
que_son_los_antoceros_2843_0_600.jpg from: https://www.ecologiaverde.com/antoceros-que-son-caracteristicas-y-ejemplos-2843.html
Exploring the Fascinating World of Anthoceros leiosporus Moss
Introduction
Mosses are some of the most ancient and resilient plants on Earth, having evolved over 400 million years ago. One particularly interesting species is Anthoceros leiosporus Gottsche ex Steph.

14C8B769E1F9FF218096CE336403847C.jpg from: https://definicion.edu.lat/academia/FDBEC648C0F6846D3B335EB4D5721409.html
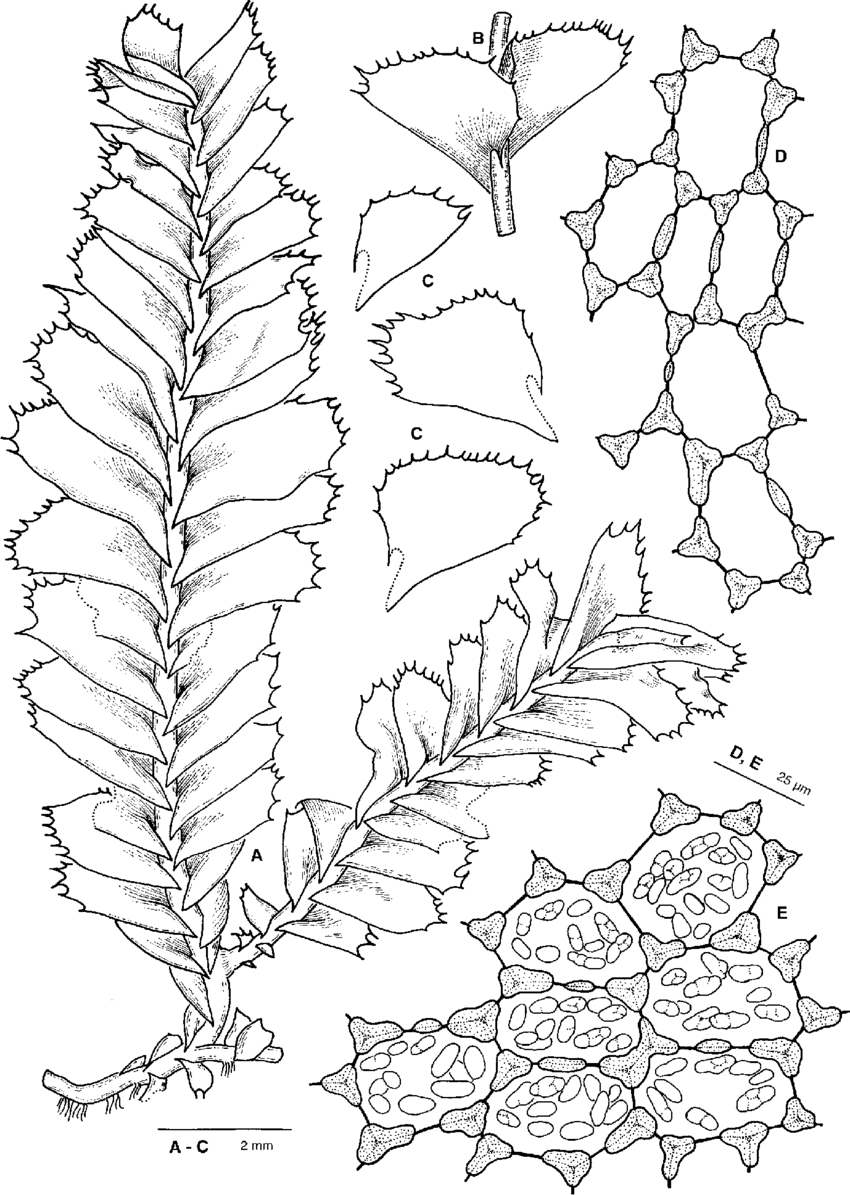
Plagiochila-maderensis-Gottsche-ex-Steph-A-Shoot-dorsal-view-B-part-of-shoot.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plagiochila-maderensis-Gottsche-ex-Steph-A-Shoot-dorsal-view-B-part-of-shoot_fig3_29813448
, a type of hornwort moss in the Leiosporocerotaceae family. In this post, we’ll dive into the unique characteristics and ecological importance of this tiny but mighty plant.
