
nBnauM3XwETO4cjNzgDO3IjN0QTM0EzNzITNzQTNwAzMwIzL4gzLzYzLt92YucmbvRWdo5Cd0FmLyE2LvoDc0RHa.jpg from: https://www.jendow.com.tw/wiki/密枝粗枝蘚
Gollania elbertii Broth.: The Fascinating Moss of the Hypnaceae Family
Introduction
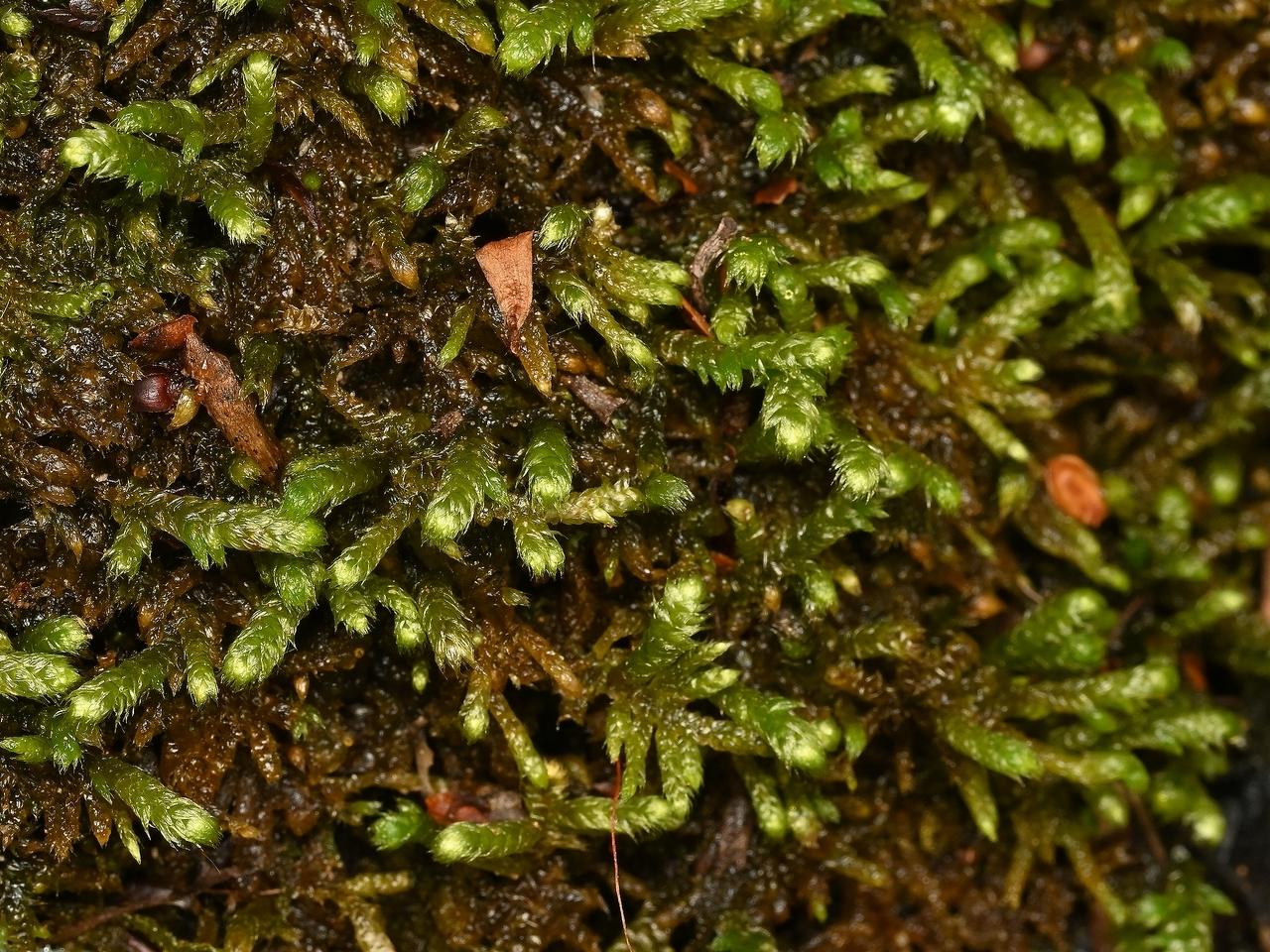

siwarakkogoke220608_1.jpg from: https://soyokaze2jp.blogspot.com/2022/06/blog-post_21.html
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting moss is
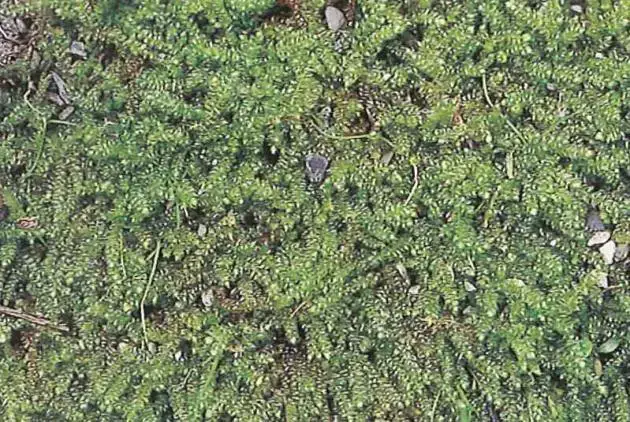

B058-02_0.jpg from: http://taibif.tw/zh/namecode/200595
Gollania elbertii Broth., also known simply as Gollania. This small but mighty plant is part of the Hypnaceae family and has some unique characteristics. