
ea618f0f725517b65e1c9ace47ea3f44.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/8574
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Leucoloma molle (Müll.Hal.) Mitt. moss stands out as a remarkable representative of the Dicranaceae family. Often referred to simply as Leucoloma, this unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Leucoloma molle, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, play a crucial role in various ecosystems worldwide. They are often overlooked due to their diminutive size, but their ecological significance cannot be overstated.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
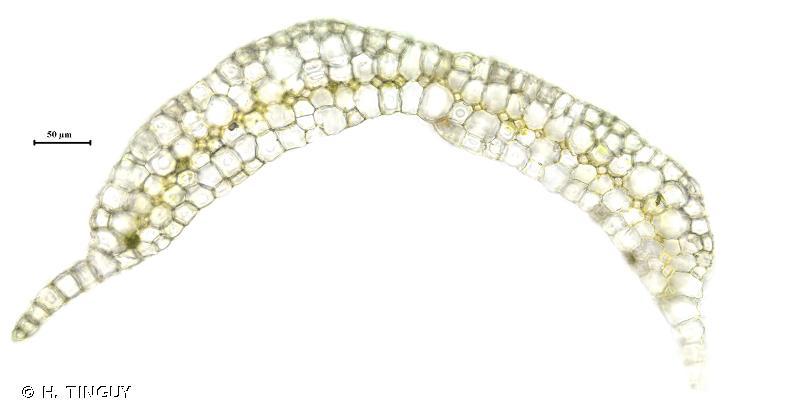
Leucoloma molle is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its gametophytes are typically unbranched, with leaves arranged in a spiral pattern around the stem. The leaves themselves are lanceolate in shape, tapering to a fine point, and possess a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends nearly to the leaf tip.
One of the most striking features of Leucoloma molle is its leaf cells. These cells are elongated and

209936.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4771/tab/fiche
