
medium.JPG from: https://www.naturalista.mx/taxa/164656-Leucolejeunea-unciloba
Leucolejeunea unciloba: The Tiny Moss with a Big Story
Leucolejeunea unciloba (Lindenb.) A.Evans is a fascinating species of moss in the Lejeuneaceae

Cheilolejeunea_conchifolia_BA1_1545241229.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/portal/imagelib/imgdetails.php?imgid=1745901
family. This tiny plant, commonly known as just
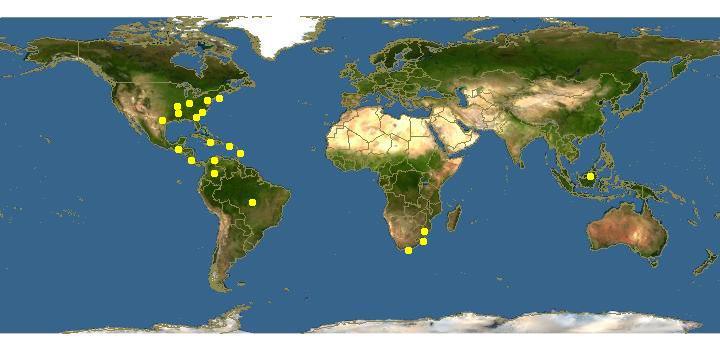
map_of_Leucolejeunea.jpg from: https://www.discoverlife.org/mp/20q?search=Leucolejeunea
Leucolejeunea, may be small in stature but it has an outsized role in the ecosystems where it grows. Let’s take a closer look at this marvelous moss.
Background on Bryophytes
