
medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/163685-Herbertus-dicranus
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Herbertus dicranus (Taylor) Trevis. moss stands out as a remarkable species within the Herbertaceae family. This unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s diversity.
Background
The Herbertaceae family, a member of the Marchantiophyta division and Jungermanniopsida class, encompasses a diverse array of liverworts and mosses. Among them, the Herbertus dicranus (Taylor) Trevis. moss, commonly referred to as Herbertus, has garnered attention for its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
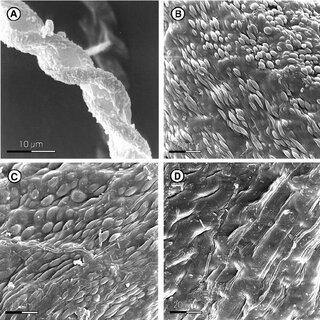
SEM-micrographs-of-Herbertus-sendtneri-A-C-and-H-dicranus-D-A-part-of-elater_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/SEM-micrographs-of-Herbertus-sendtneri-A-C-and-H-dicranus-D-A-part-of-elater_fig1_226571718
Herbertus dicranus is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on various substrates. Its delicate, feathery appearance is a result of the intricate branching pattern of its stems. The leaves are deeply divided, giving the plant a fern-like appearance. One of the distinguishing features of this moss is the presence of underleaves, which are small, scale-like structures found on the underside of the stem.
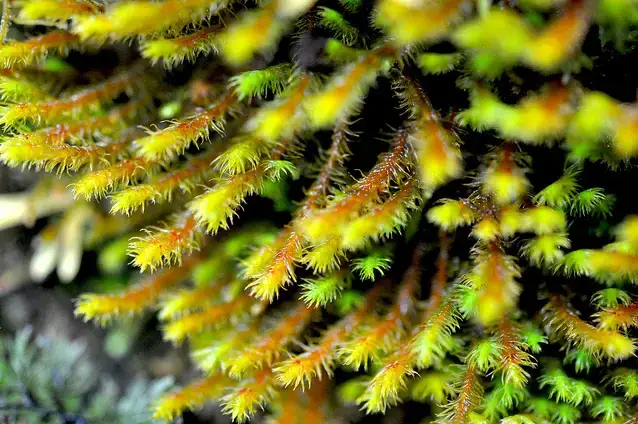

28584749697785883herbertusruncinatus1.png from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Herbertaceae/herbertus-buchii/en/
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a widespread distribution, occurring in various regions across the globe, including North and South America, Europe, Asia, and Oceania. It thrives in a variety of habitats, such as moist, shaded areas in forests, on rotting logs, and on the bark of trees. Herbertus dicranus is particularly well-adapted to humid environments, where it can flourish and contribute to the intricate web of life.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Herbertus dicranus plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. It serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates and provides a moist, sheltered environment for other organisms to thrive. Additionally, this moss contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, helping to maintain the delicate balance of its surroundings.

