
1131922.jpg from: https://www.bio-forum.pl/messages/3280/1131921.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out as a true marvel – the Timmia bavarica Hessl., commonly known as Timmia. This unassuming yet extraordinary member of the Timmiaceae family has captured the hearts and minds of moss enthusiasts worldwide, offering a unique glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background
Before delving into the fascinating details of Timmia bavarica Hessl.

25185_2421_4.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/Timmia bavarica-2421
, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which this moss thrives. Bryophytes, a diverse group of non-vascular plants, encompass mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. These ancient organisms have been around for millions of years, predating even the earliest vascular plants. Their ability to survive and thrive in a wide range of environments is a testament to their remarkable adaptability and resilience.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
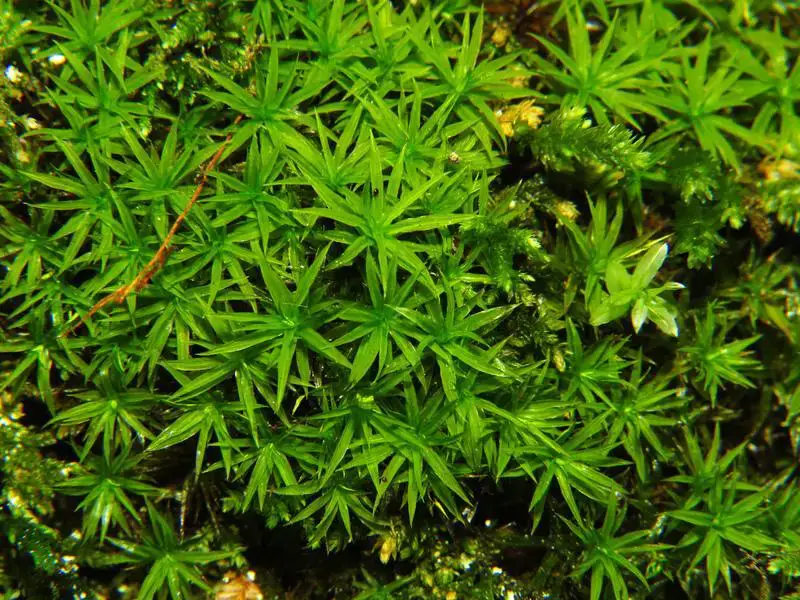
Timmia bavarica Hessl. is a striking moss species, easily recognizable by its distinctive features. Its slender, upright stems are adorned with delicate, lance-shaped leaves that form a beautiful, feathery appearance. The leaves themselves are keeled, meaning they have a prominent midrib that creates a distinct ridge along their length. This unique characteristic is one of the key identifiers of the
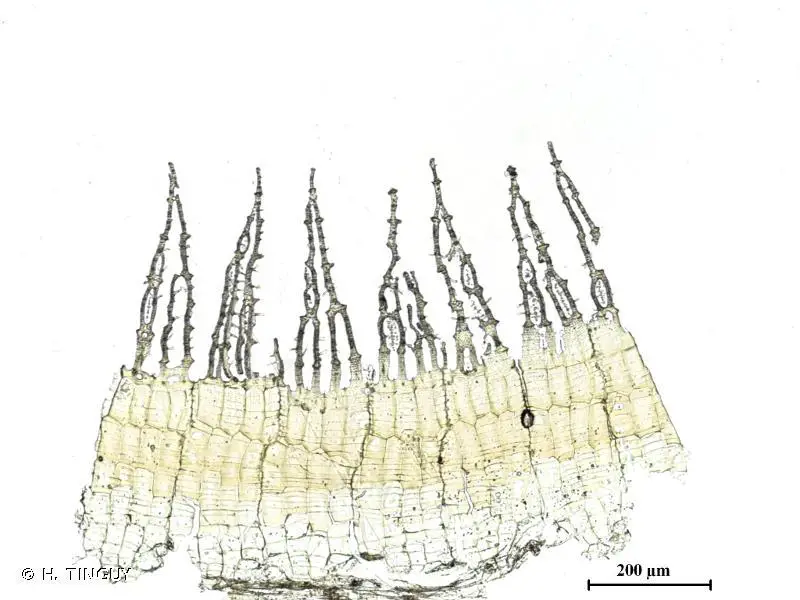
382617.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5001
Timmia genus.
