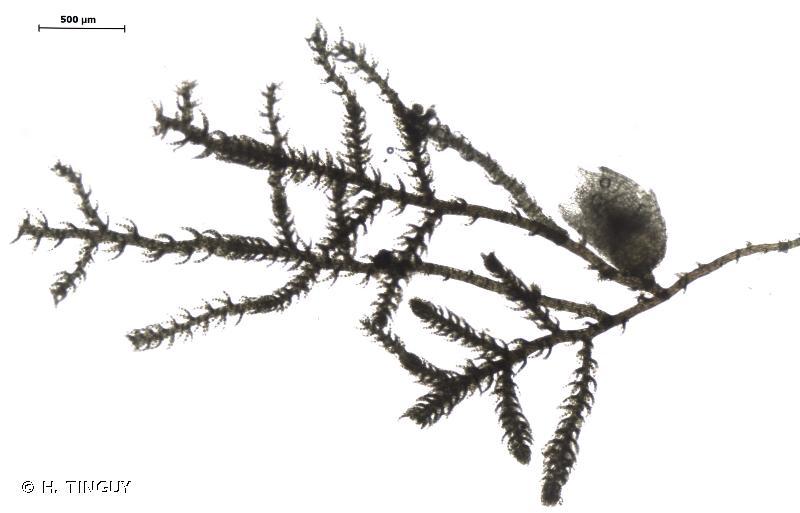

413145.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6619
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Kurzia trichoclados (Müll.Frib.) Grolle moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Lepidoziaceae family. Often referred to simply as Kurzia, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Kurzia trichoclados, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. This moss belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida, which encompasses a diverse array of liverworts and mosses. The Lepidoziaceae family, to which Kurzia belongs, is known for its intricate and delicate members, often found thriving in moist and shaded environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
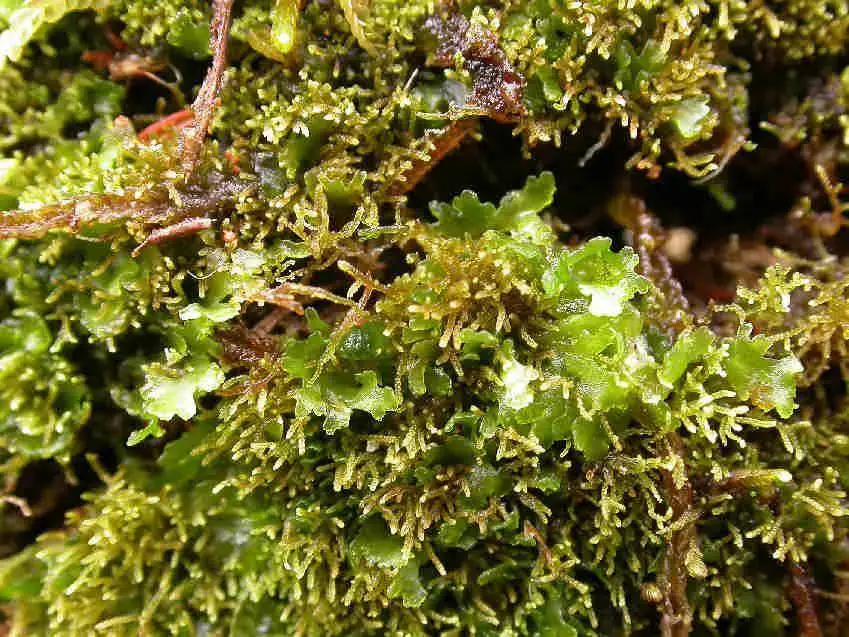
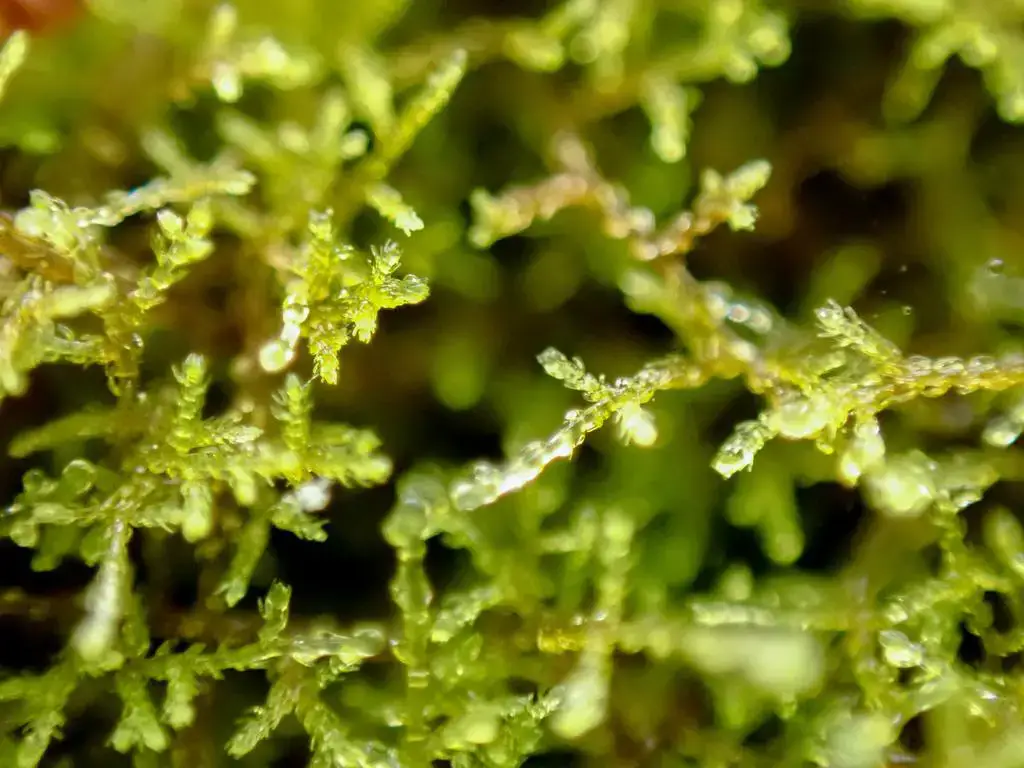
Kurzia trichoclados is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the substrate it inhabits. Its stems are slender and wiry, bearing numerous branches that give the plant a feathery appearance. The leaves are deeply divided, resembling tiny ferns, and are arranged in a spiral pattern along the stem. This intricate leaf structure is one of the defining characteristics that aid in the identification of this moss species.