
24-Isopterygium-minutirameum-Muell-Hal-A-Jaeger-from-SIZK-K-3178-stems-with_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/24-Isopterygium-minutirameum-Muell-Hal-A-Jaeger-from-SIZK-K-3178-stems-with_fig2_270427958
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Leucoloma caespitulans (Müll.Hal.) A.Jaeger moss stands out as a remarkable species. Belonging to the Dicranaceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating moss is commonly referred to as Leucoloma
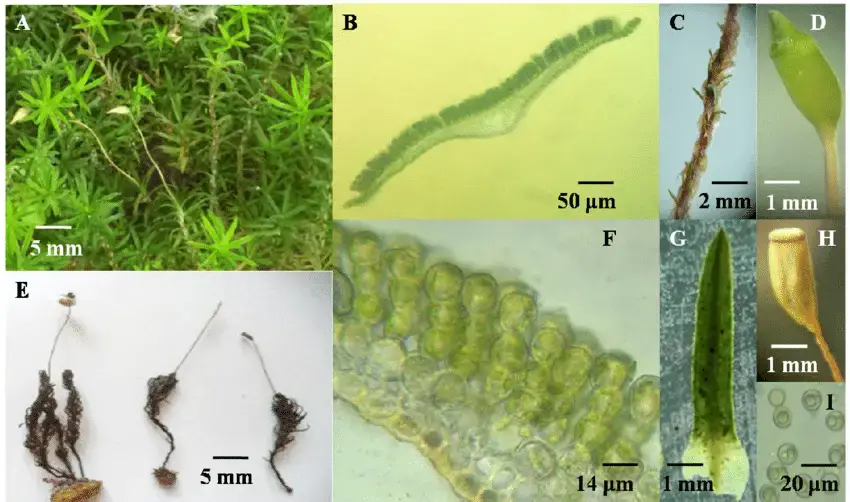

Pogonatum-subtortile-Muell-Hal-A-Jaeger-A-female-gametophytes-with-sporophytes-B.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Pogonatum-subtortile-Muell-Hal-A-Jaeger-A-female-gametophytes-with-sporophytes-B_fig9_331675612
. Despite its diminutive stature, it plays a crucial role in the intricate tapestry of ecosystems worldwide.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. Leucoloma caespitulans
Figuras-66-69-Leucophanes-molleri-Muell-Hal-66-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-67.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figuras-66-69-Leucophanes-molleri-Muell-Hal-66-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-67_fig5_240765931
is a member of the Bryophyta phylum, which encompasses all bryophytes, including mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. Within this phylum, it belongs to the class Bryopsida, the true mosses.
Main Content
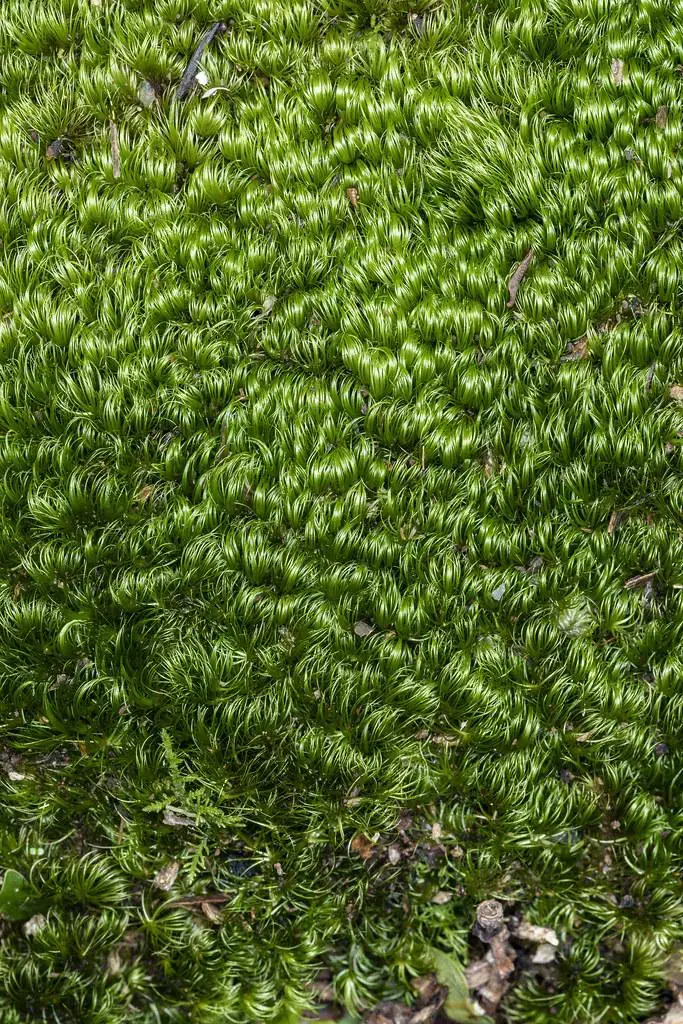