2022-06-09-08-15-51.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/dicranum-scoparium/
One of the remarkable adaptations of Herbertus dicranus is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. When conditions become dry, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up and appearing lifeless. However, upon the return of moisture, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to withstand environmental challenges.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region, researchers discovered a diverse array of invertebrates, including mites, springtails, and nematodes, residing within the intricate mats formed by Herbertus dicranus. This finding highlights the importance of this moss as a microhabitat and its contribution to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.
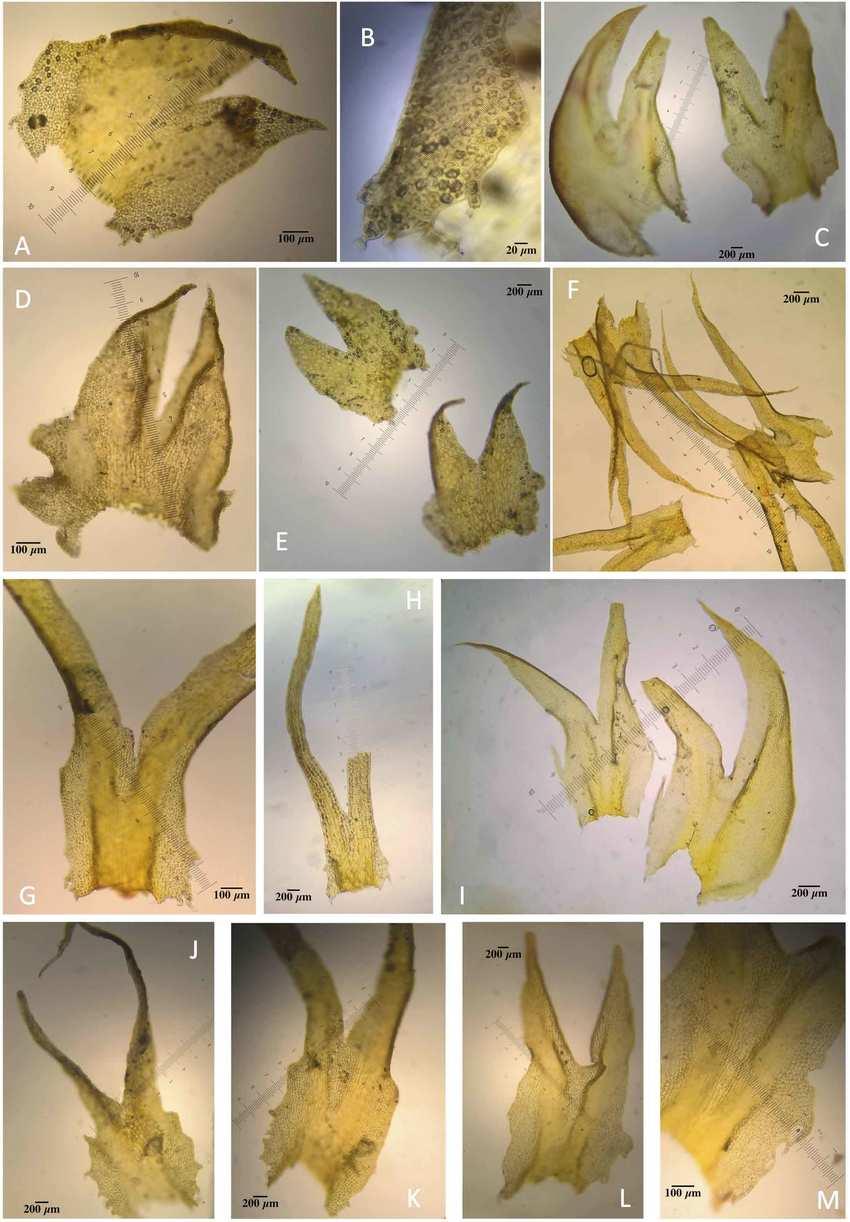

