Sulzbacheromyces-bicolor-holotype-a-Habit-b-Algal-cells-of-the-thallus-c.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Sulzbacheromyces-bicolor-holotype-a-Habit-b-Algal-cells-of-the-thallus-c_fig3_322509669
Meiothecium hamatulum: The Tiny Moss with a Big Story

13a6c79d18e8a89069fff5114cf64a0d.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/627689266785216639/
Introduction
When it comes to the world of mosses, Meiothecium hamatulum (Besch.) Broth., also known simply as Meiothecium, may not be a household name. But this tiny moss from the Sematophyllaceae

Baeomyces_placophyllus_Hackett_29June2012%251.jpg from: https://www.waysofenlichenment.net/lichens/Baeomyces placophyllus
family has a fascinating story to tell. In this post, we’ll dive into the details of this diminutive but captivating species.
Background on Mosses
Before we get into the specifics of M. hamatulum, let’s briefly review what mosses are. Mosses are small, non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead having structures that serve similar functions. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in diverse habitats worldwide.
Morphology and Identification
Meiothecium hamatulum is a small pleurocarpous moss, meaning its sporophytes grow laterally from the stem. Its scientific name comes from the Greek words “meion” meaning smaller and “theke” meaning a container, referring to its small capsules. The species epithet “hamatulum” means hooked, describing the curved shape of the leaves.
The key identification features of M. hamatulum include:
- Small size, typically under 1 cm tall
- Glossy, yellowish-green leaves
- Leaves curved or hooked at the tips

commonbladdermoss_RyanBatten-540×272.jpg from: http://saltspringconservancy.ca/portfolio_category/mosses/
- Capsules ovoid and inclined, with a small peristome
Global Distribution and Habitat
Meiothecium hamatulum has a pantropical distribution, found in tropical regions around the world including Central and South America, Africa, Southeast Asia, and Oceania. It grows as an epiphyte on the bark and leaves of trees and shrubs in lowland to montane tropical forests. The moss is well-adapted to high humidity and shaded conditions in these habitats.
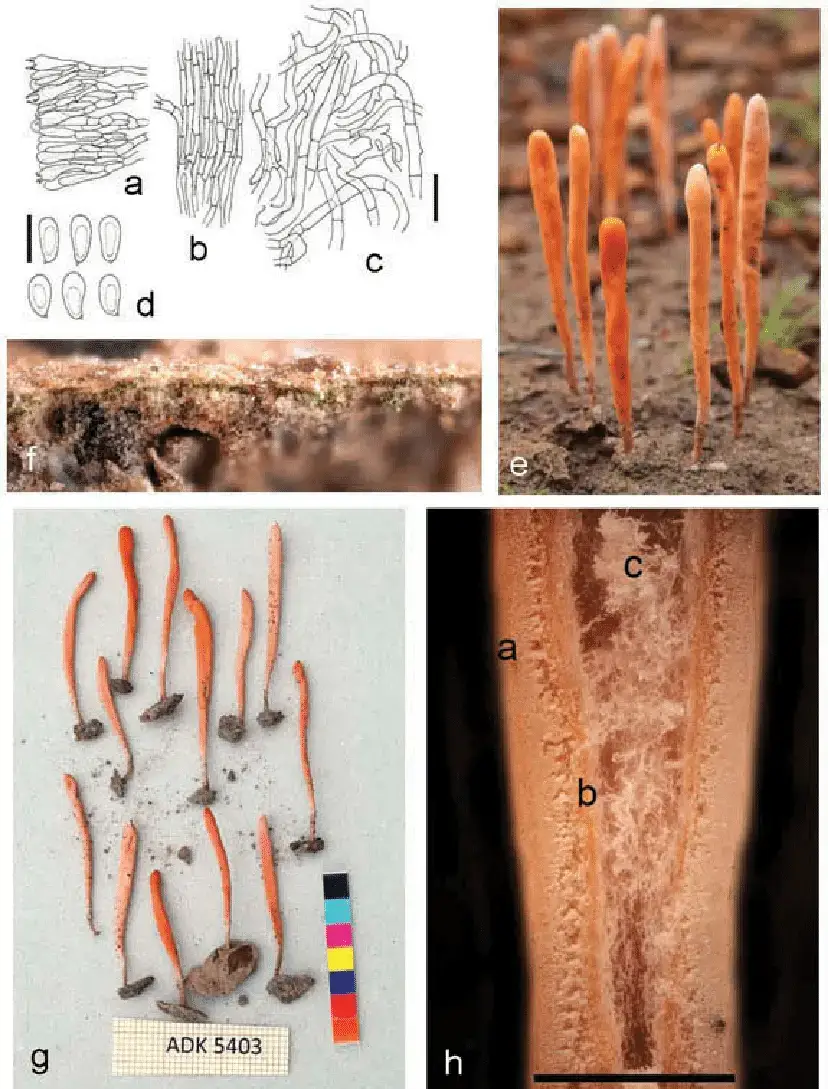

Sulzbacheromyces-miomboensis-A-De-Kesel-5403-BR-a-Auxohymenium-taken-at-half-height.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Sulzbacheromyces-miomboensis-A-De-Kesel-5403-BR-a-Auxohymenium-taken-at-half-height_fig5_322509669
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, M. hamatulum
Meiothecium%2BBORYANUM.jpg from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/02/musgos-hypnales-meiothecium-boryanum.html
plays important ecological roles:

d7ed39c024675bbf3fd0017ade44b87f.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/bf7e5eeaf8a578b6413d823dbe679935
- Helps retain moisture and prevent erosion
- Provides shelter for micro-organisms
- Serves as a bioindicator of air quality and habitat conditions
The moss has several adaptations for its epiphytic lifestyle:
- Small size allows it to grow on small substrates
- Leaves can efficiently absorb water and nutrients
- Tolerates periods of desiccation by drying out and rehydrating
Conclusion
Meiothecium hamatulum may be a tiny moss, but it has an outsized story to tell. From its distinct hooked leaves to its pantropical distribution to its ecological importance, this unassuming species is a prime example of how even the smallest organisms can hold great scientific interest.
The next time you find yourself in a tropical forest, take a closer look at the trees and shrubs around you – you just might spot a patch of Meiothecium making its quiet but vital contribution to the ecosystem. What other small but mighty mosses might be out there, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?