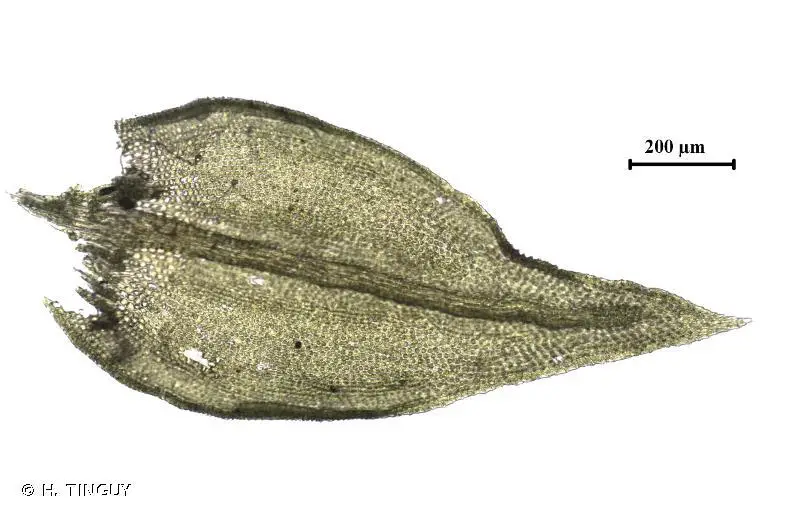
207323.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/436151
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Lescuraea patens Lindb. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Pseudoleskeaceae family. Often referred to simply as Lescuraea, this unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Lescuraea patens Lindb., it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest and most resilient life forms on our planet. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.
Lescuraea-patens_23-01-19-13-02-55-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/lescuraea-patens/
Main Content
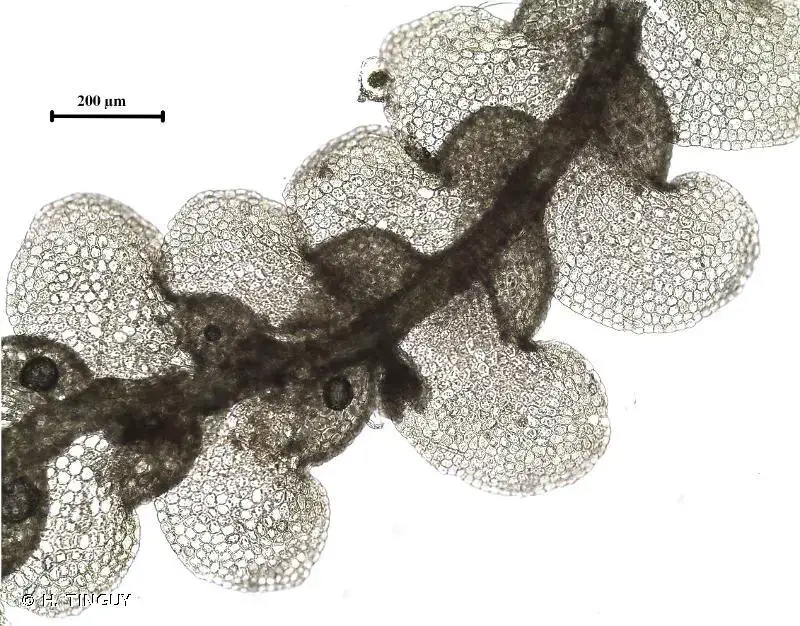
227410.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6711
Morphology and Identification
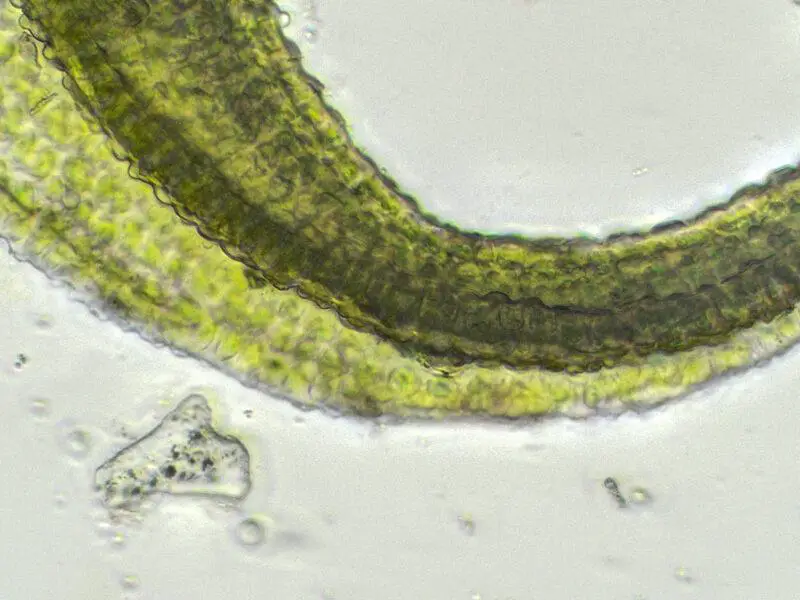
Lescuraea patens Lindb. is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its stems are slender and branched, typically reaching heights of 1-3 centimeters. The leaves are ovate to lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a short awn or hair-like projection.

physcomitrella.jpg from: https://www.plants.ox.ac.uk/article/genetic-regulation-2d-3d-growth-transition-moss-physcomitrella-patens
One of the most striking features of Lescuraea patens Lindb. is its vibrant green color, which can take on a golden or reddish hue when exposed to direct sunlight or during periods of stress. This coloration is due to the presence of specialized pigments that help protect the moss from harmful UV radiation.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Lescuraea patens Lindb. is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, with populations found in Europe, Asia, and North America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, including rocky outcrops, cliffs, boulders, and even tree bark in moist, shaded environments.