Morphological-variations-of-the-leaves-of-Herbertus-sendtneri-a-B-Germany-Arnold.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Morphological-variations-of-the-leaves-of-Herbertus-sendtneri-a-B-Germany-Arnold_fig2_320243669
Technical Table
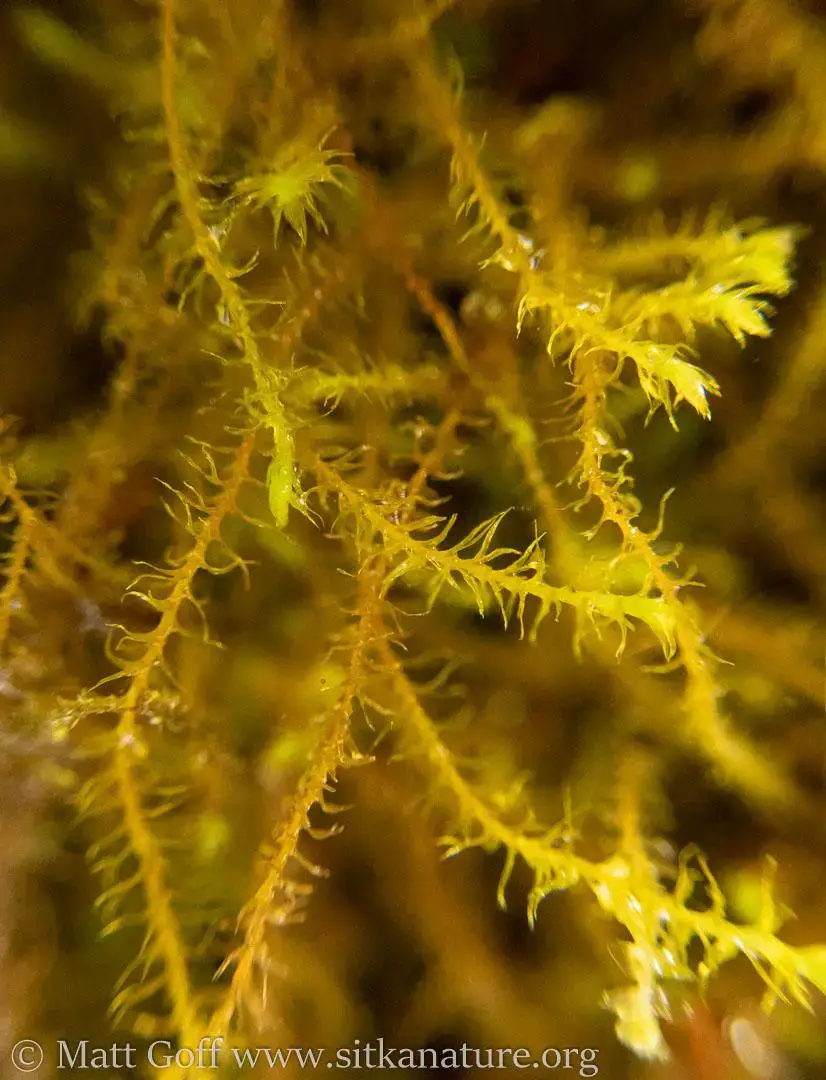

20220216-_2160002-Edit.jpg from: https://www.sitkanature.org/photojournal/2022/02/16/herring-cove-cryptogams/
Herbertus-sendtneri-A-epidermal-cells-of-capsule-wall-surface-view-B-cross-section-of.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Herbertus-sendtneri-A-epidermal-cells-of-capsule-wall-surface-view-B-cross-section-of_fig2_226571718

medium.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/445446-Herbertus-borealis
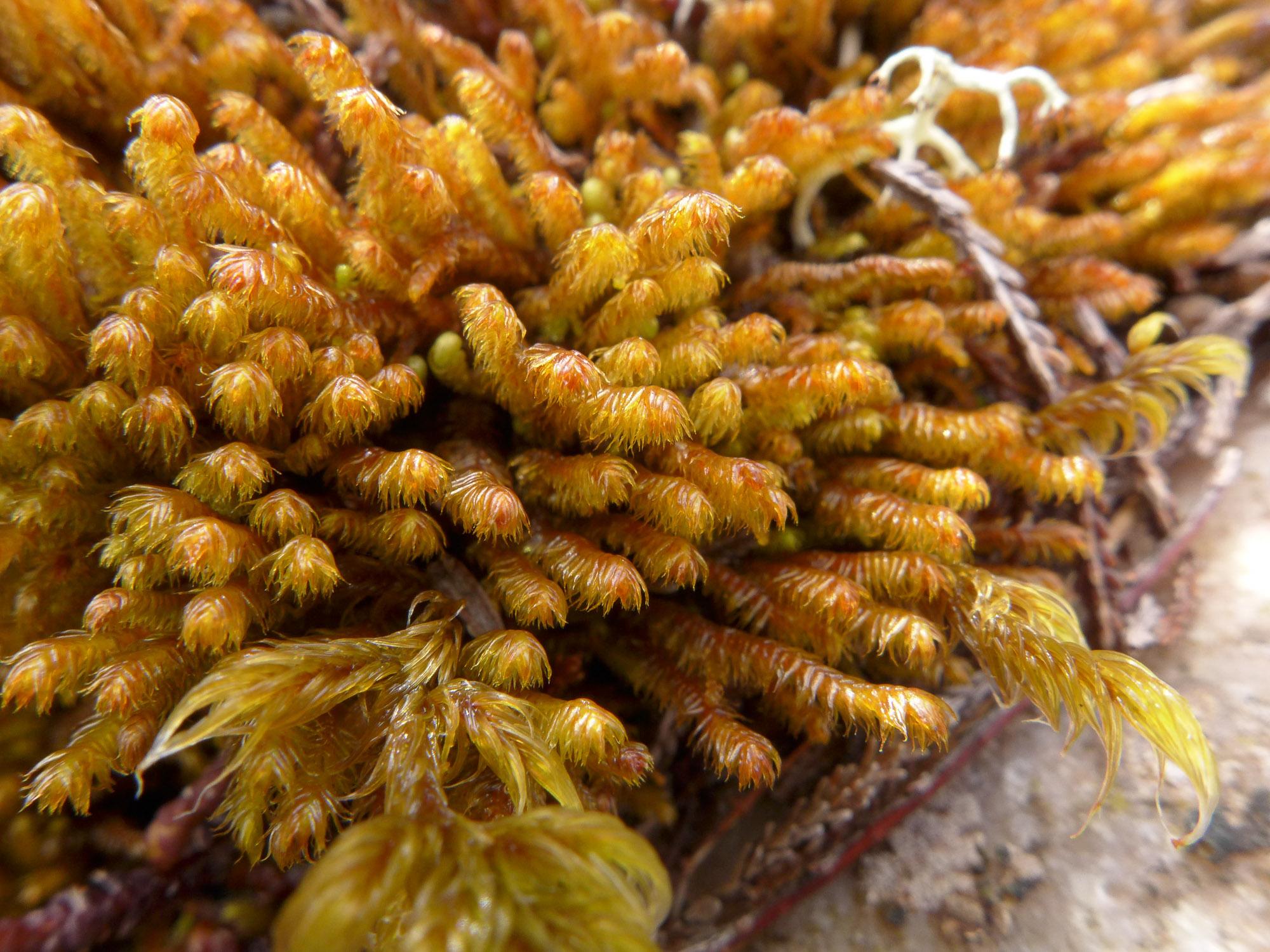