smooth, giving the moss a glossy appearance. Additionally, the leaf margins are often entire (without teeth or serrations), further contributing to the moss’s unique appearance.
Global Distribution and Habitat
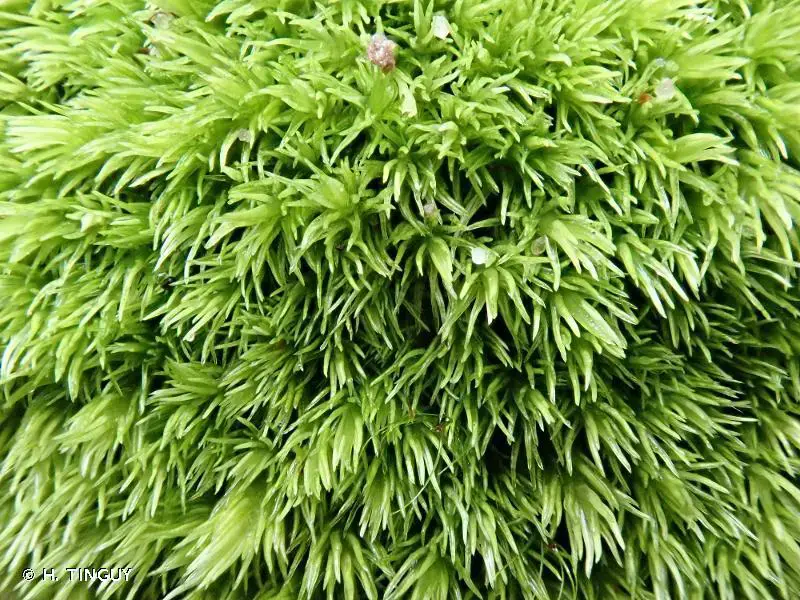
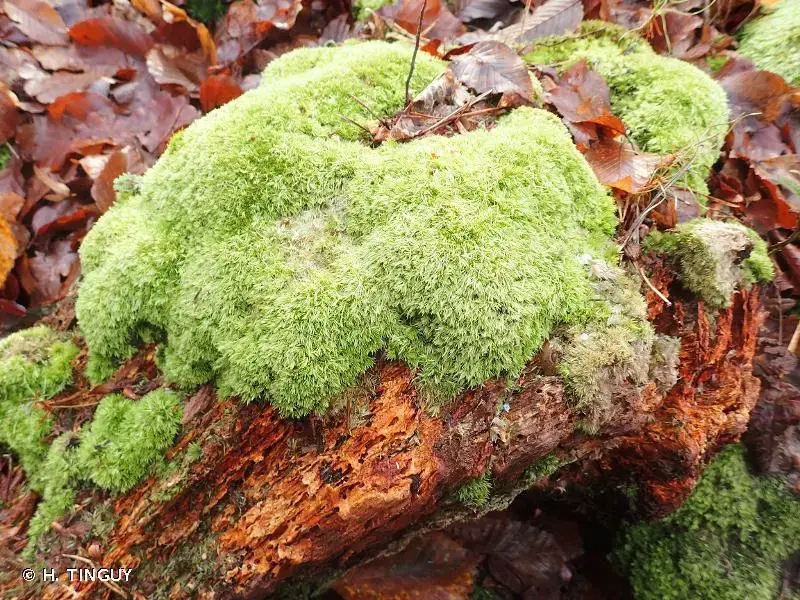
Leucoloma molle is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including tropical and subtropical areas. It can be found growing on a variety of substrates, such as tree bark, rocks, and soil, often forming dense mats or cushions.
This moss thrives in humid and shaded environments, making it a common sight in tropical rainforests, cloud forests, and other moist habitats. Its ability to tolerate a wide range of environmental conditions has contributed to its widespread distribution.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Leucoloma molle plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps in the colonization of new habitats and the formation of soil. Its dense mats can provide a suitable microhabitat for other organisms, such as invertebrates and fungi, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
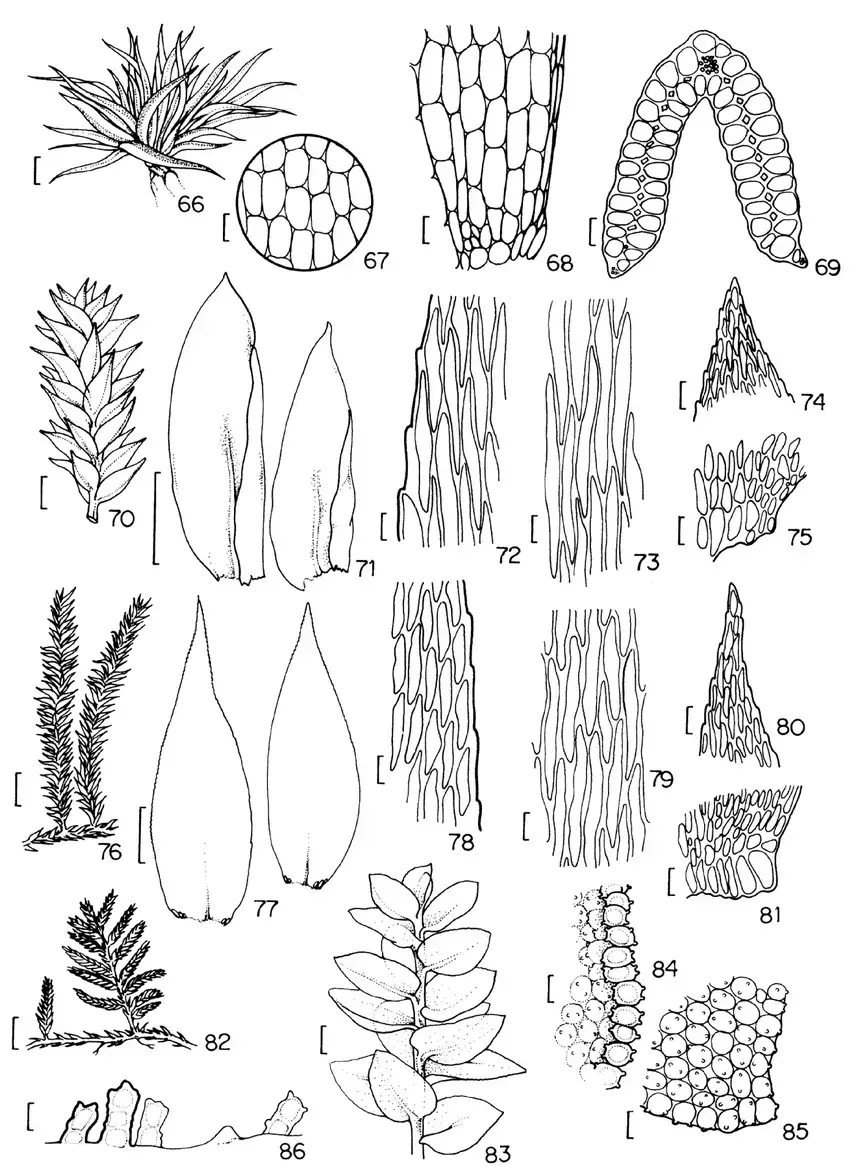