Mosses like L. unciloba are non-vascular plants in the division Marchantiophyta, class Jungermanniopsida. Unlike the more familiar vascular plants, mosses lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have root-like rhizoids, stem-like structures called gametophores, and leaf-like structures called phyllids. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds.

lrLeucolejeunea_sp1.jpg from: https://james-vankley.com/PineywoodsPlants/Bryophytes_Charophytes/Liverworts/Lejeuneaceae/Lejeuneaceae.html
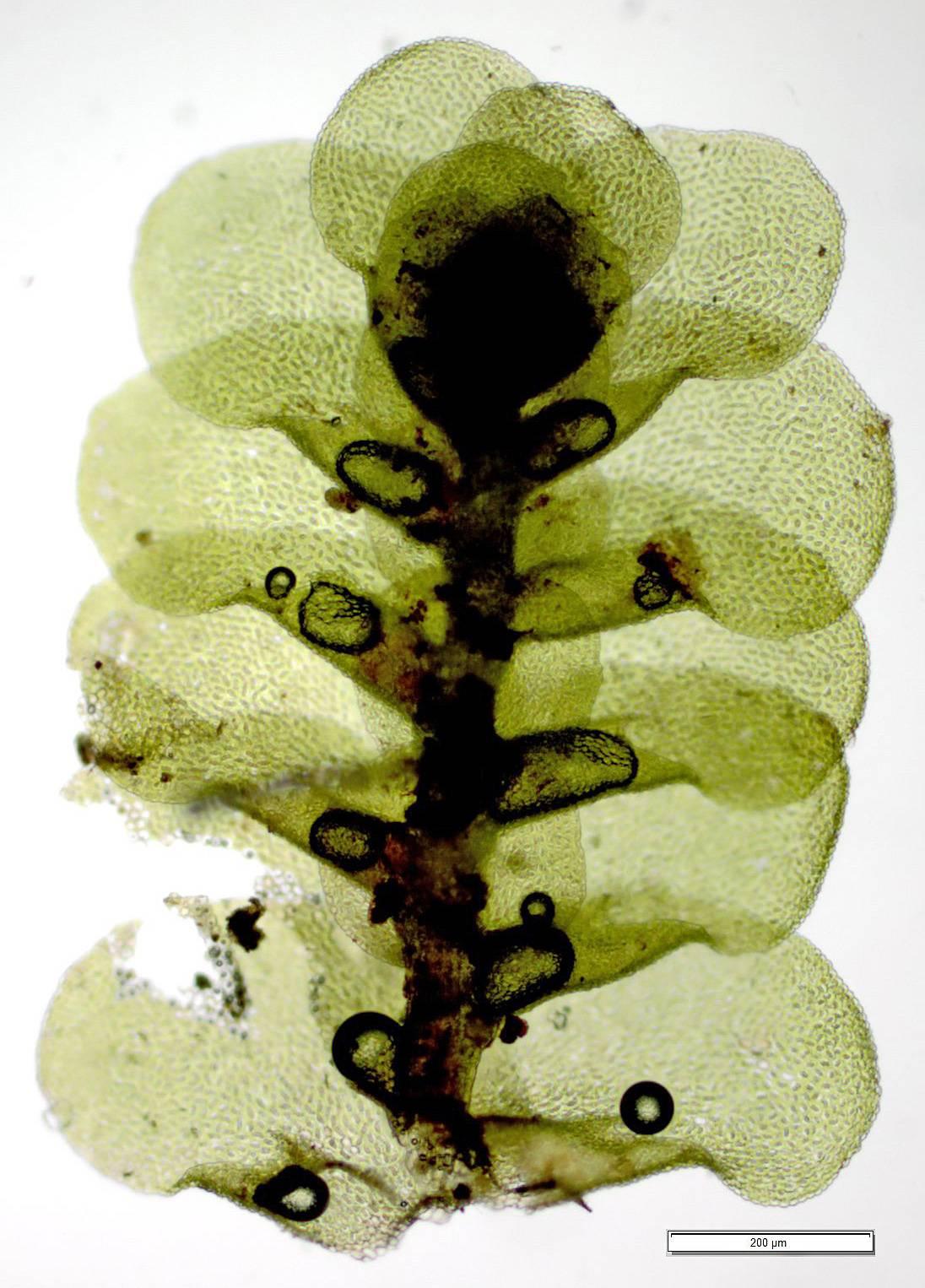
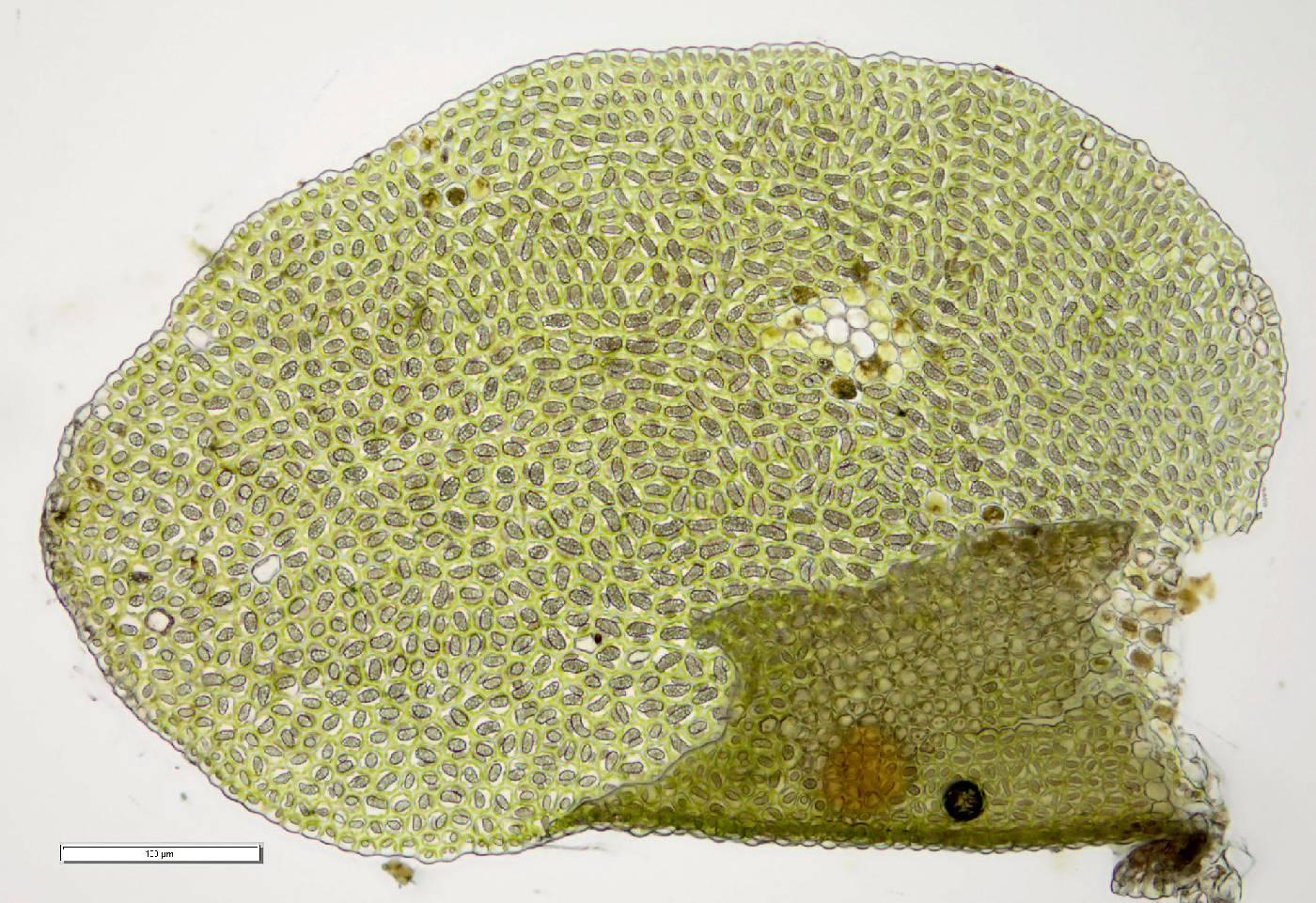
Morphology and Identification
L. unciloba is a very small moss, with shoots typically less than 1 cm long. The phyllids are ovate to oblong and have a characteristic uncinate (hooked) tip, which gives the species its name “unciloba“. The