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Kurzia trichoclados is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, such as forests, rock crevices, and decaying logs. This moss prefers acidic substrates and is often found growing in association with other bryophytes, forming intricate and diverse moss communities.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Kurzia trichoclados plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich the soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and sustenance for these tiny creatures.
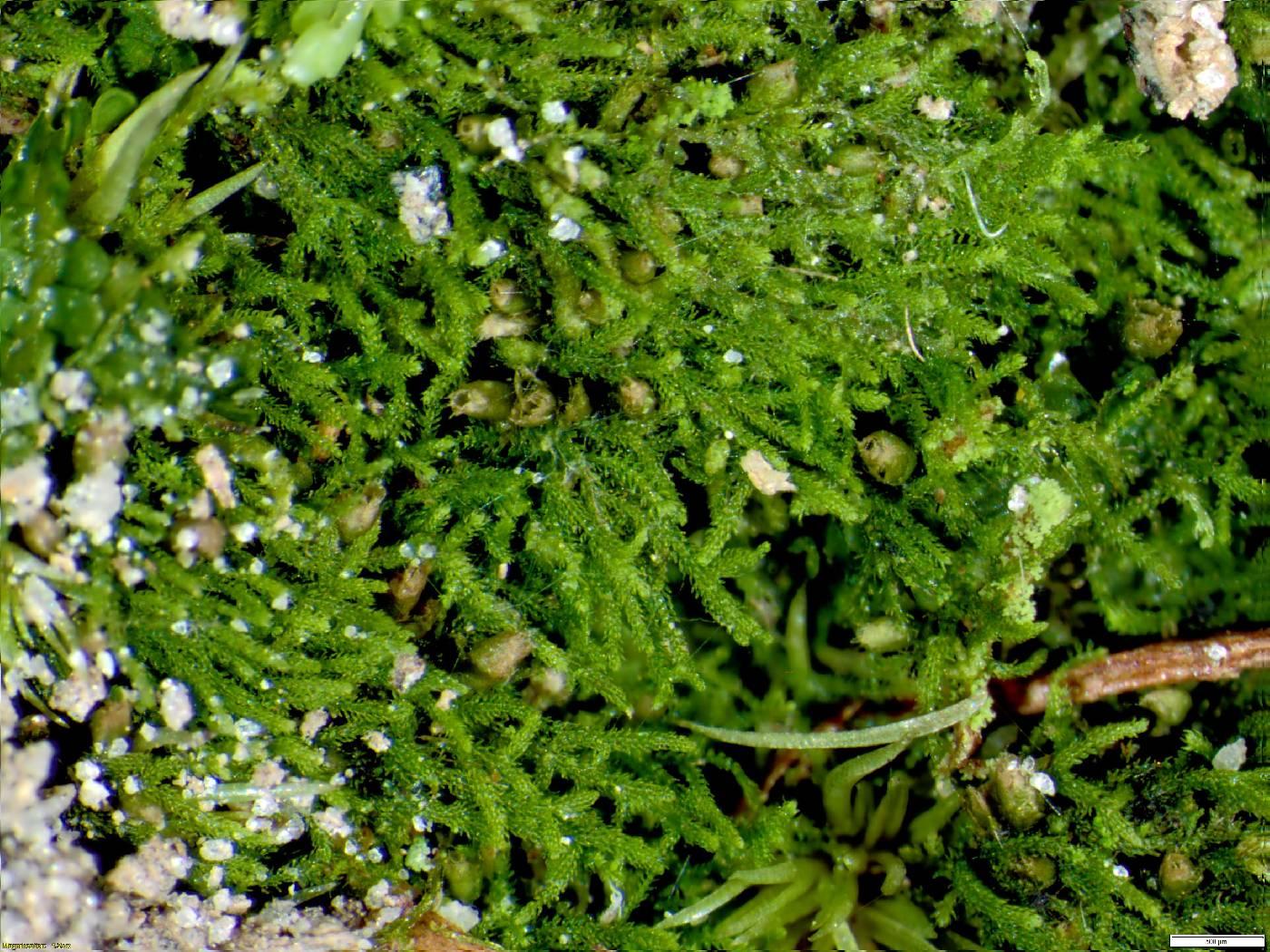

Kurzia_BA19540_DS_5_6x_0_5obj__1545241561.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/portal/imagelib/imgdetails.php?imgid=1745904
One of the remarkable adaptations of
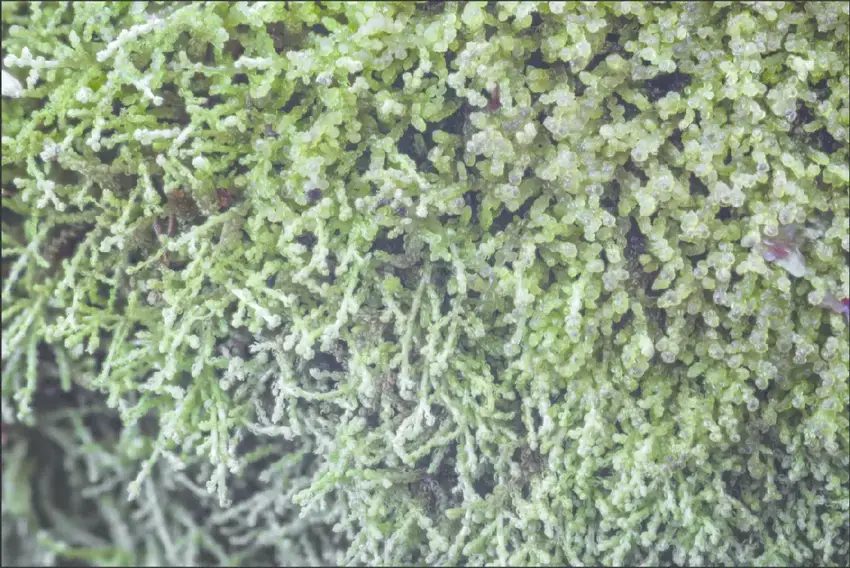

Kurzia-trichoclados-a-small-and-pleasantly-sweet-aromatic-liverwort-that-can-be-sniffed.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Kurzia-trichoclados-a-small-and-pleasantly-sweet-aromatic-liverwort-that-can-be-sniffed_fig2_306092258