Figuras-66-69-Leucophanes-molleri-Muell-Hal-66-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-67.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figuras-66-69-Leucophanes-molleri-Muell-Hal-66-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-67_fig5_240765931
Additionally, Leucoloma molle possesses remarkable adaptations that allow it to thrive in its environment. Its ability to desiccate and revive

2e9e76b8cdf976b5a656a37dd4781208.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/139048707223163725/
when moisture becomes available is a testament to its resilience. This trait, known as poikilohydry, enables the moss to survive periods of drought and rapidly resume growth when conditions improve.
Case Studies/Examples
Leucoloma molle has been the subject of numerous scientific studies, particularly in the field of bryology (the study of mosses and their relatives). One notable example is a study conducted in the Luquillo Experimental Forest in Puerto Rico, where researchers investigated the role of this moss in nutrient cycling and soil formation.

297416.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4771
The study revealed that Leucoloma molle plays a crucial role in retaining and recycling essential nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, within the ecosystem. Its dense mats act as a sponge, absorbing and storing these nutrients, which are then slowly released and made available to other organisms.
Technical Table
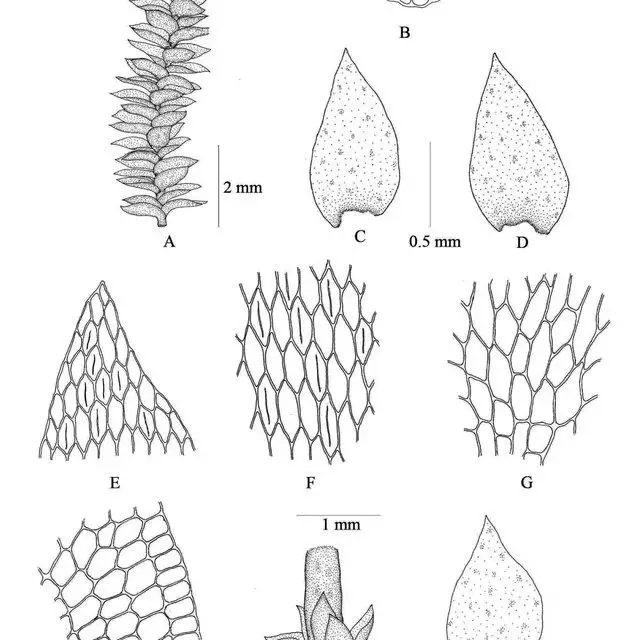
Erpodium-glaziovii-Hampe-A-Plant-B-Cross-section-of-stem-C-D-Leaves-E-Leaf_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Aulacopilum-beccarii-MuellHal-Mitt-A-Plant-B-Cross-section-of-stem-C-D-Leaves_fig1_268271958

247806.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4771/tab/taxo
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Dicranaceae |
| Genus | Leucoloma |
| Species | molle |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous, unbranched |
Leaf Shape
 original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2682901 |
Lanceolate, tapering to a fine point |
| Leaf Cells | Elongated, smooth |
| Leaf Margins | Entire (without teeth or serrations) |
| Habitat | Humid, shaded environments (tropical rainforests, cloud forests) |
| Substrates | Tree bark, rocks, soil |
| Adaptations | Poikilohydry (ability to desiccate and revive) |
