Gymnocolea Moss: A Captivating Bryophyte in the Anastrophyllaceae Family
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!
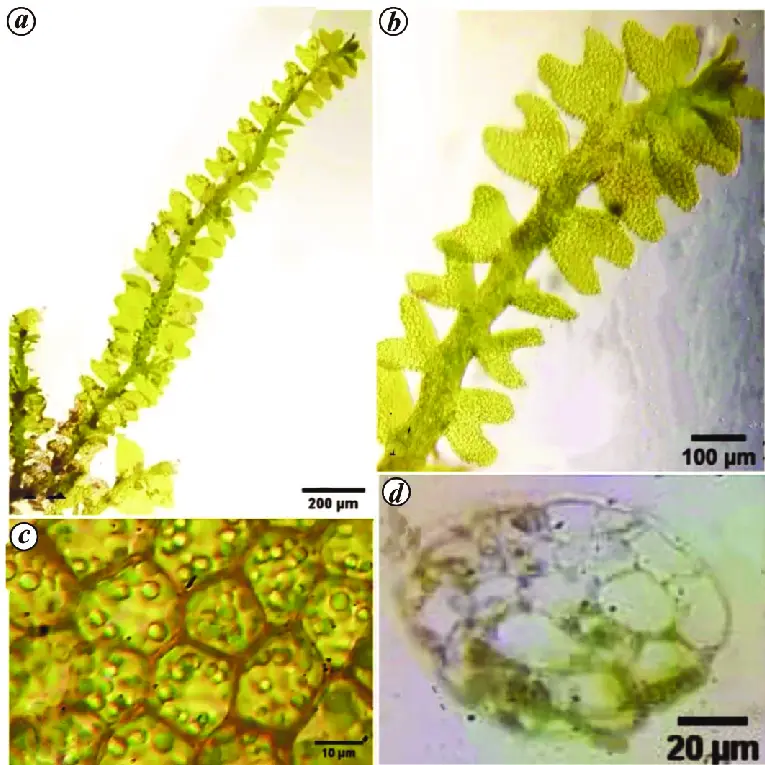
Gymnocolea-inflata-Huds-Dumort-a-Habit-b-A-portion-of-vegetative-shoot-enlarged.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Gymnocolea-inflata-Huds-Dumort-a-Habit-b-A-portion-of-vegetative-shoot-enlarged_fig1_364359743
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Gymnocolea (Dumort.) Dumort. moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Anastrophyllaceae family. This unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide, offering a unique glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s wonders.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of the Gymnocolea moss, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.

31008817112_e939ae2902_h.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/126598284@N05/albums/72157678352824224/
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
The Gymnocolea (Dumort.) Dumort. moss is a member of the phylum Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida. It is characterized by its delicate, feathery appearance and intricate branching patterns. The leaves are typically small, overlapping, and arranged in a spiral pattern along the stem. These mosses can range in color from vibrant greens to deep reds, depending on their environment and growth stage.
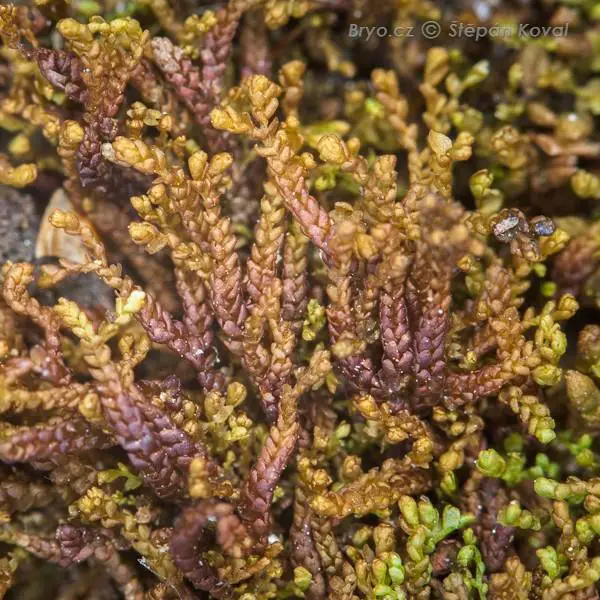

2852_Gymnocolea_inflata_2009_04_16_2629.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=en&gallery=gymnocolea_inflata&id=2852
One of the most distinctive features of the Gymnocolea moss is its unique reproductive structures. The archegoniophores (female reproductive structures) and antheridiophores (male reproductive structures) are borne on separate plants, a phenomenon known as dioecious. These structures are often visually striking, adding to the allure of this moss species.