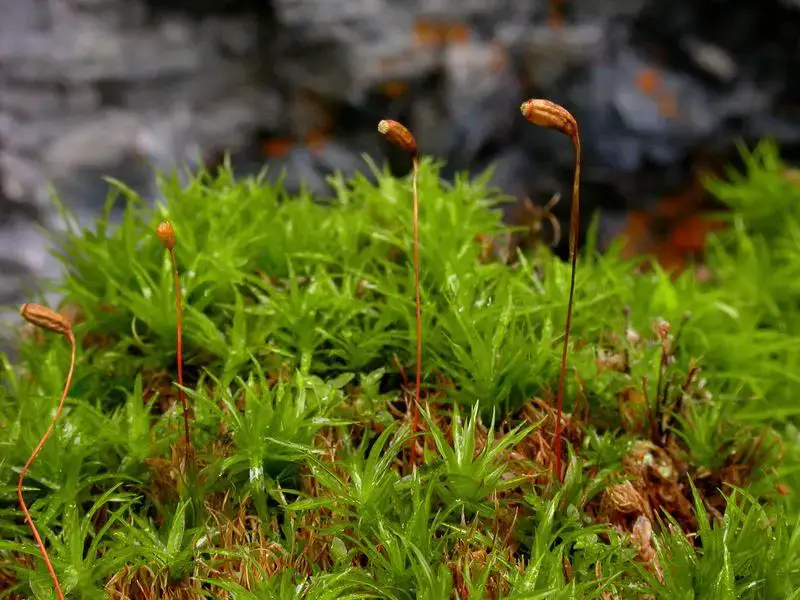
Another remarkable aspect of Timmia bavarica Hessl. is its reproductive structures. The sporophytes, which bear the spore-producing capsules, are elevated on elongated seta (stalks). These capsules are cylindrical in shape and often curved

08678fea6a09168d68ceb0004a633e03.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/507921664198575129/
, adding to the moss’s captivating visual appeal.
Global Distribution and Habitat
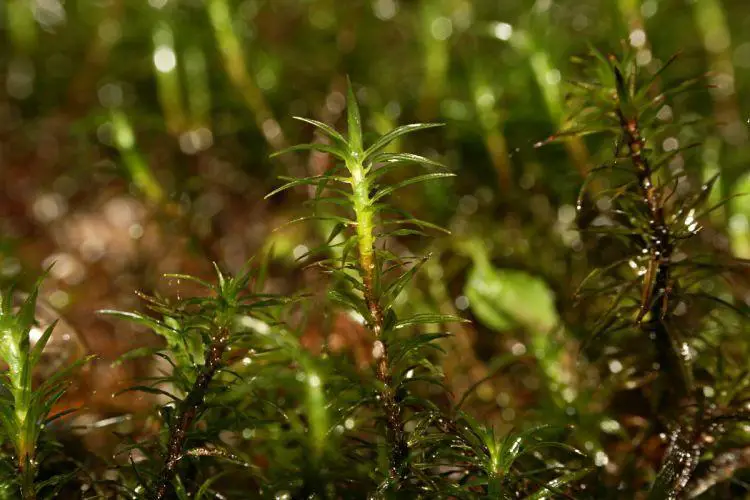
Timmia bavarica Hessl. is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, and North America. However, it is particularly abundant in

CCDB42545C01%2B1658365626.jpg from: https://v3.boldsystems.org/index.php/Taxbrowser_Taxonpage?taxid=1157020
mountainous areas and boreal forests, where it thrives in cool, moist environments. This moss species is often found growing on damp, shaded rocks
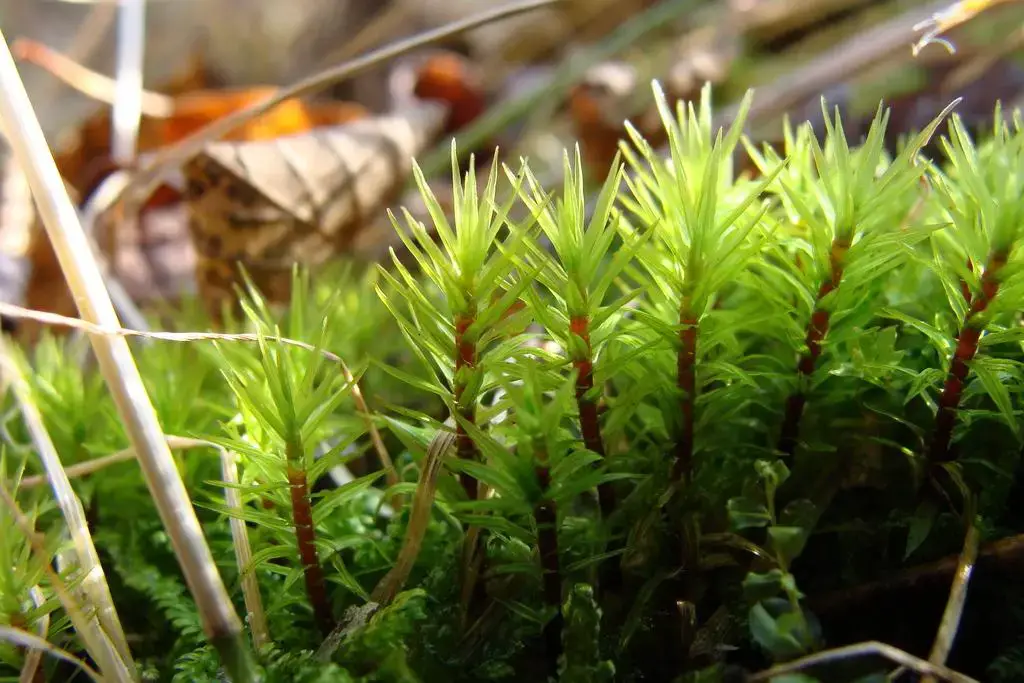

large.JPG from: https://www.inaturalist.org/guide_taxa/1836810
, rotting logs, and soil-rich areas, forming lush, verdant carpets that add a touch of vibrant green to its surroundings.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Timmia bavarica Hessl. plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it is one of the first to colonize disturbed or newly exposed areas, helping to stabilize the soil and pave the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, mosses like Timmia serve as important microhabitats for various invertebrates, providing shelter, moisture, and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Timmia bavarica Hessl. is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During periods of drought, this moss can enter a state of dormancy, effectively shutting down its metabolic processes until favorable conditions return. This remarkable trait allows it to survive in environments where water availability is unpredictable, further contributing to its widespread distribution.
