
MYRS_para_serr_158799.jpg from: https://plantidtools.fieldmuseum.org/es/rrc/catalogue/590717
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Isotachis serrulata (Sw.) Gottsche moss stands out as a remarkable species. Belonging to the Balantiopsidaceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this

green-moss-dry-blossom-alnus-serrulata-hazel-alder-tree-macro-background-detail-smooth-spring-169672990.jpg from: https://www.dreamstime.com/green-moss-dry-blossom-alnus-serrulata-hazel-alder-tree-macro-background-detail-smooth-spring-image169672990
serrulata moss, exploring its unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological significance.

dolichandrone-serrulata-flower-white-green-moss-69719105.jpg from: https://www.dreamstime.com/stock-photo-dolichandrone-serrulata-flower-white-green-moss-image69719105
Background

f69abf4cd7038544c499dca3a345f3ab.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/cleome-serrulata–151855818672789676/
Before we dive into the specifics of Isotachis serrulata, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. As members of the Marchantiophyta division and the Jungermanniopsida

the-bark-the-japanese-cherry-tree-prunus-serrulata-with-an-old-wound-covered-in-green-moss-texture-or-background-2AC742C.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/the-bark-the-japanese-cherry-tree-prunus-serrulata-with-an-old-wound-covered-in-green-moss-texture-or-background-image334529732.html
class, mosses like Isotachis contribute to the rich biodiversity of our planet.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Isotachis serrulata is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions. Its delicate leaves are arranged in two rows, giving it a distinctive feathery appearance. The leaves themselves are serrulate, meaning they have tiny teeth along their margins, which is a key identifying feature. This moss can range in color from vibrant greens to deep browns, depending on its environment and growth stage.
Global Distribution and Habitat

the-bark-the-japanese-cherry-tree-prunus-serrulata-with-warts-and-covered-in-green-moss-texture-or-background-2AC740K.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/the-bark-the-japanese-cherry-tree-prunus-serrulata-with-warts-and-covered-in-green-moss-texture-or-background-image334529683.html
While Isotachis serrulata is widely distributed across various regions, it thrives particularly well in tropical and subtropical areas. This moss can be found growing on tree bark, rocks, and soil in humid forests, often forming intricate carpets that add texture and beauty to its surroundings. Its ability to adapt to a wide range of habitats has contributed to its successful dispersal across multiple continents.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Isotachis serrulata plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and sustenance for these tiny creatures.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Isotachis serrulata is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves to conserve moisture. Once favorable conditions return, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the tropical rainforests of Costa Rica, researchers discovered that Isotachis serrulata played a crucial role in facilitating the growth and establishment of epiphytic orchids. The moss’s ability to retain moisture and create a suitable microclimate allowed orchid seeds to germinate and develop, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.
Technical Table

leptinella-serrulata_20101016_3484.jpg from: https://www.nzpcn.org.nz/flora/species/leptinella-serrulata/

1360px-Liverwort_Genus_Isotachis.JPG from: https://www.citscihub.nz/Phil_Bendle_Collection:Isotachis_(Genus_)
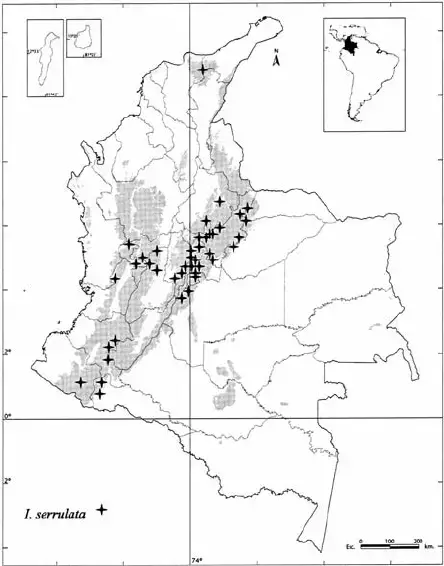
Distribution-of-Isotachis-serrulata-in-Colombia.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Distribution-of-Isotachis-serrulata-in-Colombia_fig4_259873320

cleome-serrulata2.jpg from: https://www.americansouthwest.net/plants/wildflowers/cleome-serrulata2_l.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Isotachis serrulata (Sw.) Gottsche |
| Family | Balantiopsidaceae |
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Two rows, feathery |
| Leaf Margin | Serrulate (toothed) |
| Color | Green to brown |
| Habitat | Tree bark, rocks, soil (humid forests) |
| Distribution | Tropical and subtropical regions |
Conclusion
The Isotachis serrulata (Sw.) Gottsche moss may be small in stature, but its impact on the natural world is profound. From its intricate morphology to its vital ecological roles, this unassuming bryophyte deserves our appreciation and admiration. As we continue to explore the wonders of the plant kingdom, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How many other hidden gems like Isotachis serrulata are waiting to be discovered and celebrated for their unique contributions to our planet’s biodiversity?