Global Distribution and Habitat
The Gymnocolea moss is widely distributed across various regions of the world, thriving in a diverse range of habitats. From the cool, moist forests of the northern hemisphere to the tropical rainforests of the equatorial regions, these mosses have adapted to a wide array of environmental conditions.
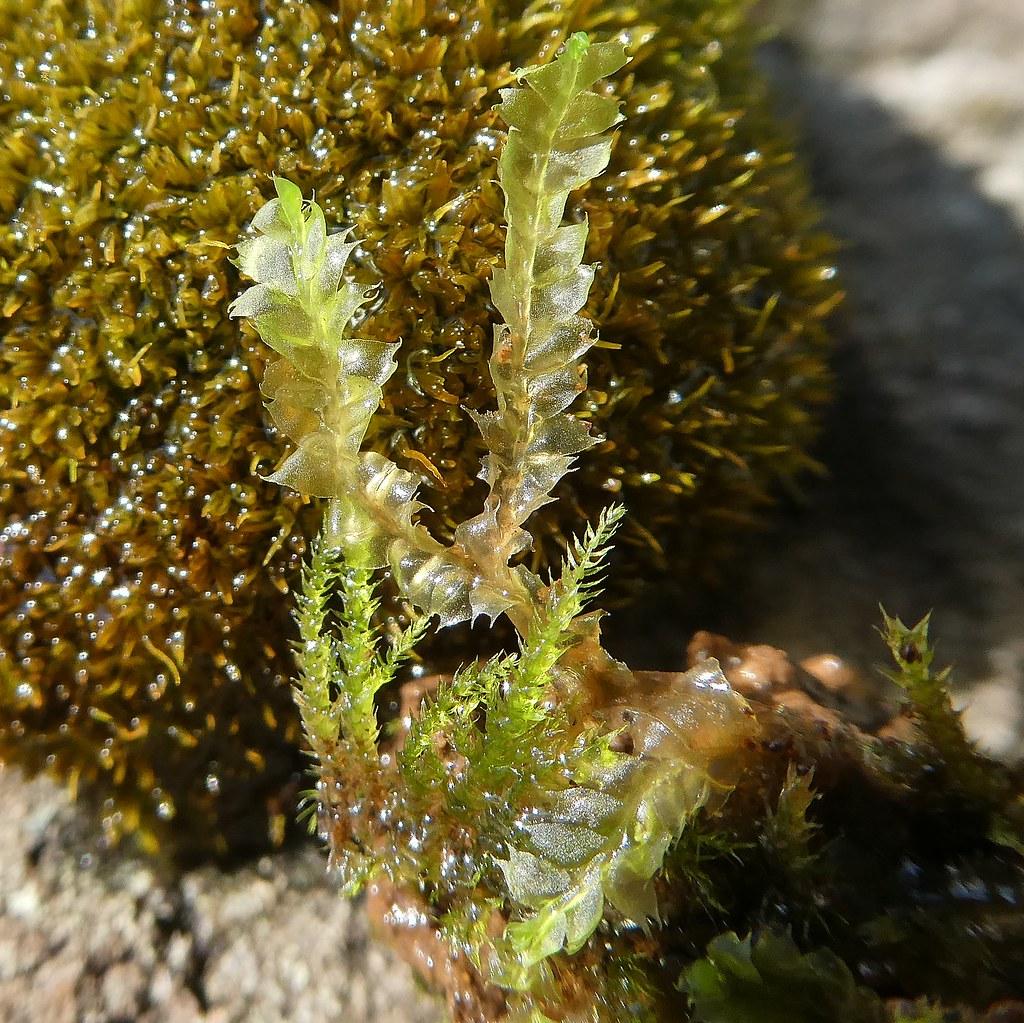

49918878671_dfcf990bb8_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/21657471@N04/49918878671/
They are commonly found growing on decaying logs, tree bark, and moist soil, forming lush carpets or intricate mats. Their ability to thrive in these environments is a testament to their resilience and adaptability.