cells in the phyllids are thin-walled. Leucolejeunea is autoicous, meaning both male and female reproductive structures are found on the same plant.
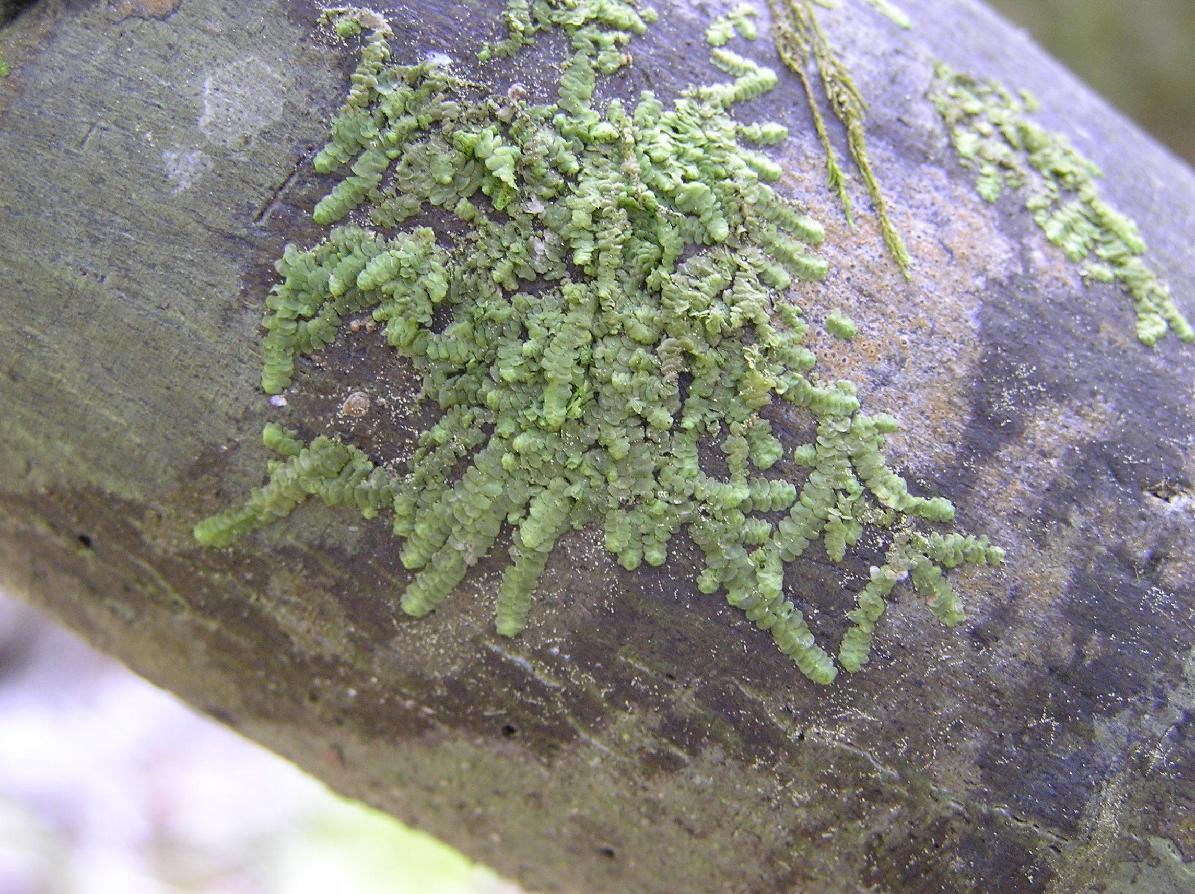
Global Distribution and Habitat
This species has a pantropical distribution, found in tropical regions around the world including the Americas, Africa, and Asia. It grows as an epiphyte on the bark and leaves of trees and shrubs in moist forests. The small size allows it to occupy microhabitats that are unavailable to larger plants.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

scan0001.jpg from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/03/hepaticas-lobuladas-lejeuneaceae.html

Cheilolejeunea_conchifolia_BA1_1545241091.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/portal/imagelib/imgdetails.php?imgid=1745898
Like other epiphytic bryophytes, L. unciloba plays important roles in its ecosystem:
- Nutrient cycling: It efficiently absorbs nutrients from rainwater and traps organic debris, later releasing these nutrients to its host tree.
Cheilolejeunea_conchifolia_BA1_1545241131.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/portal/imagelib/imgdetails.php?imgid=1745899
- Microhabitat creation: The mats of moss create moist, sheltered microhabitats for invertebrates and other small organisms.

medium.jpg from: https://inaturalist.ca/taxa/164654-Leucolejeunea-clypeata
- Water retention: Leucolejeunea helps regulate humidity in the forest by absorbing water when it is wet and slowly releasing it as the environment dries.