Background on Anthoceros Mosses
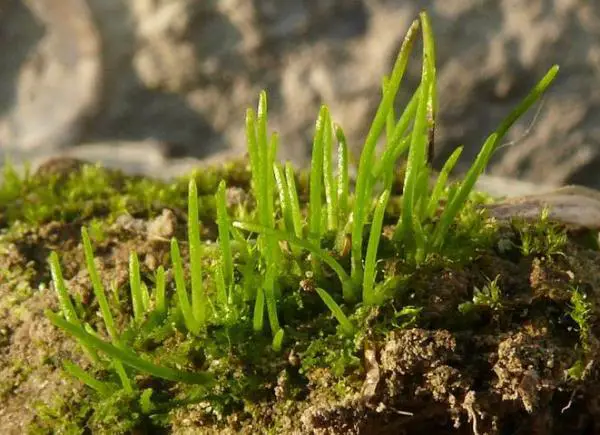
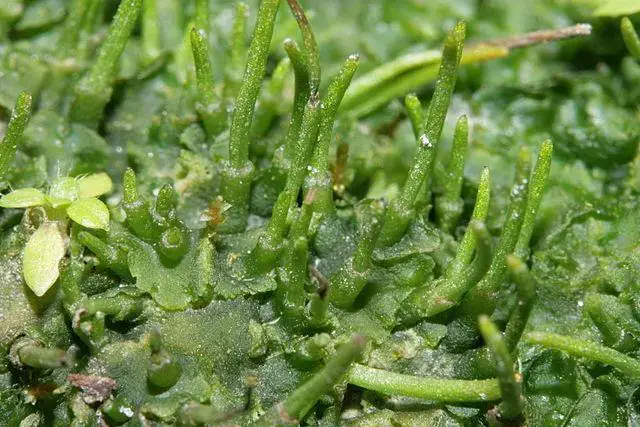
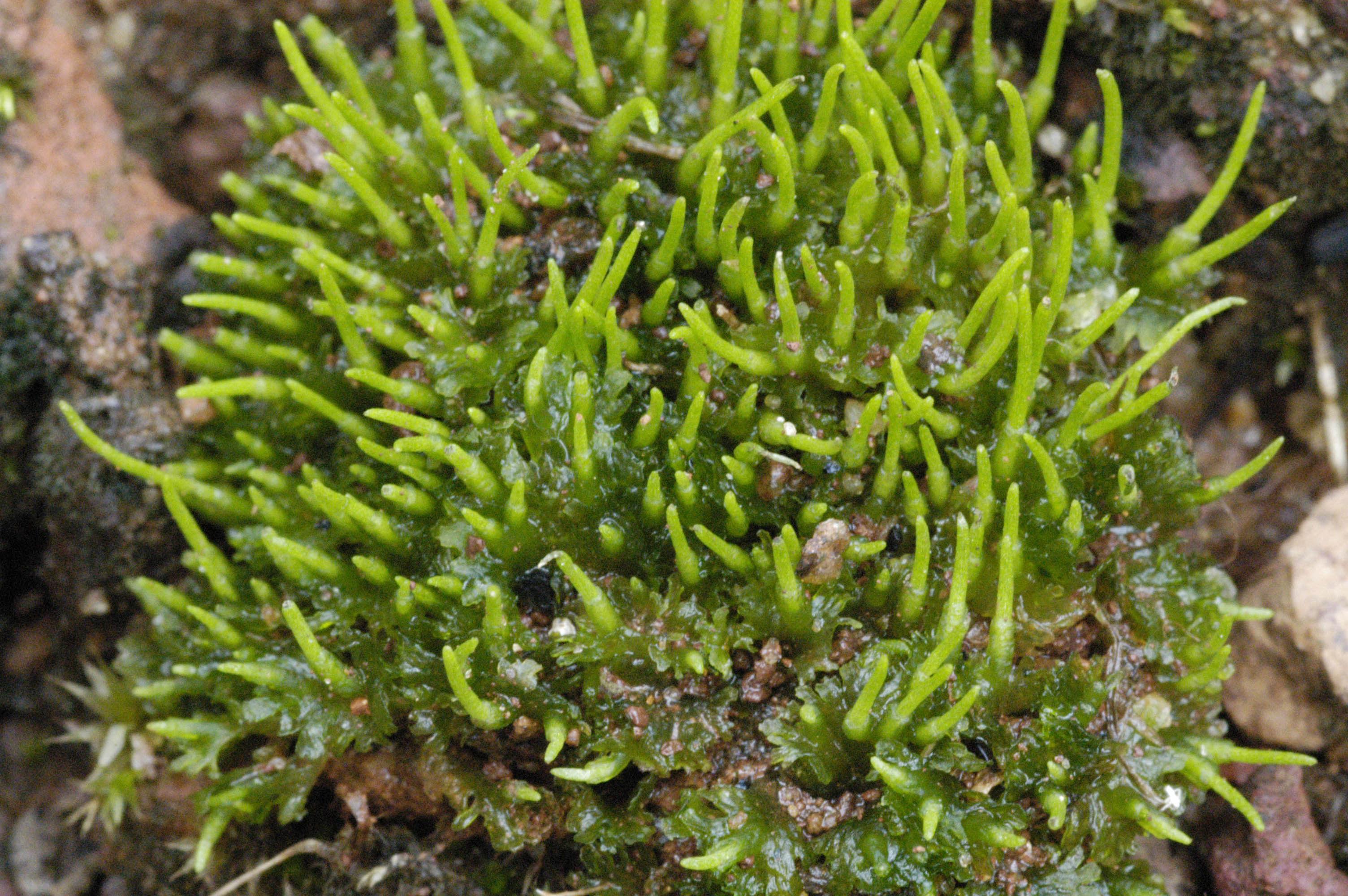
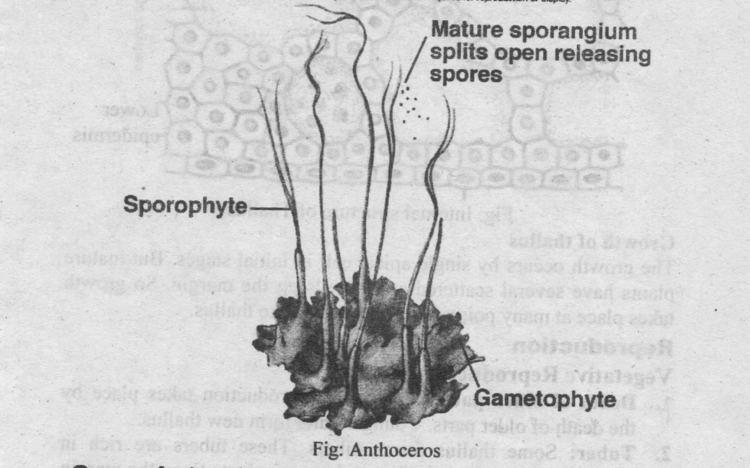
The genus Anthoceros contains around 150 species of hornworts found across the globe. These primitive non-vascular plants lack true stems, roots, and leaves. Instead, they have flattened, lobed structures called thalli. Hornworts get their name from the elongated horn-like sporophytes that grow from the thalli and release spores.

601.26223266.jpg from: https://eol.org/pages/3678/media
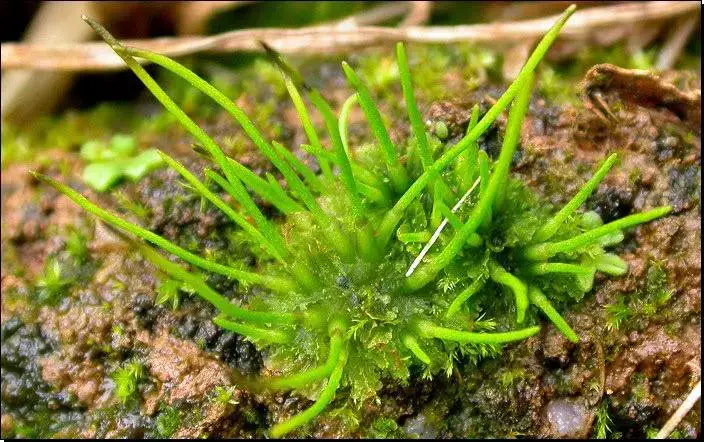

downloadfile.jpg from: https://plantlet.org/anthoceros-the-hornworts/
Morphology and Identification of A. leiosporus
A. leiosporus has a relatively simple structure:
- Thalli are small (5-20 mm), flat, and irregularly lobed or dissected
- Thalli are dark green and lack a midrib