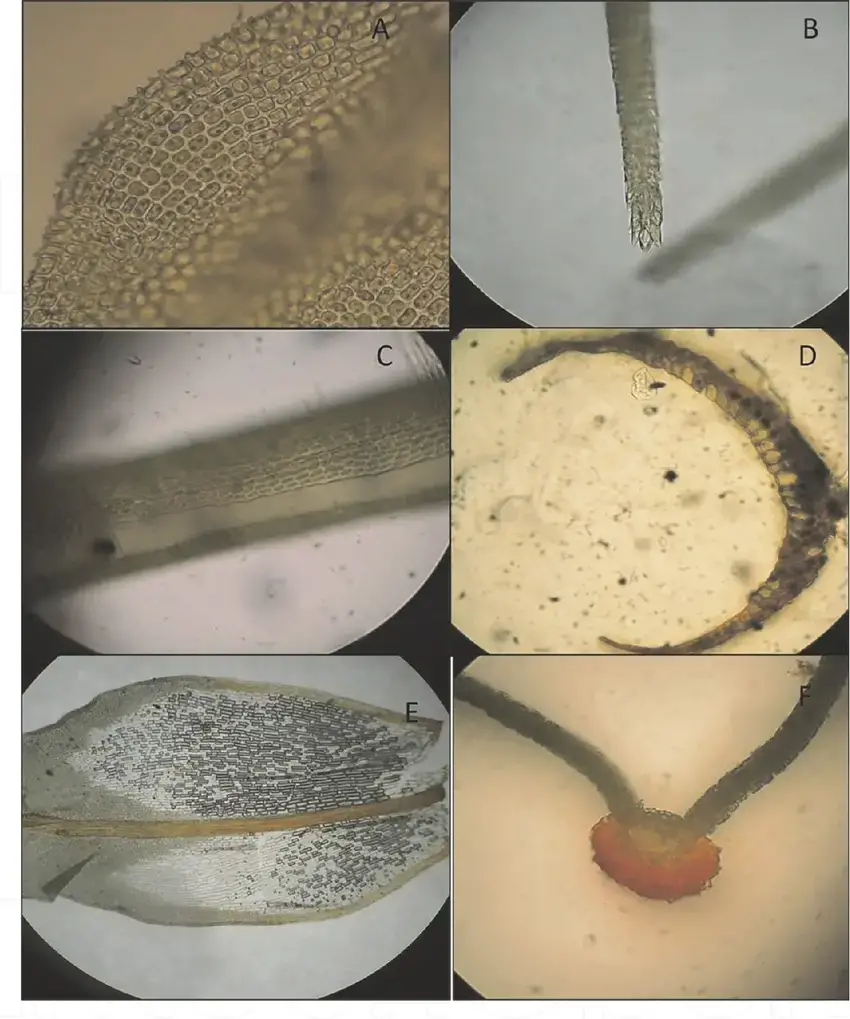
A-Cells-with-two-papillae-in-Thuidium-peruvianun-Mitt40x-B-leave-apex-in-Campylopus.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-Cells-with-two-papillae-in-Thuidium-peruvianun-Mitt40x-B-leave-apex-in-Campylopus_fig3_365328140
Conclusion
The Leucoloma molle (Müll.Hal.) Mitt. moss, a member of the Dicranaceae
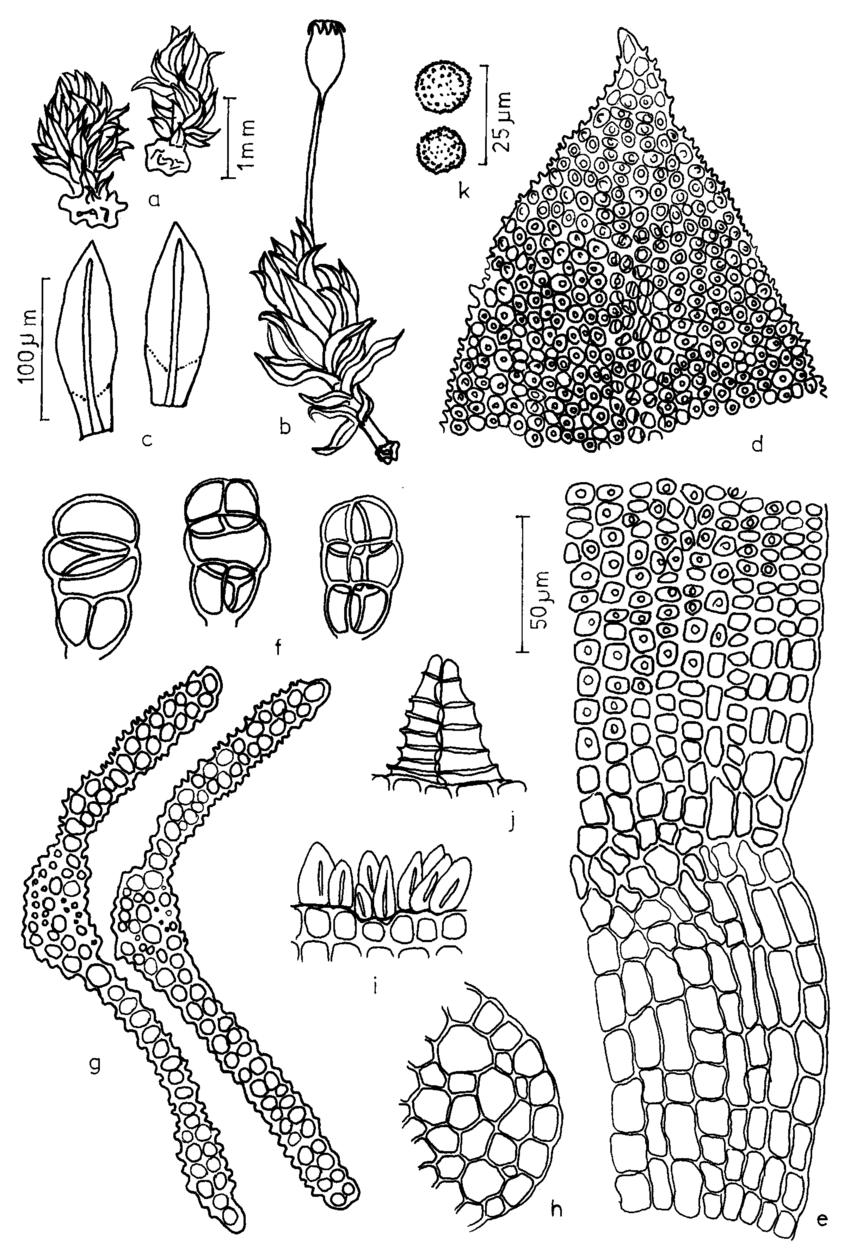
Figura-15-Uleastrum-palmicola-Muell-Hal-RH-Zander-a-b-Aspecto-geral-do.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-15-Uleastrum-palmicola-Muell-Hal-RH-Zander-a-b-Aspecto-geral-do_fig13_259822623
family, is a remarkable example of the diversity and resilience found within the world of bryophytes. Its unique morphological features, widespread distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, the study of unassuming organisms like Leucoloma molle may hold the key to unlocking new insights and understanding the intricate web of interconnections that sustain our ecosystems.
Ponder this: In a world where we often overlook the smallest of creatures, what other wonders might be hidden in plain sight, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?