
Moss-Sporophytes.jpg from: https://www.nps.gov/acad/learn/nature/moss.htm
Exploring the Fascinating World of Warburgiella concavifolia Thér. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Warburgiella concavifolia Thér., a moss in the Sematophyllaceae
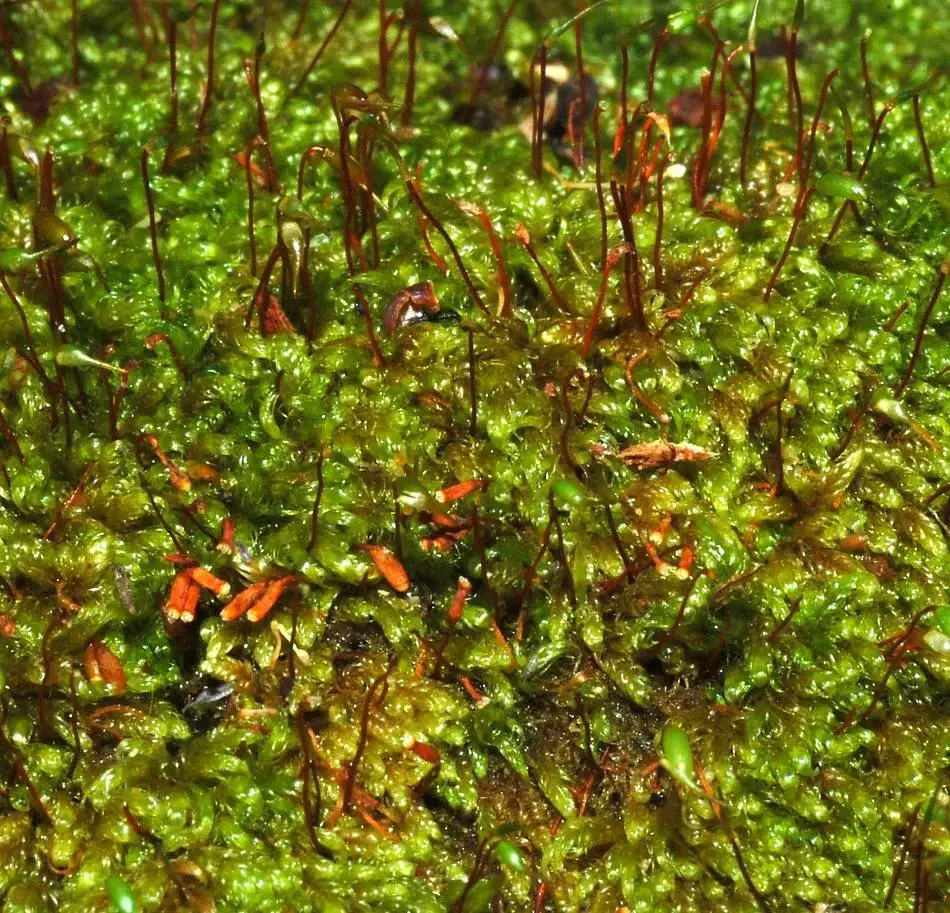

DT_Warburgiella_leucocytus_1.jpg from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/01_Semat_images.html
family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of this fascinating plant, from its unique morphology to its global distribution and ecological importance. Get ready to discover the wonders of Warburgiella!
Background on Mosses
Before we focus on W. concavifolia specifically, let’s review some background on mosses in general. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead having structures that serve similar functions. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in a wide range of habitats worldwide, from arctic tundra to tropical rainforests.
Morphology and Identification
Warburgiella concavifolia is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its reproductive structures (sporophytes) grow laterally from the stems. Its scientific name comes from its concave (curved inward) leaves – “concavifolia” means “concave-leaved”. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate in shape and have a distinct border of elongated cells.
Warburgiella plants form dense mats with creeping stems. The stems are irregularly branched and covered in small, overlapping leaves. Sporophytes are common, with smooth seta (stalks) and ovoid to cylindrical capsules.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a wide distribution, being found in tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas, Africa, and Asia. It grows on various substrates including tree bark, rocks, and soil, generally in humid forests from lowlands to mountains.
Some countries/regions where W. concavifolia has been documented include:

sphagnum-moss-big-5734ddb75f9b58723db9ee0e.jpg from: https://www.thespruce.com/moss-plants-shade-alternative-to-lawns-2130879

Moss4.jpg from: https://billsbirding.blogspot.com/2014/03/mellow-mosses.html

_20200411_105036.JPG from: https://www.naturespot.org.uk/node/191637

Moss+041+hydrated.jpg from: https://usinggeorgianativeplants.blogspot.com/2011/12/marvelous-moss.html
| Continent | Countries/Regions |
|---|---|
| Americas | Brazil, Venezuela, Costa Rica, Mexico |
| Africa | South Africa, Tanzania, Madagascar |
| Asia | India, China, Indonesia, Philippines |
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Warburgiella plays important roles in its ecosystems:
Nutrient cycling: Mosses trap and retain nutrients, releasing them slowly over time. This helps maintain soil fertility.
Water regulation: The dense mats formed by W. concavifolia help absorb and retain moisture, regulating humidity and reducing erosion.
Providing habitat: Many small invertebrates live among the stems and leaves of moss mats.

Syntrichia-princeps-1-1280×855.jpg from: https://mcrcd.org/willits/flowers-of-winter-the-mosses
Warburgiella has adaptations that allow it to thrive in its preferred humid, shady habitats. Its concave leaves help channel water down to the stem bases. The leaves also contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis even in low light conditions under forest canopies.
Conclusion
From its eye-catching concave leaves to its important ecological roles, Warburgiella concavifolia Thér. is a prime example of how fascinating and important mosses can be. Next time you’re in a tropical forest, take a closer look – you might just spot a patch of Warburgiella

2020-12-06-12-21-07-1024×768.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/some-common-bryophytes/common-mosses-in-lawns/
working its magic! What other overlooked wonders of nature have you discovered?
img157.jpg from: https://moss-notes.blogspot.com/2013/01/mniums-bryums-other-wide-leaved-ground.html

Moss-foliage.jpg from: https://www.canr.msu.edu/resources/mosses-division-bryophyta