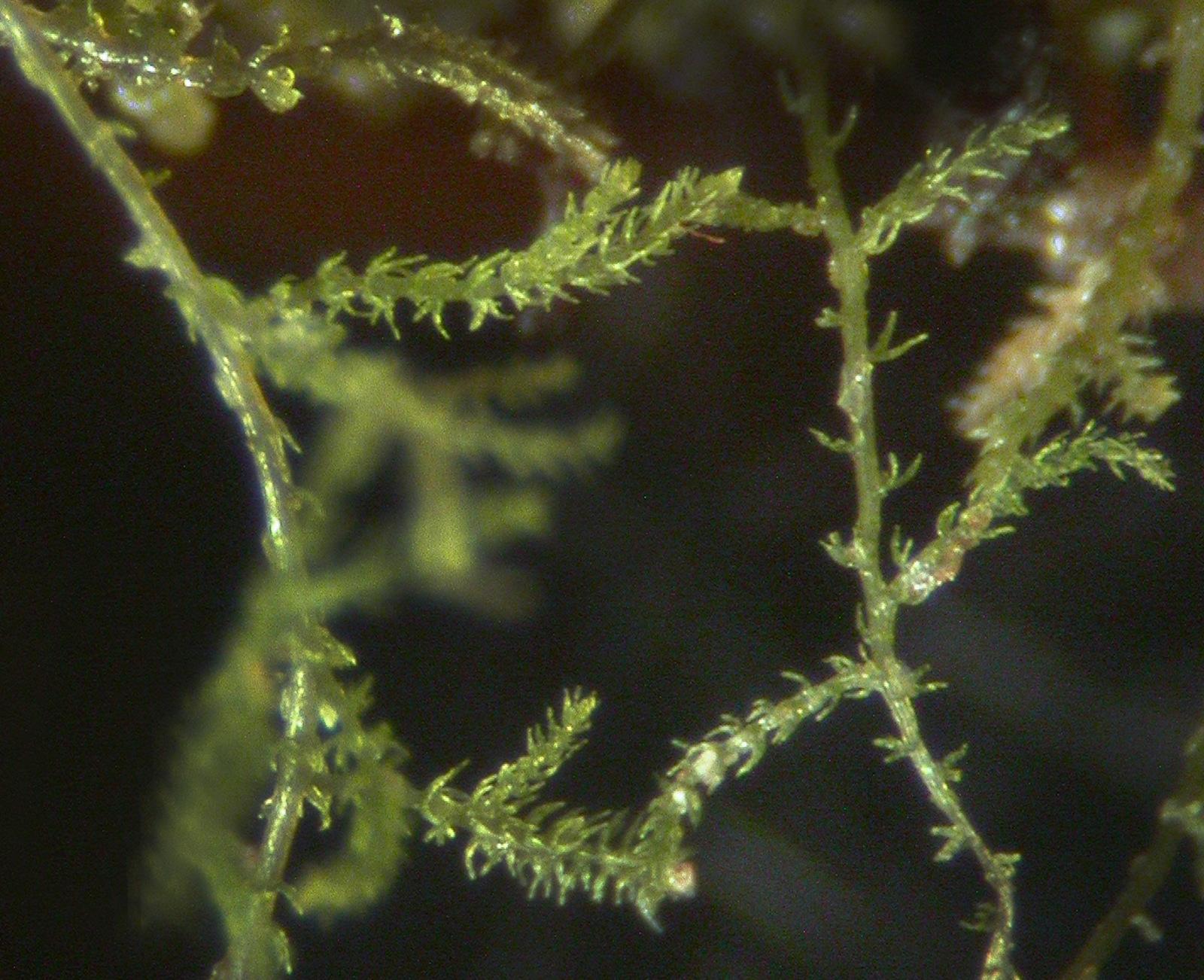
48038_906_5.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/906
Kurzia trichoclados is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves and stems to conserve moisture. Once favorable conditions return, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered a diverse assemblage of bryophytes, including Kurzia trichoclados, thriving on decaying logs in an old-growth forest. This moss played a crucial role in the decomposition process, facilitating nutrient cycling and providing a suitable habitat for various microorganisms and invertebrates.
Technical Table
Peltolepis-quadrata-Saut-Muell-Frib-a-thallus-with-androcial-ostioles-in.ppm from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Peltolepis-quadrata-Saut-Muell-Frib-a-thallus-with-androcial-ostioles-in_fig3_368829424

6feefd8306e85d57ee0719cb69dac65a.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.co.uk/pin/kurzia-pauciflora–308637380693939274/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta
 large.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/137877767 |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Lepidoziaceae |
| Genus | Kurzia |
| Species | trichoclados |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spiral |
| Leaf Shape | Deeply divided, fern-like |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North America, South America |
Conclusion
The Kurzia trichoclados (Müll.Frib.) Grolle moss, a member of the Lepidoziaceae
4-Lophocladia-trichoclados-Mertens-ex-C-Agardh-Schmitz-Fig-1-Aspecto-general-del.ppm from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/4-Lophocladia-trichoclados-Mertens-ex-C-Agardh-Schmitz-Fig-1-Aspecto-general-del_fig1_357017655
family, is a true marvel of nature. Its intricate morphology, global distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject for moss enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, this unassuming moss serves as a reminder of the intricate beauty and resilience that can be found in the smallest of organisms. Perhaps the next time you venture into a moist, shaded forest, you’ll take a moment to appreciate the delicate Kurzia trichoclados and the vital role it plays in its ecosystem.