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of Gollania elbertii and explore what makes it so fascinating.
Background
Gollania elbertii is a species of moss named after Elbert Broth, the botanist who first described it. It belongs to the Bryophyta division and Bryopsida class, which includes most mosses. The Hypnaceae family that Gollania is part of contains over 2,000 species found all over the world.
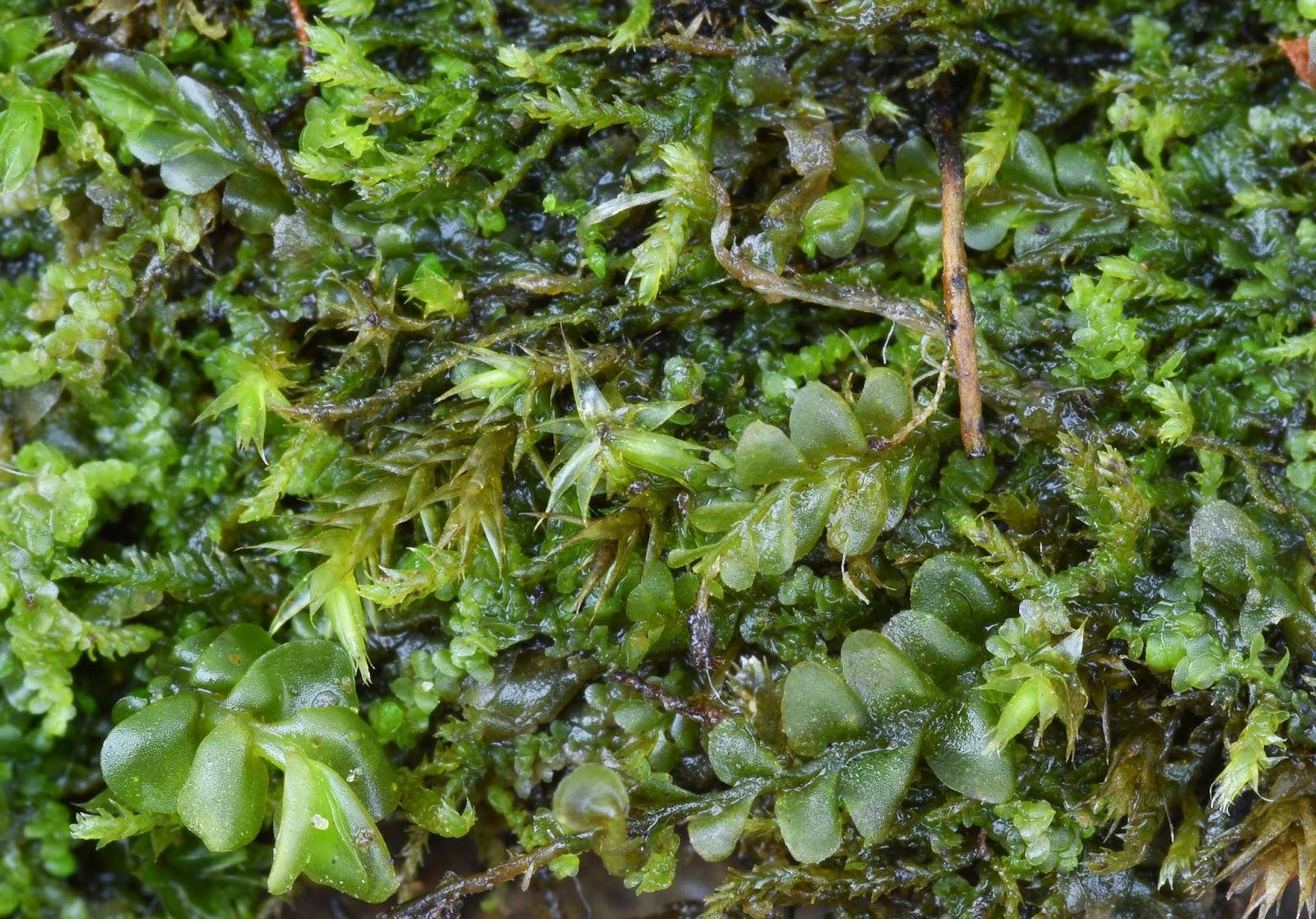

Jamesoniella%2Bepiphytic%2Bon%2BOak%2BDulais%2BValley.jpg from: https://southwalesbryos.blogspot.com/2015/02/dulais-valley.html
Morphology and Identification
Gollania elbertii is a small, pleurocarpous moss, meaning it has a branching, feather-like growth form. Its stems are creeping and irregularly branched, typically reaching 1-3 cm long. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate, around 1-1.5 mm long, and have a short, double costa (midrib). They are often falcate-secund, meaning curved to one side in a sickle shape.
Gollania stands out due to its papillose leaf cells. Papillae are small protuberances on the cell surface that give the leaves a rough texture. Under a microscope, the papillae on Gollania leaves are very noticeable. Additionally, Gollania has a characteristic reddish-brown coloration, especially in older parts of the plant.