50923345617_33e9d1580e_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/47945928@N02/50923345617/
Morphology and Identification
Leucoloma caespitulans is a small, tufted moss that forms dense cushions or mats. Its leaves are narrow, lance-shaped, and often curved or twisted when dry. The leaf margins are entire, and the costa (midrib) is prominent, extending to the leaf apex or slightly beyond. The sporophytes, when present, bear capsules on short setae (stalks), and the calyptrae (caps covering the developing capsules) are cucullate (hood-shaped).
Global Distribution and Habitat
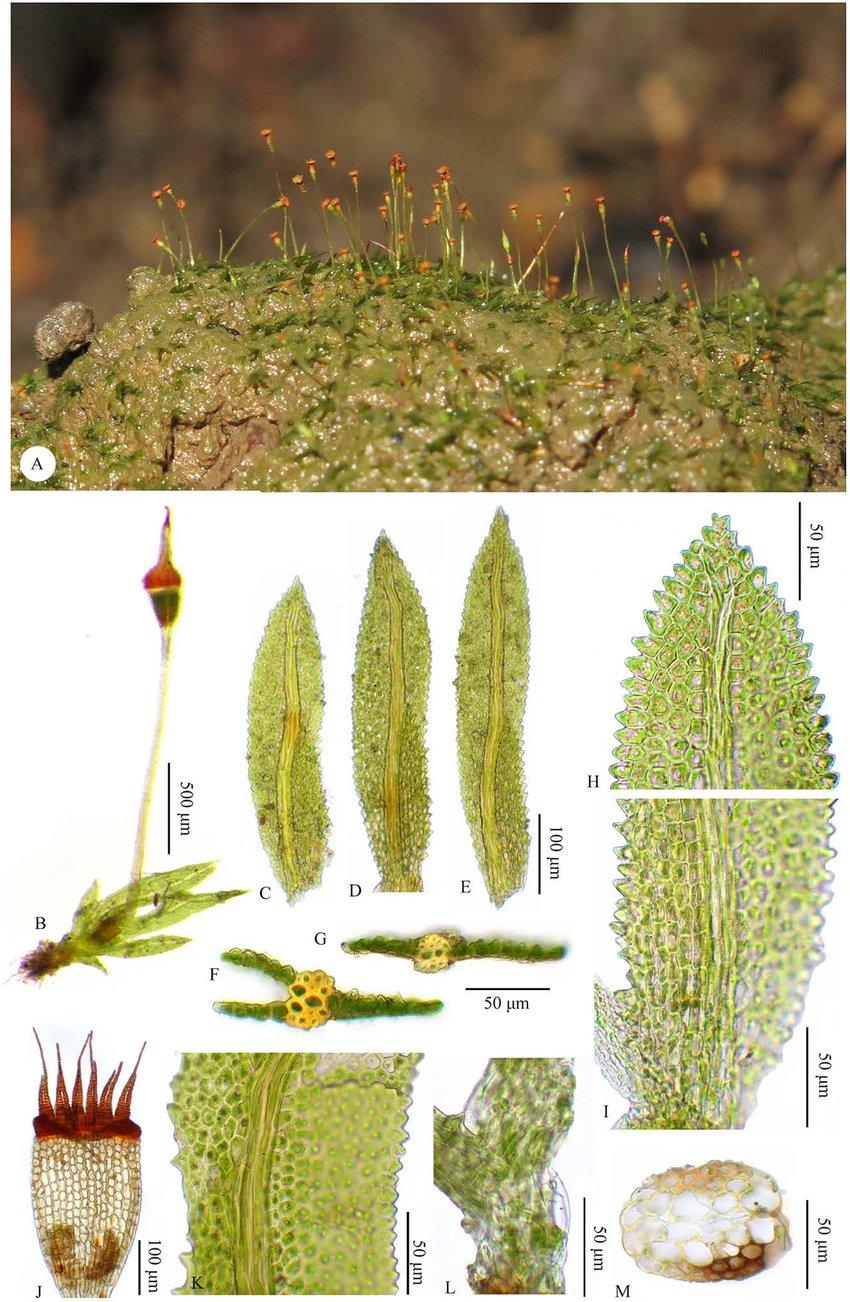