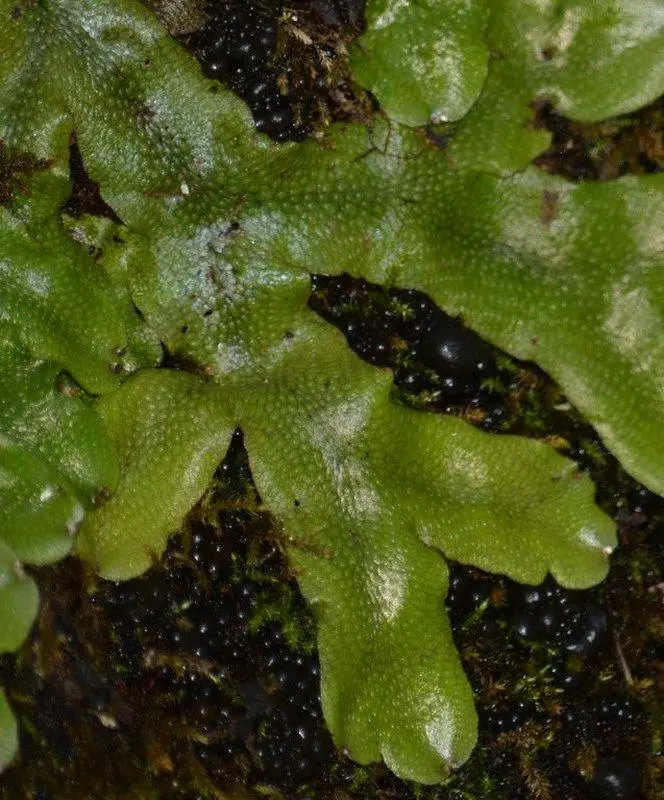

Conocephalum-conicum-(L.)-Dumort.-486922.jpg from: https://www.biodiversidadvirtual.org/herbarium/Conocephalum-conicum-(L.)-Dumort.-img486922.html
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite their diminutive size, the Gymnocolea moss plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems. These mosses act as sponges, absorbing and retaining moisture, creating microhabitats for other organisms to thrive. They provide shelter and food for various invertebrates, contributing to the intricate web of life.
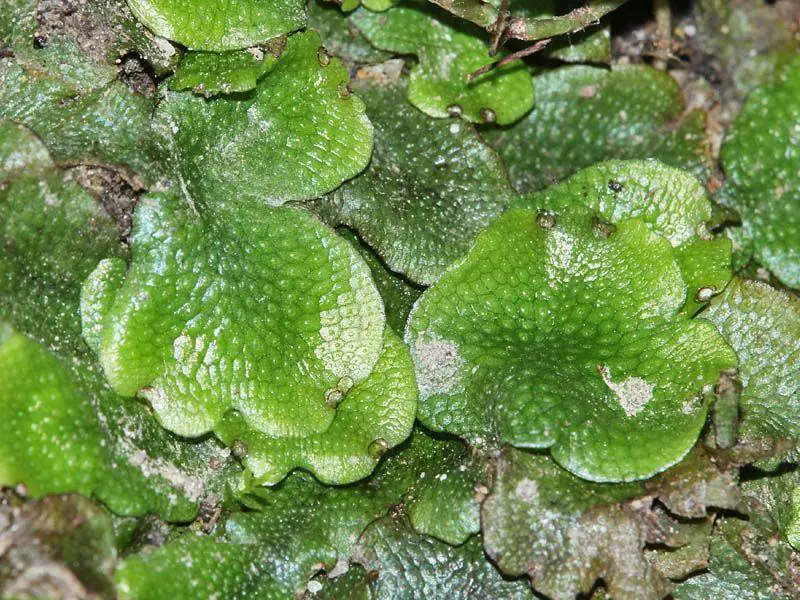

Conocephalum-conicum-(L.)-Dumort.-450945.jpg from: https://www.biodiversidadvirtual.org/herbarium/Conocephalum-conicum-(L.)-Dumort.-img450945.html
Moreover, the Gymnocolea moss possesses remarkable adaptations that allow it to survive in challenging environments. Their ability to withstand desiccation and rapidly rehydrate when moisture becomes available is a testament to their evolutionary prowess. These adaptations have enabled them to colonize a wide range of habitats, from arid regions to the harshest of environments.