Global Distribution and Habitat
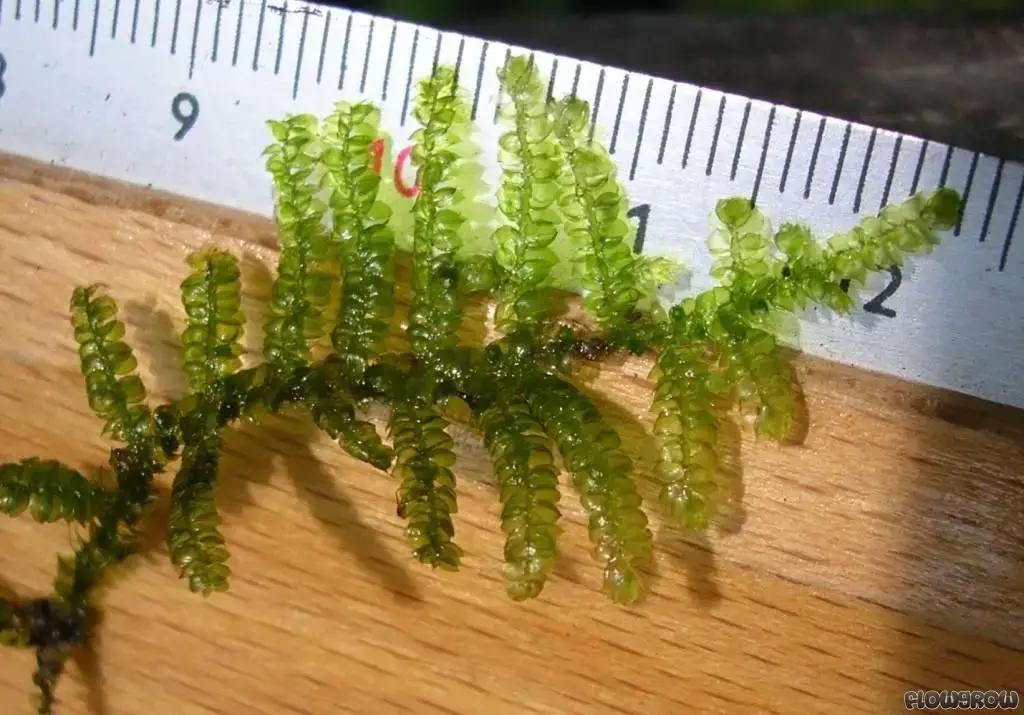

vesicularia-montagnei-christmas-moss-4f7a024c41575.jpg from: https://www.flowgrow.de/db/aquaticplants/vesicularia-montagnei-christmas-moss
Gollania elbertii has a wide distribution, being found in many parts of the world including Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Americas. It grows in a variety of habitats, from lowland to montane forests. Gollania prefers shaded, humid environments and is often found growing on tree trunks, logs, and rocks.
In tropical regions, Gollania is a common epiphyte in cloud forests and rainforests. It can form extensive mats on tree branches and trunks. In temperate areas, it tends to grow at the bases of trees and on decaying wood on the forest floor.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Gollania plays important roles in its ecosystems:
- Moisture retention: Gollania mats help trap and retain moisture, regulating humidity in the microenvironment.
- Nutrient cycling: As Gollania decomposes, it releases nutrients back into the soil for other plants.
- Habitat provision: Many small invertebrates live among Gollania plants, which provide shelter and maintain humid conditions.
Gollania has several adaptations that allow it to thrive:
- Papillose leaves help trap water droplets from fog and dew.

OS0149365_1577822715.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/portal/taxa/index.php?taxauthid=1&taxon=158184&clid=210
- Reddish pigments protect chlorophyll from UV damage in bright, exposed sites.
- Clonal reproduction through fragmentation allows Gollania to spread locally.
Andreaea-rupestris-from-Russia-Republic-of-Sakha-Yakutia-Mus-Khaya-Mt-Ivanov-sn_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/World-distribution-of-Gollania-turgens-based-on-Higuchi-1985-list-of-localities-map_fig2_270428072

fdbee12b116e6f20d713b1f28b626111.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/8731
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Size | Small, 1-3 cm long |
| Leaf shape | Ovate-lanceolate, 1-1.5 mm |
Leaf cells
 Gollania-ruginosa01L.jpg from: https://digital-museum.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~museum/habit/moss_habit/Gollania ruginosa/Gollania_ruginosa.html |
Papillose |
Color
 49d7ca4dfcc933bc051454b55dcadd6a.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/8739 |
Reddish-brown |
| Habitat | Shaded, humid forests |
| Substrate | Tree trunks, logs, rocks |
Conclusion
Gollania elbertii may be small, but it is a prime example of how mosses are fascinating and important plants with unique adaptations. Next time you’re in a humid forest, take a closer look and see if you can spot some reddish Gollania mats! What other cool mosses have you noticed in your local ecosystem?