- Horn-shaped sporophytes are 1-3 cm long, growing vertically from the thallus
- Spores are yellow and have a netted or pitted surface
Global Distribution and Habitat
This species is found scattered across Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Americas. It grows in a variety of habitats, including:
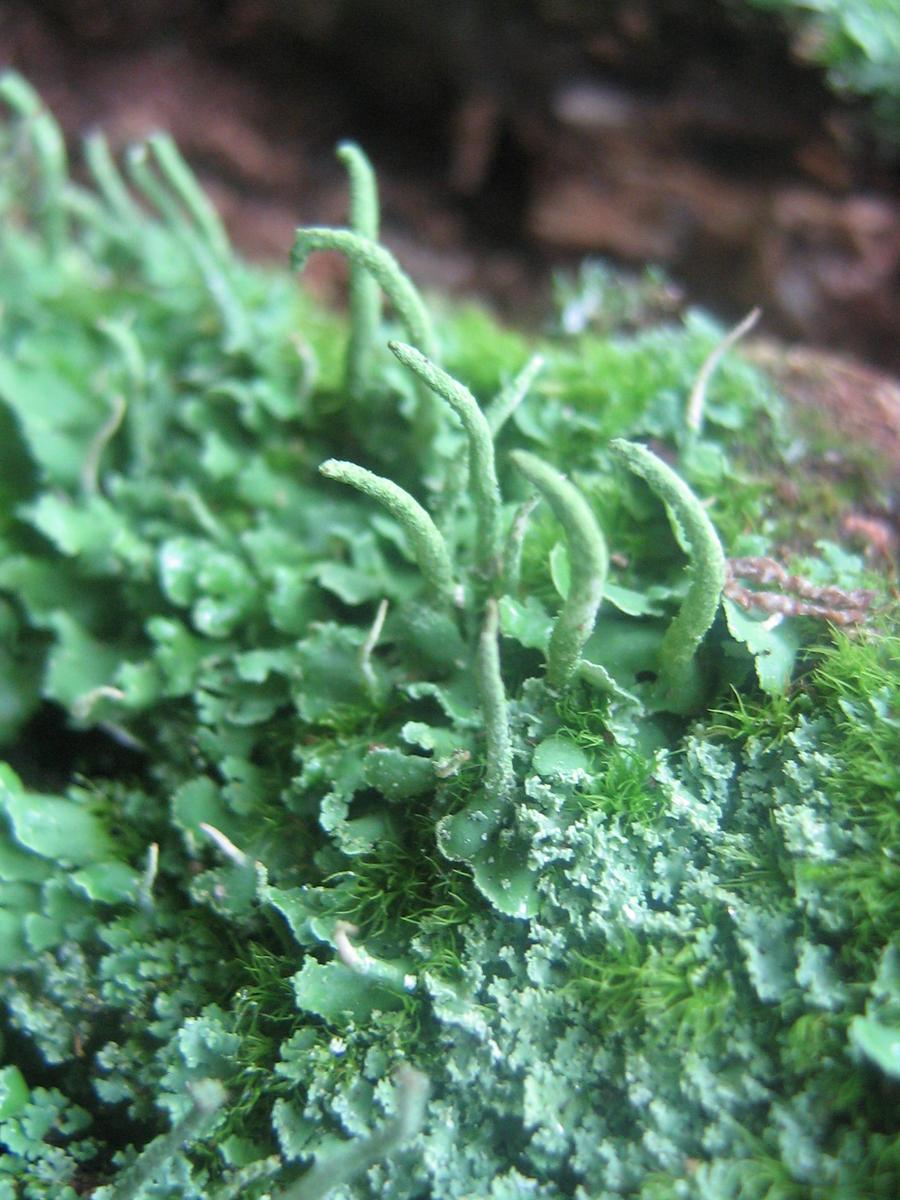

anthoceros_01_by_cotystock.jpg from: https://www.deviantart.com/cotystock/art/Anthoceros-01-167672308
- Damp, shaded soil banks
- Cliff faces and rock crevices
- Rotting logs and tree bases
- Disturbed areas like roadsides or fields
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite their small size, Anthoceros mosses play important roles in their ecosystems:
- They help retain moisture and prevent soil erosion
- Provide shelter and food for tiny invertebrates
- Act as pioneer species, colonizing bare ground
- Have symbiotic relationships with fungi and cyanobacteria
A. leiosporus
anthoceros-dde902da-9ee3-42db-a334-cc80bd4ce4d-resize-750.jpeg from: https://alchetron.com/Anthoceros
has several adaptations that allow it to thrive:
- Thick, protective cuticle to prevent water loss
- Sunken reproductive structures to maintain moisture
- Ability to survive long periods of desiccation
- Spores dispersed by wind and water
Conclusion

Bri_Anthoceros_caucasicus_2.jpg from: http://azoresbioportal.uac.pt/pt/especies-dos-acores/anthoceros-caucasicus-12159/
From its unique morphology to its ecological significance, Anthoceros leiosporus is a prime example of how even the most unassuming organisms can be endlessly fascinating. The next time you’re out in nature, take a closer look – you might just spot one of these ancient wonders growing right beneath your feet! What other secrets do you think the world of mosses still holds?

38875045.jpeg from: https://www.yclky.net/productinfo/1713539.html