Case Studies/Examples
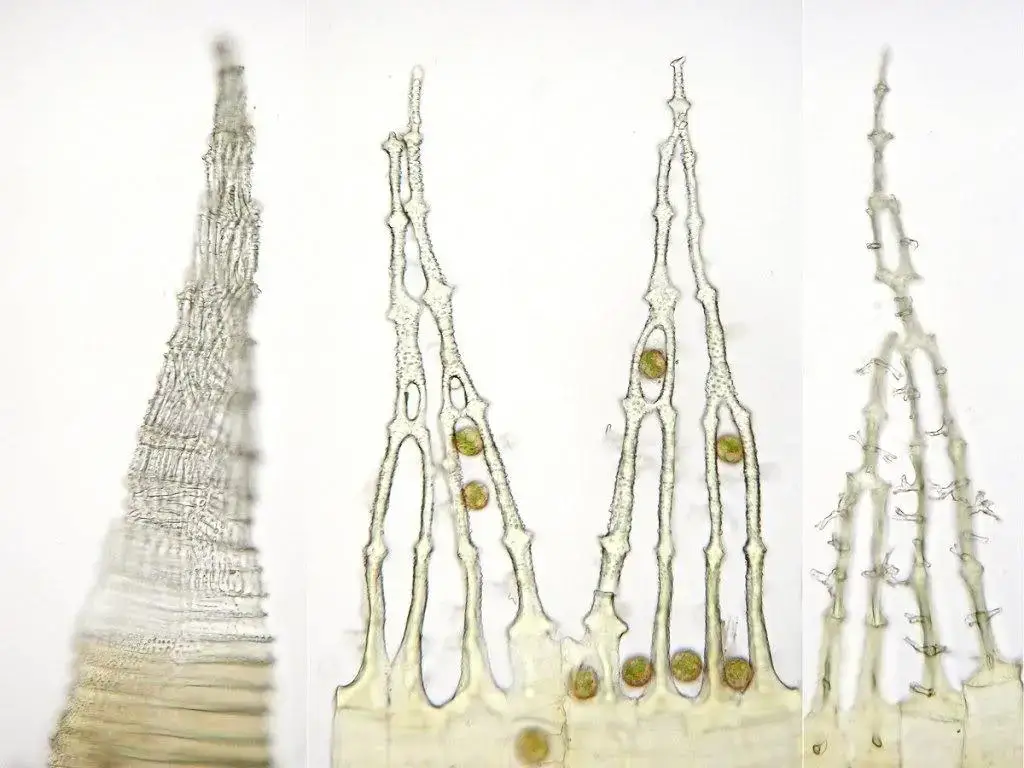
98426_34930376.jpg from: http://www.mikroskopie-forum.de/index.php?topic=13098.0
In the Great Smoky Mountains National Park in the United States, Timmia bavarica Hessl. plays a vital role in the park’s diverse bryophyte community. Researchers have documented its presence in various habitats, including moist rock outcrops and decaying logs, where it forms vibrant green carpets that add to the park’s natural beauty.
Technical Table
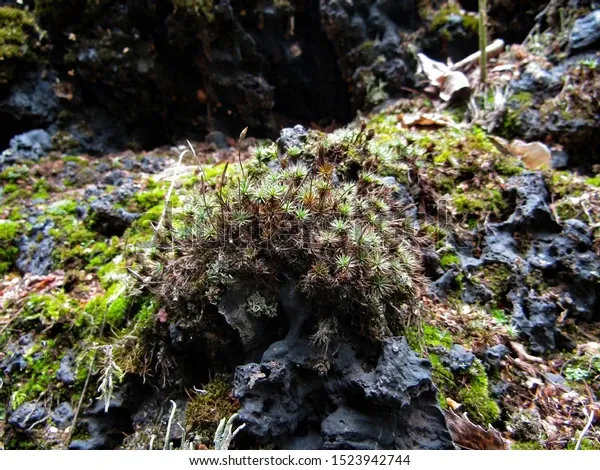

timmia-moss-on-slag-substrate-600w-1523942744.jpg from: https://www.shutterstock.com/image-photo/timmia-moss-on-slag-substrate-close-1523942744
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Timmiaceae |
| Genus | Timmia |
| Species | Timmia bavarica Hessl. |
| Growth Form | Upright, slender stems |
| Leaf Shape | Lance-shaped, keeled |
| Sporophyte | Cylindrical, curved capsules on elongated seta |
Habitat
 203879.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5001/tab/statut |
Damp, shaded rocks, rotting logs, soil-rich areas |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North America (particularly mountainous and boreal regions) |
Conclusion
Timmia bavarica Hessl., a true gem among mosses, serves as a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. From its captivating morphology to its vital ecological roles, this unassuming moss species has much to offer to those who take the time to appreciate its beauty and significance. As we continue to explore and understand the intricate world of mosses, perhaps the greatest question that remains is: What other wonders await discovery in the realm of these ancient, resilient organisms?

141873.jpg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=14232