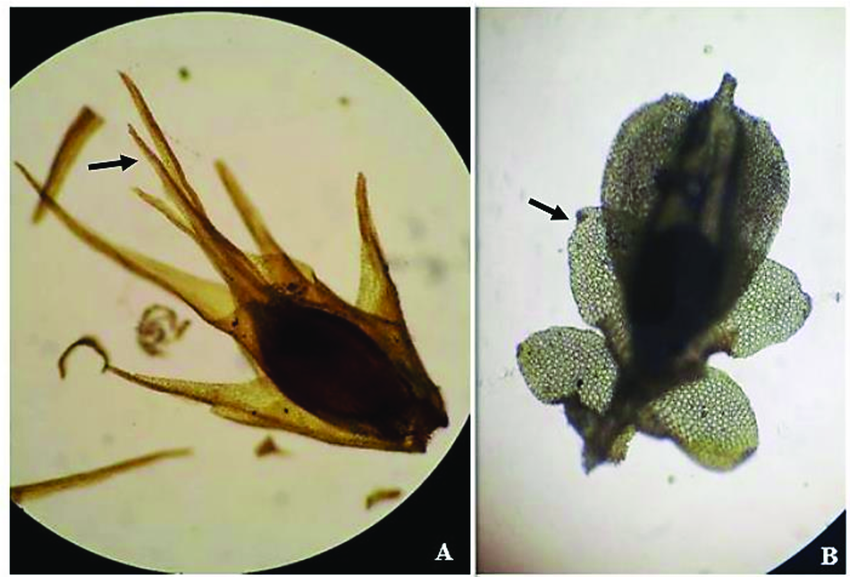

A-Filidios-periqueciais-no-apice-do-gametofito-de-um-musgo-Trematodon-Michx-sp-B.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-Filidios-periqueciais-no-apice-do-gametofito-de-um-musgo-Trematodon-Michx-sp-B_fig19_353353452
yumidaigoke-saku.jpg from: https://flora-of-mikawa.sakura.ne.jp/koke/yumidaigoke.htm
Trematodon longicollis Michx.
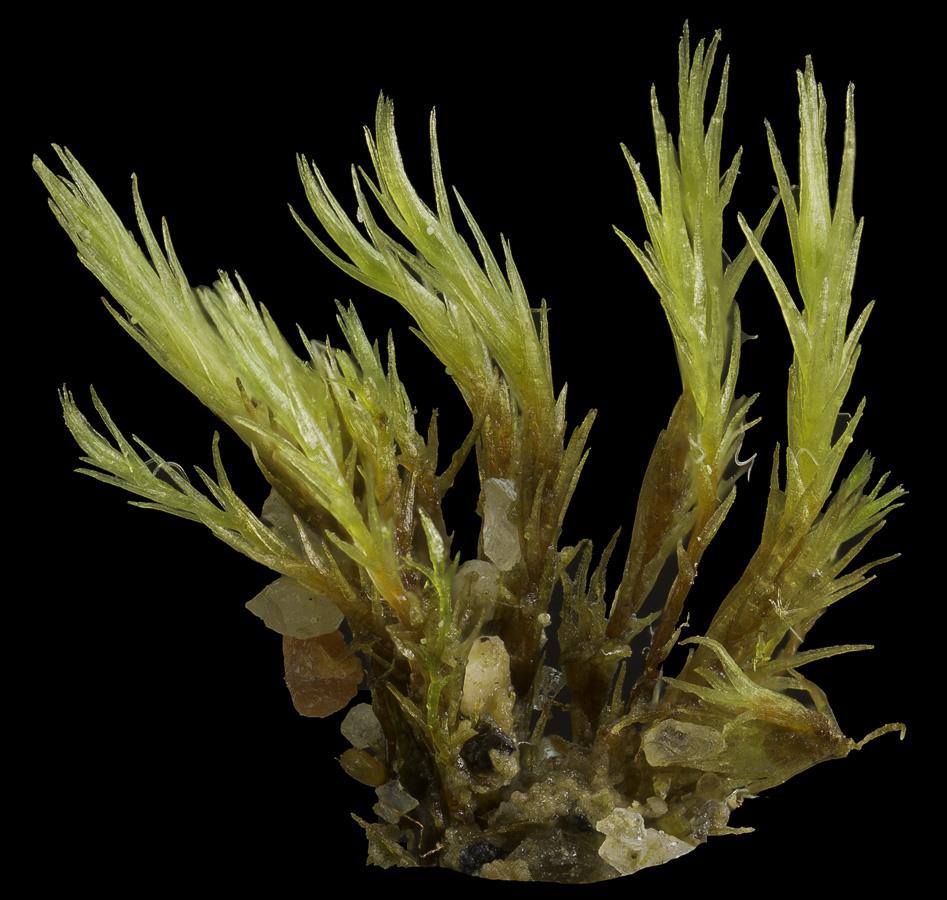

NFA-Bryos-Trematodon-longicollis-00963.jpg from: https://northernforestatlas.org/atlas-image-category/trematodon-longicollis/
is particularly fond of acidic substrates and is often found in coniferous forests or areas with decaying wood.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Trematodon longicollis Michx. plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide microhabitats for various invertebrates and serve as a food source for some animals.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Trematodon longicollis Michx. is its ability to survive in harsh environments. Its compact growth form and twisted leaves help it retain moisture, while its tolerance for acidic conditions allows it to thrive in areas where other plants may struggle.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a temperate forest in North America, researchers found that Trematodon longicollis Michx. played a crucial role in facilitating the establishment of tree seedlings. The moss’s dense mats provided a suitable microclimate and protected the seedlings from desiccation, ultimately contributing to the regeneration of the forest ecosystem.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Bryales |
| Family | Bruchiaceae |
| Genus | Trematodon |
| Species | longicollis Michx. |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Narrow, lance-shaped, often twisted when dry |
| Seta | Long, slender |
| Capsule | Cylindrical, slightly curved |
| Habitat | Moist soil, rotting logs, disturbed areas, acidic substrates |
| Distribution | North America, Europe, Asia |
Conclusion
Trematodon longicollis Michx., a humble yet remarkable moss species, serves as a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. Its unique morphology, ecological roles, and adaptations have captivated enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of mosses, perhaps we can ponder this thought-provoking question: What other hidden wonders lie within the realm of these diminutive yet extraordinary plants?