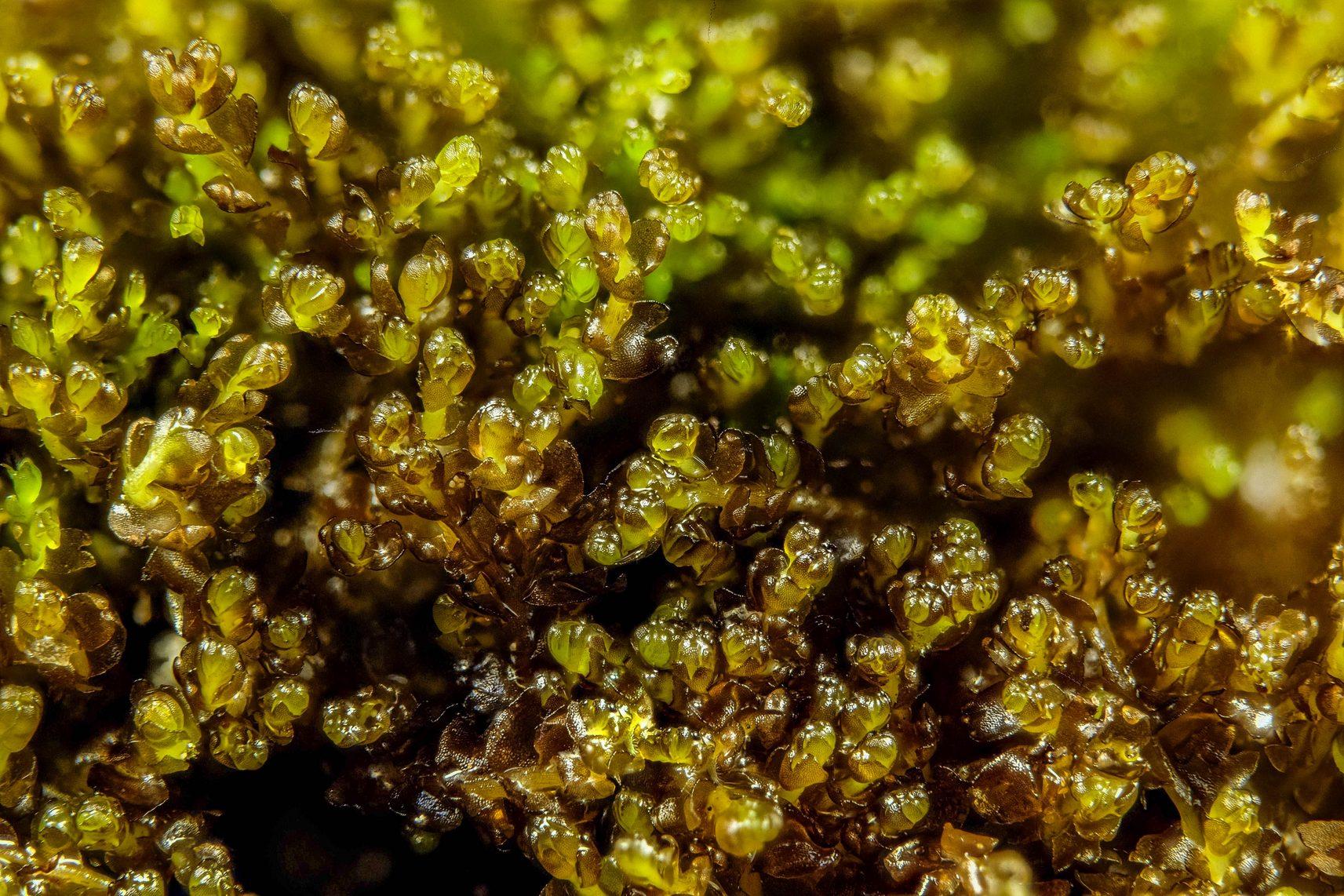

gymnocolea_fascinifera.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Anastrophyllaceae/gymnocolea-fascinifera/en/
Case Studies/Examples
One notable example of the Gymnocolea moss’s ecological significance can be found in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. Here, these mosses form a crucial component of the forest floor, contributing to nutrient cycling and soil formation. Their presence helps maintain the delicate balance of these ecosystems, supporting a diverse array of plant and animal life.