Fissidens-serratus-MuellHal-A-Habit-B-Plant-C-D-Leaves-E-Perichaetial-leaf-F-G.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fissidens-serratus-MuellHal-A-Habit-B-Plant-C-D-Leaves-E-Perichaetial-leaf-F-G_fig8_351104512
This moss has a widespread distribution, occurring on various continents, including North America, South America, Europe, Asia, Africa, and Oceania. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist and shaded rock surfaces to tree bark, soil, and even disturbed areas. Leucoloma caespitulans is particularly well-adapted to survive in dry conditions, making it a resilient species.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its unassuming appearance, Leucoloma caespitulans plays a vital role in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide microhabitats for various invertebrates, contributing to biodiversity.
One of the remarkable adaptations of this moss is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, it can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. When moisture returns,
Figura-12-Orthostichopsis-tortipilis-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-Habito-b-Filidios-c.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-12-Orthostichopsis-tortipilis-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-Habito-b-Filidios-c_fig12_309232610
Leucoloma caespitulans quickly revives, resuming its growth and photosynthetic activities.

a-m-In-vitro-growth-of-Entodon-macropodus-Hedw-Muell-Hal-a-Germinated-spores-b-c_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-m-In-vitro-growth-of-Entodon-macropodus-Hedw-Muell-Hal-a-Germinated-spores-b-c_fig1_269775914
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Appalachian Mountains of North America, researchers found Leucoloma caespitulans to be a dominant species in disturbed areas, such as abandoned mining sites. Its ability to colonize these harsh environments highlights its resilience and ecological importance in facilitating the recovery of degraded landscapes.
Technical Table

239257.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/786477
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Family | Dicranaceae |
| Genus | Leucoloma |
| Species | caespitulans
 Atrichum-androgynum-MuellHal-Jaeger-A-Habito-B-E-Hoja-B-Vista-ventral-C.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Atrichum-androgynum-MuellHal-Jaeger-A-Habito-B-E-Hoja-B-Vista-ventral-C_fig1_318217800 |
| Growth Form | Tufted, cushion-forming |
| Leaf Shape | Narrow, lance-shaped |
| Leaf Margin | Entire |
| Costa | Prominent, extending to leaf apex or beyond |
| Sporophyte | Capsules on short setae, calyptrae cucullate |
Conclusion
Leucoloma caespitulans is a remarkable moss that deserves our appreciation and admiration. Its ability to thrive in diverse habitats, its resilience in the face of adversity, and its ecological contributions make it a true champion of the bryophyte world. As we continue to explore and understand the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, this unassuming moss serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and adaptability that nature has to offer. Perhaps the next time you encounter a small, tufted moss, you’ll pause and wonder if it’s the remarkable

209935.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4771/tab/fiche
Leucoloma caespitulans, a true survivor in the world of bryophytes.