The moss has several adaptations for its epiphytic lifestyle:
- Small size for growing on small substrates
- Ability to dry out and rehydrate quickly
- Specialized structures for efficiently absorbing water and nutrients
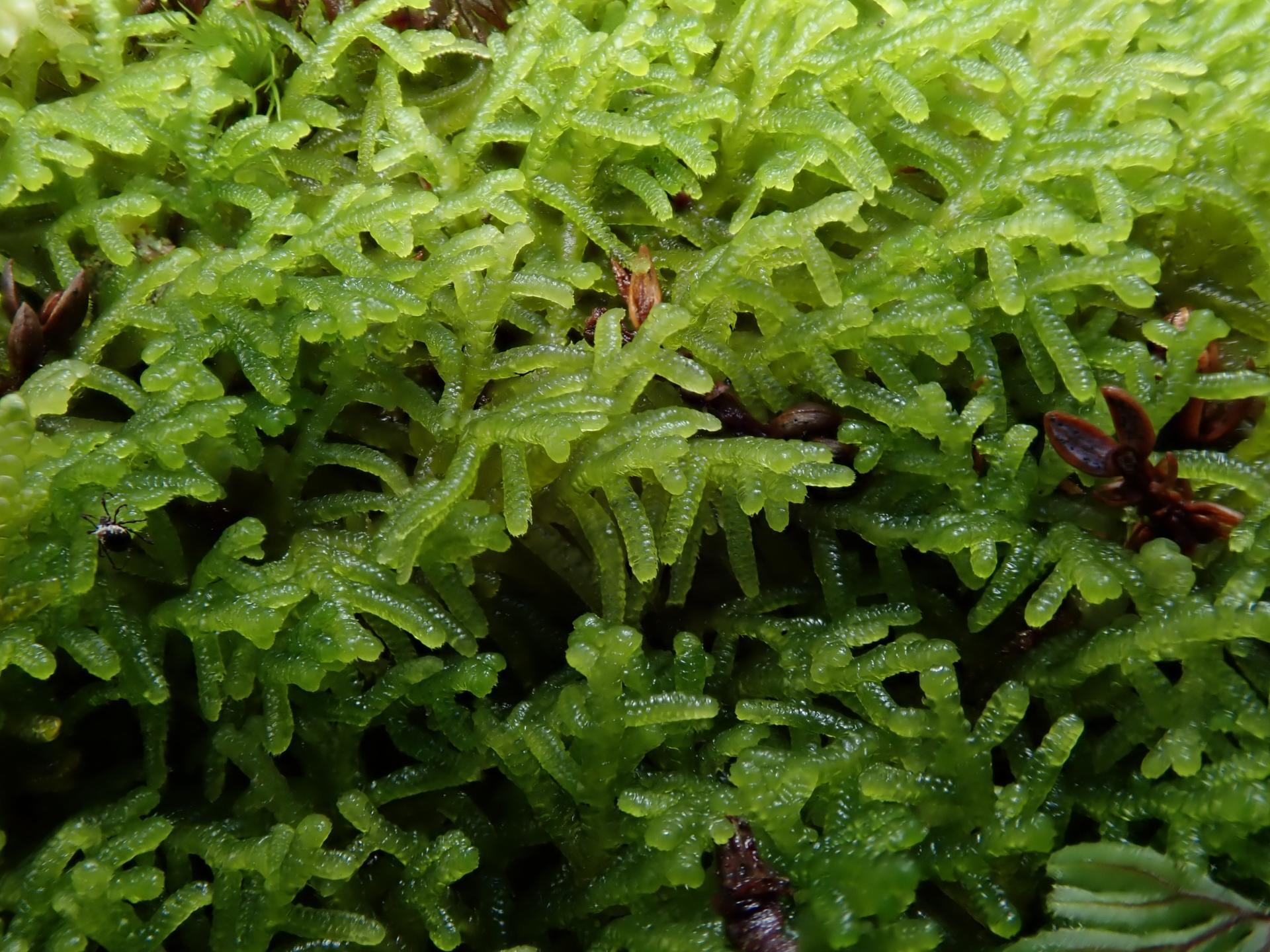

lepidozia-cupressina-t00376-85.jpg from: https://azoresbioportal.uac.pt/pt/especies-dos-acores/lepidozia-cupressina-9834/
Conclusion
Leucolejeunea unciloba may be an unassuming moss, but it exemplifies the remarkable diversity and ecological importance of bryophytes. For a plant that is often measured in millimeters, it has an outsized impact on its environment. The next time you are in a tropical forest, take a moment to appreciate the tiny world of epiphytic mosses like Leucolejeunea – you may be surprised by what you discover! What other secrets might these small but mighty plants hold?

fileget-768×566.jpeg from: https://www.floridamuseum.ufl.edu/science/good-parenting-evolved-multiple-times-in-moss-animals/