
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Jaegerina-scariosa-A-Gametophyte-B-Leaf-Potamium-lonchophyllum-C-Gametophyte-D_fig3_347938312
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Jaegerina scariosa (Lorentz) Arzeni moss stands out as a remarkable species. Belonging to the Pterobryaceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating moss, commonly known as Jaegerina, has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this Bryopsida

image from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/01/musgos-pleurocarpicos-jaegerina-scariosa.html
marvel and unravel its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the intricate details of Jaegerina scariosa, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content

image from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Pterobryaceae/jaegerina-scariosa/en/
Morphology and Identification
Jaegerina scariosa is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts. Its leaves are ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a hair-like structure. The leaf margins are entire, and the cells are elongated and smooth. The sporophytes, when present, are erect and bear a cylindrical capsule atop a reddish-brown seta (stalk).

image from: https://floranorthamerica.org/Jaegerina
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss has a widespread distribution, found across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas.

image from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/01/musgos-pleurocarpicos-jaegerina-scariosa.html
Jaegerina scariosa thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from rocky outcrops and cliffs to soil banks and tree bases. Its ability to colonize and persist in these environments is a testament to its resilience and adaptability.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Jaegerina scariosa plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating microhabitats for other organisms. Additionally, this moss serves as a pioneer species, helping to stabilize and prepare the way for other plants to establish themselves.

image from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/01/musgos-pleurocarpicos-jaegerina-scariosa.html
One of the remarkable adaptations of Jaegerina scariosa is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. When moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its remarkable resilience.
Case Studies/Examples

image from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/01/musgos-pleurocarpicos-jaegerina-scariosa.html
In a recent study conducted in the Appalachian Mountains, researchers discovered that Jaegerina scariosa played a crucial role in stabilizing soil on steep slopes, preventing erosion and facilitating the growth of other plant species. This highlights the importance of this unassuming moss in maintaining the integrity of fragile ecosystems.
Technical Table

image from: https://www.societequebecoisedebryologie.org/mousses/Zygodon_rupestris.html
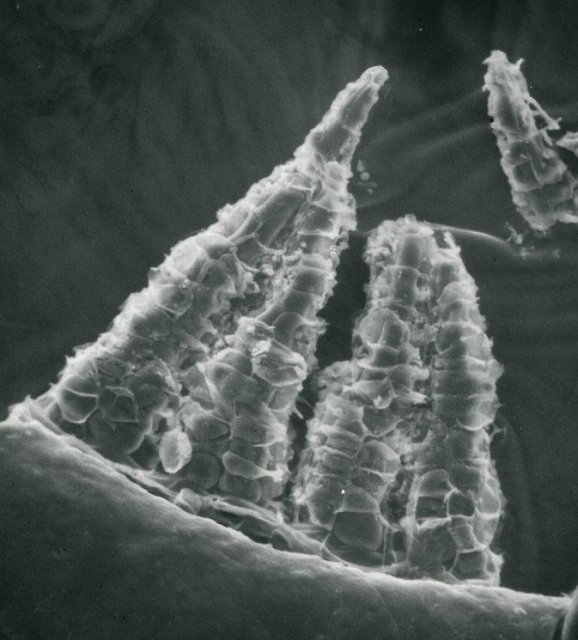
image from: https://idfg.idaho.gov/species/taxa/4685
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida
 image from: https://popmicrosoftnueva.blogspot.com/2020/01/briofitas-pleurocarpicas-leucodontales_19.html |
| Family | Pterobryaceae |
| Genus | Jaegerina |
| Species | scariosa |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Margin | Entire |
| Leaf Cells | Elongated, smooth |
| Sporophyte | Erect, cylindrical capsule on reddish-brown seta |