Tomentum-of-Leptodontium-tricolor-The-pink-stain-implies-the-present-of-pectic-mucilage.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Tomentum-of-Leptodontium-tricolor-The-pink-stain-implies-the-present-of-pectic-mucilage_fig8_289991659
Leptodontium syntrichioides: The Fascinating Moss of the Pottiaceae Family
Introduction
Leptodontium syntrichioides (Müll.Hal.) Paris, commonly known as
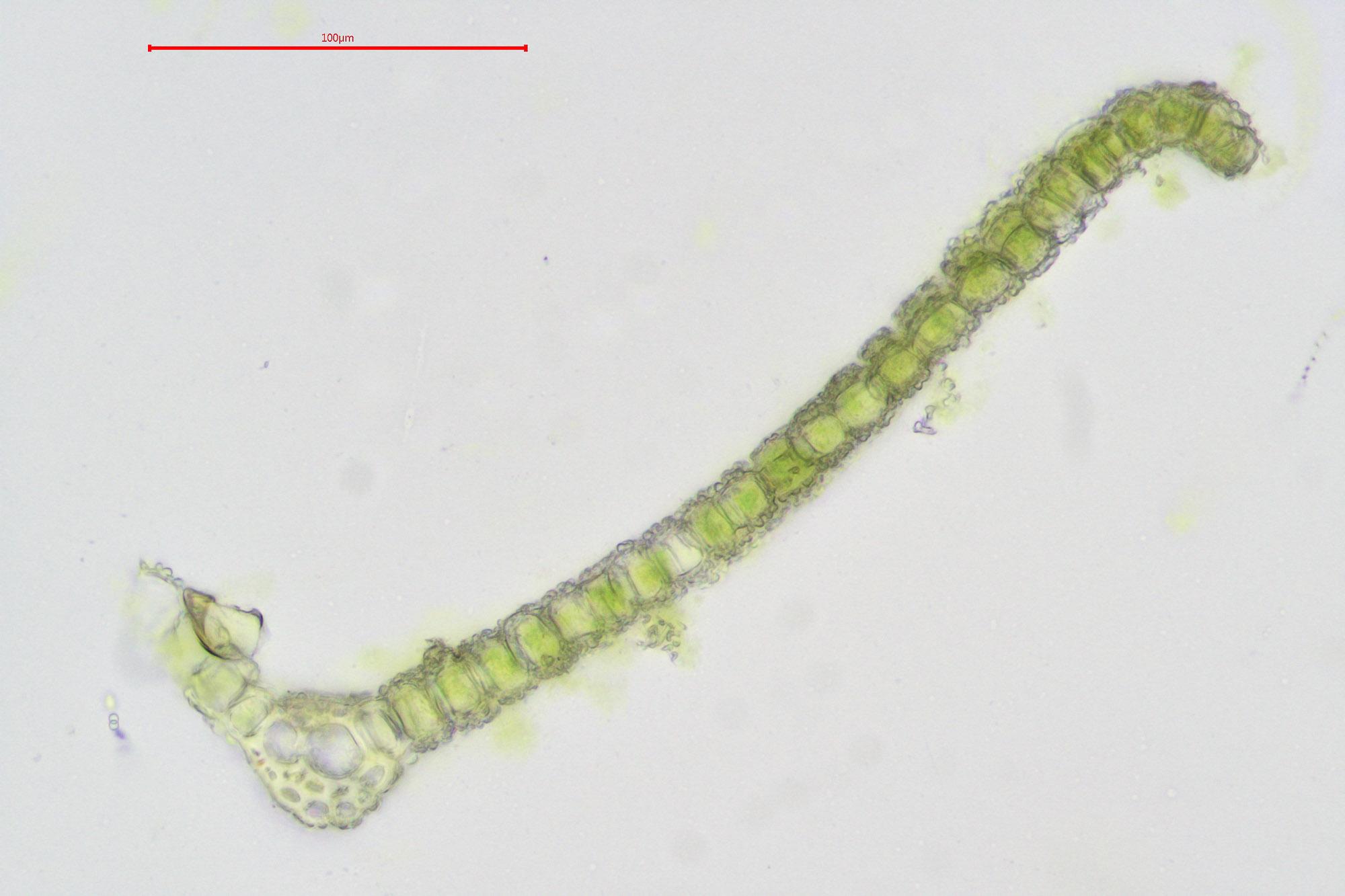

2021-10-15-15-08-18.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/leptodontium-flexifolium/
Leptodontium, is a captivating moss species belonging to the Pottiaceae family. This tiny but mighty plant plays a significant role in its ecosystems and boasts unique adaptations that allow it to thrive in various habitats worldwide. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of Leptodontium syntrichioides and explore its morphology, distribution, ecological roles, and more!
Background
Mosses are small, non-vascular plants belonging to the division Bryophyta and the class Bryopsida. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead possessing simple structures that perform similar functions. Mosses play crucial roles in their ecosystems, including water retention, erosion control, and providing habitat for other organisms.
Morphology and Identification
Leptodontium syntrichioides is a small, cushion-forming moss that typically grows in dense tufts or mats. Its leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, measuring about 1-2 mm long. The leaf margins are usually recurved, and the leaf apex is acute to acuminate. The moss capsules are cylindrical and borne on short setae. Leptodontium syntrichioides can be identified by its distinctive leaf shape and the presence of a peristome with 16 teeth.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Leptodontium syntrichioides has a wide global distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. It grows in a variety of habitats, including rock outcrops, soil banks, tree trunks, and even man-made structures like walls and roofs. This moss is particularly well-adapted to dry, exposed environments and can tolerate periods of desiccation.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Leptodontium syntrichioides plays several important ecological roles:
Water retention: The dense growth form of this moss helps to trap and retain water, reducing soil erosion and maintaining moisture in its immediate environment.
Nutrient cycling: As the moss decomposes, it releases nutrients back into the soil, contributing to the overall health of the ecosystem.
Habitat provision: The small, intricate structure of Leptodontium syntrichioides provides shelter and microhabitats for various invertebrates and microorganisms.
To survive in its often harsh habitats, Leptodontium syntrichioides has developed several key adaptations:
Desiccation tolerance: This moss can withstand extended periods of dryness by entering a dormant state and quickly reviving when moisture becomes available.
Efficient water uptake: The leaf structure and arrangement of Leptodontium syntrichioides facilitate rapid water absorption, allowing the moss to take advantage of even brief periods of moisture.
UV resistance: The moss produces protective pigments that shield it from harmful ultraviolet radiation, which is particularly important in exposed habitats.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Leaf shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf size | 1-2 mm long |
| Leaf margins | Usually recurved |
| Leaf apex | Acute to acuminate |
| Capsule shape | Cylindrical |
| Seta length | Short |
| Peristome teeth | 16 |
Conclusion
Leptodontium syntrichioides may be small, but it is a remarkable moss with a wide-reaching impact on its ecosystems. Its unique adaptations and global distribution make it a fascinating subject for bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike. The next time you find yourself in a dry, rocky environment, take a closer look—you might just spot a patch of Leptodontium syntrichioides quietly going about its business. What other secrets might this tiny plant hold?