Herbertus-borealis-2-0613.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/herbertus-borealis/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Herbertaceae |
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Deeply divided, fern-like |
| Underleaves | Present |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas, rotting logs, tree bark |
| Distribution | Widespread globally |
Conclusion
The Herbertus dicranus (Taylor) Trevis. moss, a member of the Herbertaceae family, is a remarkable species that deserves our appreciation and admiration. Its intricate morphology, global distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject of study. As we delve deeper into the world of bryophytes, we are reminded of the incredible diversity and resilience of these often overlooked organisms. Perhaps the next time you encounter a lush, verdant carpet of moss, you’ll pause and wonder if the unassuming
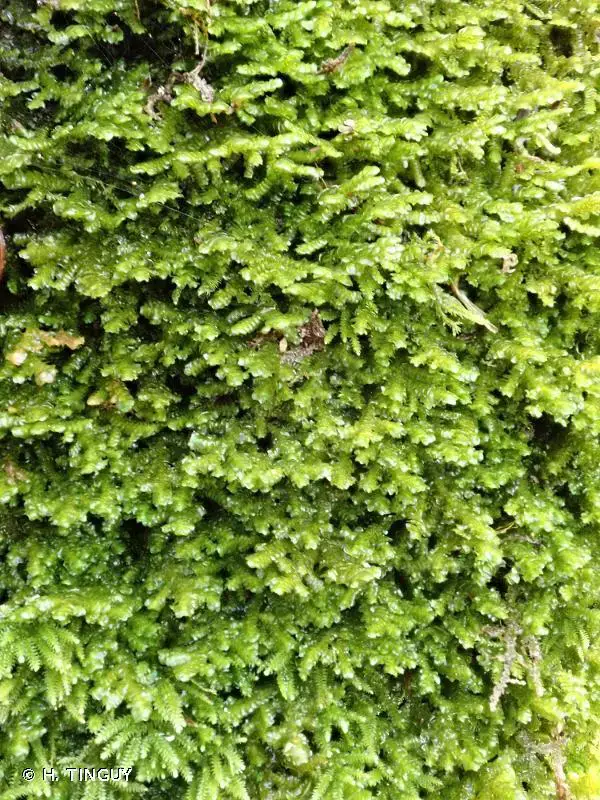

392413.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6667
Herbertus dicranus is among its residents, silently contributing to the intricate web of life.