| Scientific Name | Common Name | Family | Habitat | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gymnocolea inflata | Inflated Gymnocolea | Anastrophyllaceae | Moist soil, decaying logs | North America, Europe, Asia |
| Gymnocolea acutiloba | Sharp-lobed Gymnocolea | Anastrophyllaceae | Tree bark, rocks | South America, Australia |
| Gymnocolea breviramea | Short-branched Gymnocolea | Anastrophyllaceae | Moist forests | Central America, Southeast Asia |
Conclusion
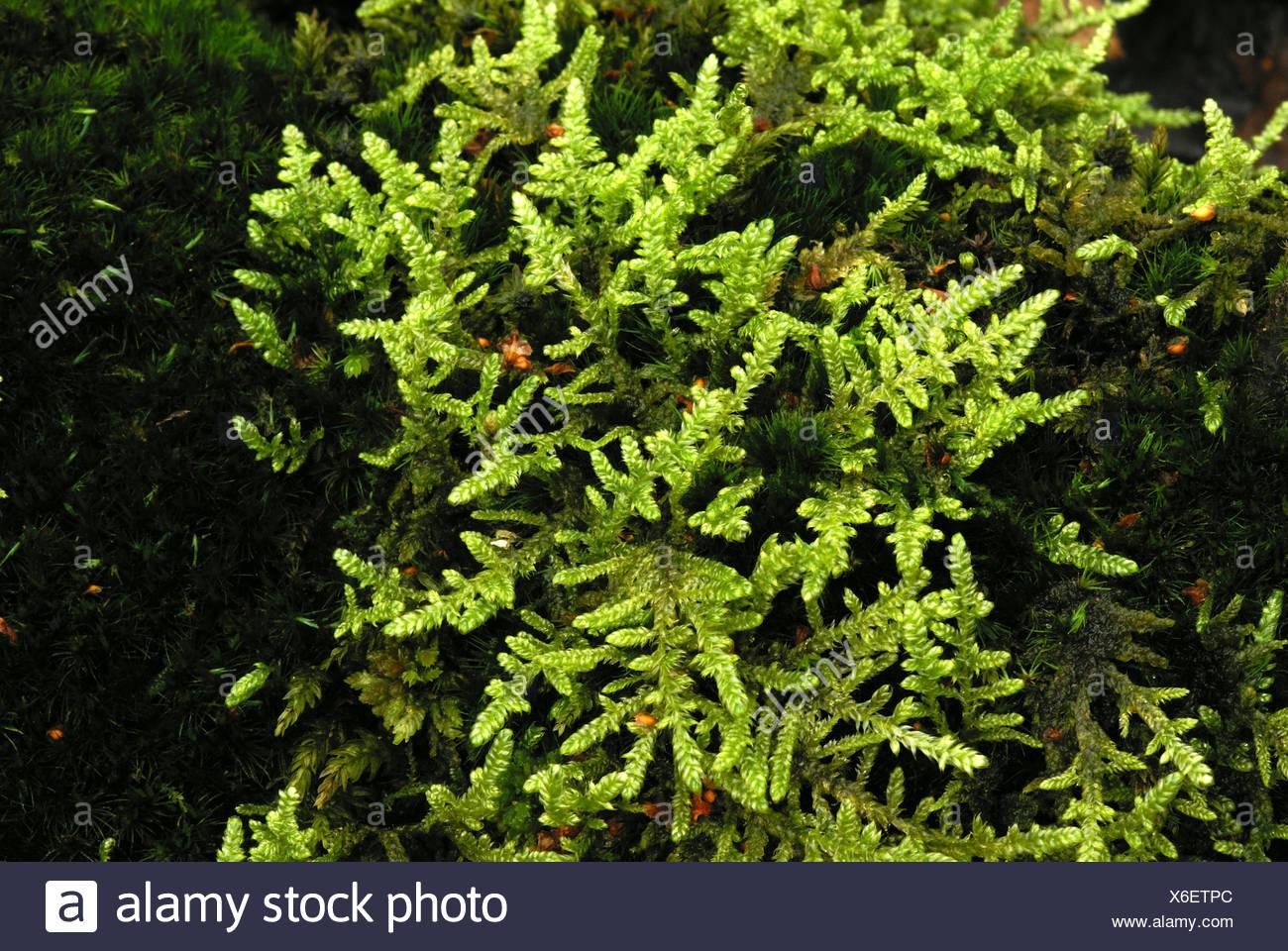