This moss is particularly well-adapted to cool, humid conditions and is often found in mountainous regions, where it can form extensive carpets on the forest floor or cling to the sides of rocks and boulders.
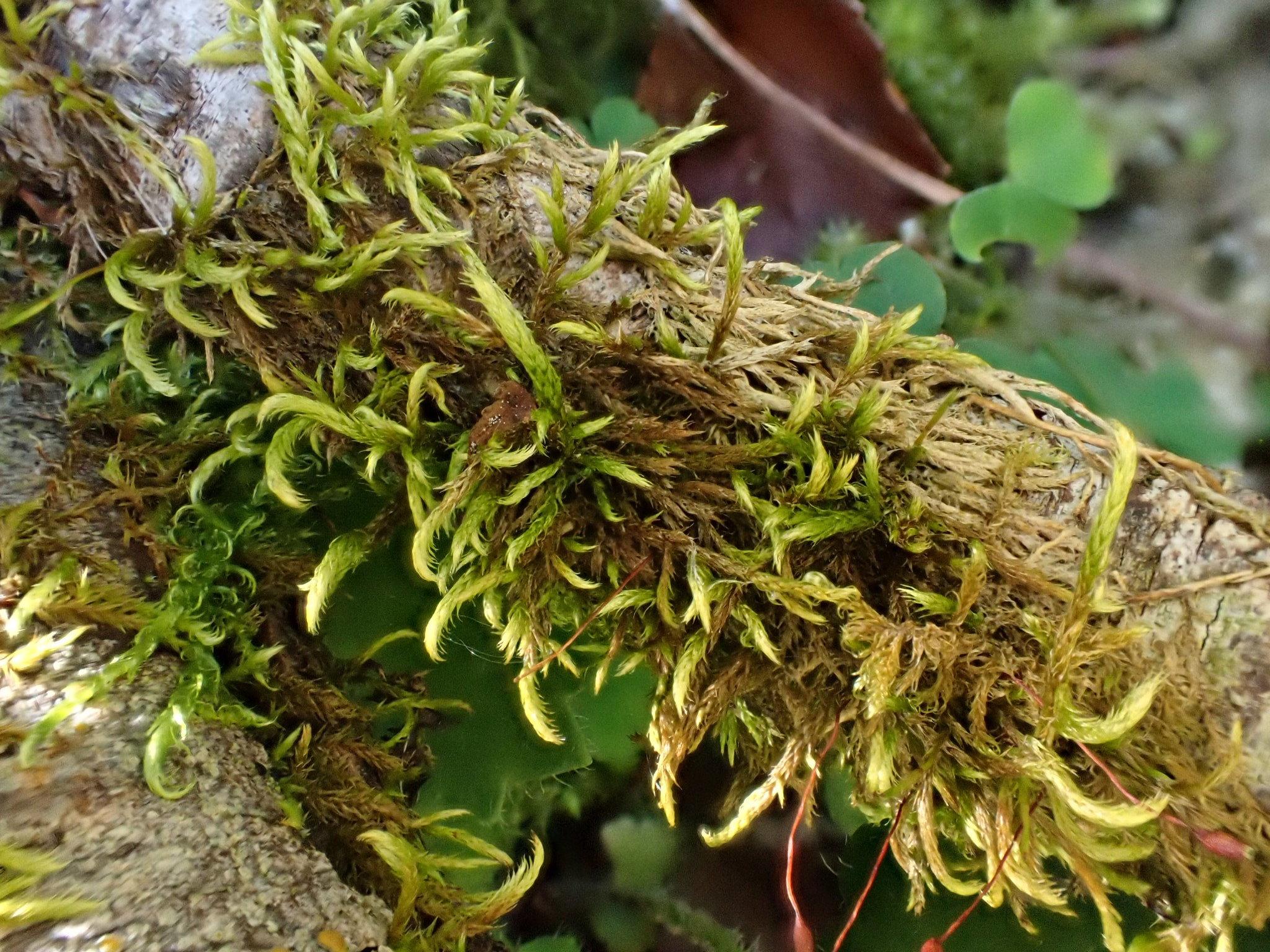

original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/pt/species/2681255
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Lescuraea patens Lindb. plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide shelter and moisture for a wide range of invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Lescuraea patens Lindb. is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, resuming its growth and photosynthetic activities.
Case Studies/Examples
In the Pacific Northwest region of North America, Lescuraea patens Lindb. is a common sight in old-growth forests, where it forms lush carpets on decaying logs and stumps. These moss mats provide crucial microhabitats for a variety of organisms, including fungi, insects, and amphibians.
In Europe, Lescuraea patens Lindb. has been used as an indicator species for monitoring air pollution levels. Its sensitivity to atmospheric contaminants makes it a valuable tool for assessing environmental quality and guiding conservation efforts.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pseudoleskeaceae |
| Genus | Lescuraea |
| Species | patens Lindb. |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to lanceolate, with a costa extending beyond the leaf apex |
| Color | Vibrant green, golden or reddish hues |
| Habitat | Rocky outcrops, cliffs, boulders, tree bark in moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere (Europe, Asia, North America) |
Conclusion
The Lescuraea patens Lindb. moss, a member of the Pseudoleskeaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its unique morphology, adaptations, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these remarkable organisms, ensuring their continued existence and contribution to our planet’s ecosystems?