begroeiing-van-gesnaveld-klauwtjesmos-en-boskronkelsteeltje-op-de-bodem-van-een-berkenbroekbos-X6ETPC.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/gymnocolea-flexuosus.html
The Gymnocolea (Dumort.) Dumort. moss, a member of the
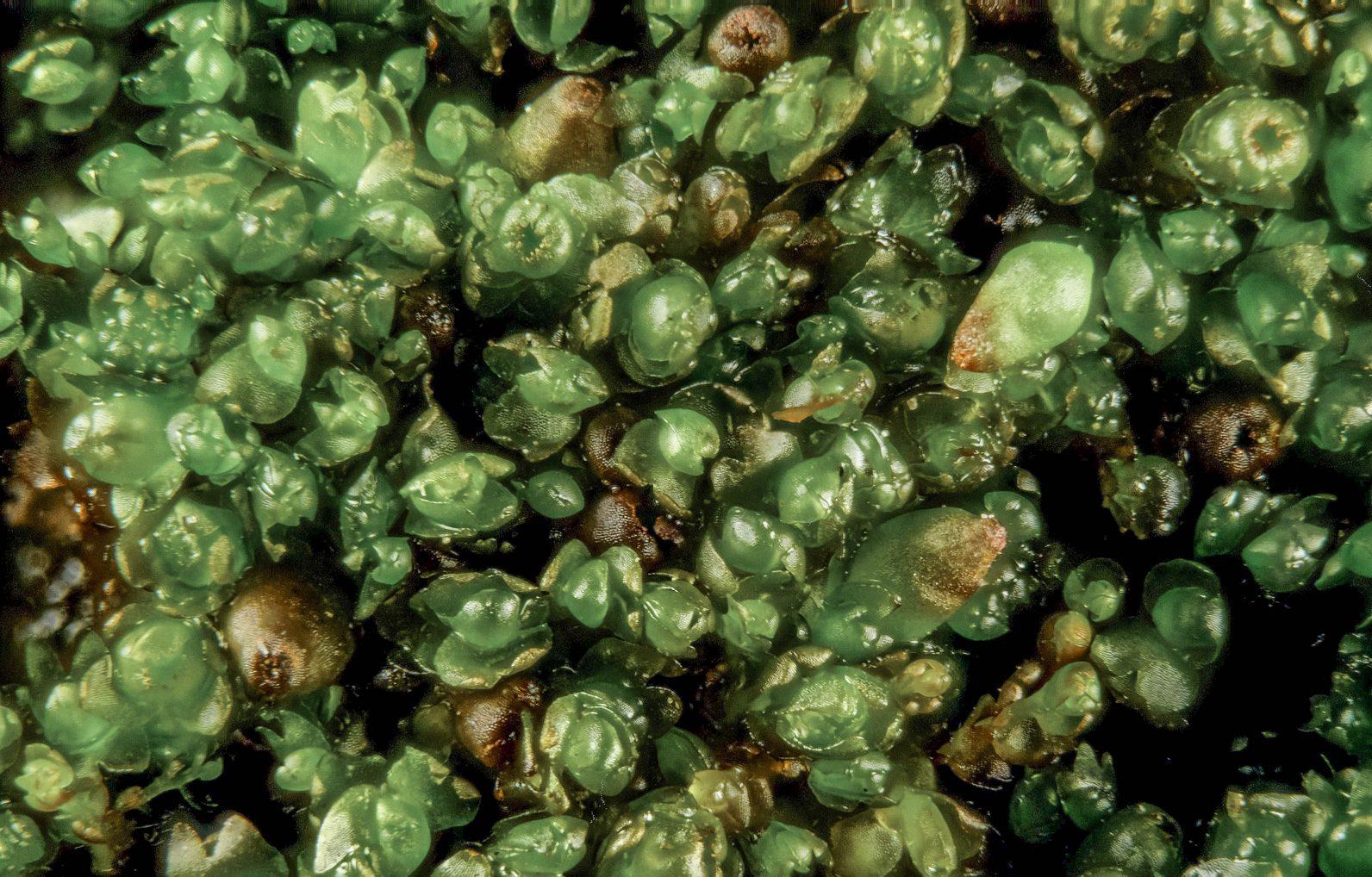

gymnocolea_borealis.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Anastrophyllaceae/gymnocolea-borealis/en/
Anastrophyllaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its intricate morphology, global distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject for moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the bryophyte world, the Gymnocolea moss serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and resilience found in even the smallest of organisms.
Ponder this: In a world where we often overlook the intricate details, what other hidden gems might we be missing, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?
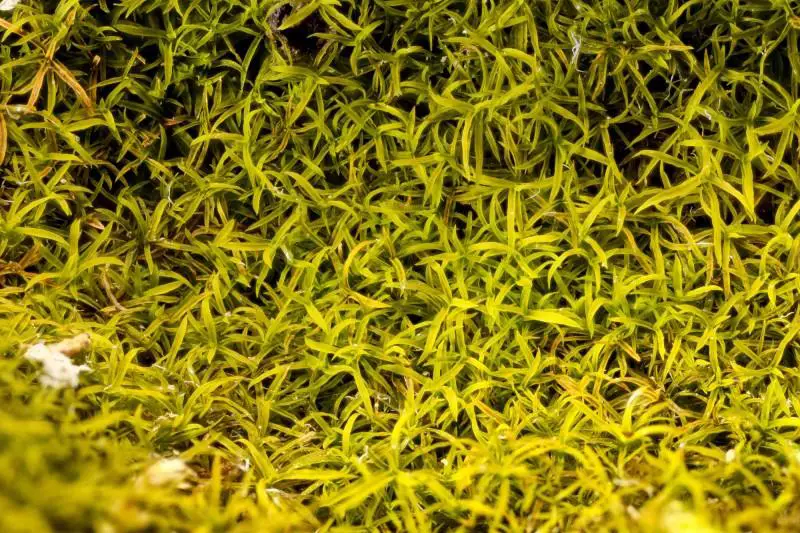

Gymnostomum-aeruginosum-71-800×533.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-gymnostomum-aeruginosum/
