large.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/guide_taxa/1836776
Mielichhoferia elegans Herzog: A Fascinating Moss of the Mniaceae Family
Mielichhoferia elegans Herzog, also known simply as Mielichhoferia, is a captivating species of moss belonging to the

1621165_orig.jpg from: https://www.centralcoastbiodiversity.org/herzogiella-moss-bull-herzogiella-adscendens.html
Mniaceae family. This tiny but remarkable plant has garnered the attention of bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike for its unique characteristics and ecological significance. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of Mielichhoferia elegans Herzog and explore its morphology, distribution, habitat, and ecological roles.

5586926645_beb0cf462b_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/47945928@N02/5586926645/
Background
Mosses are small, non-vascular plants that belong to the division Bryophyta. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, contributing to moisture retention, nutrient cycling, and providing habitats for microorganisms and small invertebrates. Mielichhoferia elegans Herzog is one such moss species that has captured the interest of researchers due to its distinct features and adaptations.

2022-09-07-13-36-49.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/bryophyte-of-the-month/mielichhoferia-elongata/
Morphology and Identification
Mielichhoferia elegans Herzog is a small, acrocarpous moss, meaning it bears sporophytes at the tips of its stems. The plants form dense, compact tufts or cushions, typically measuring 1-3 cm in height. The leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a pointed apex and serrated margins. The leaf cells are elongated and thin-walled, giving the leaves a translucent appearance. The seta (stalk bearing the capsule) is slender and elongated, often reaching 1-2 cm in length. The capsules are erect and cylindrical, with a conical operculum
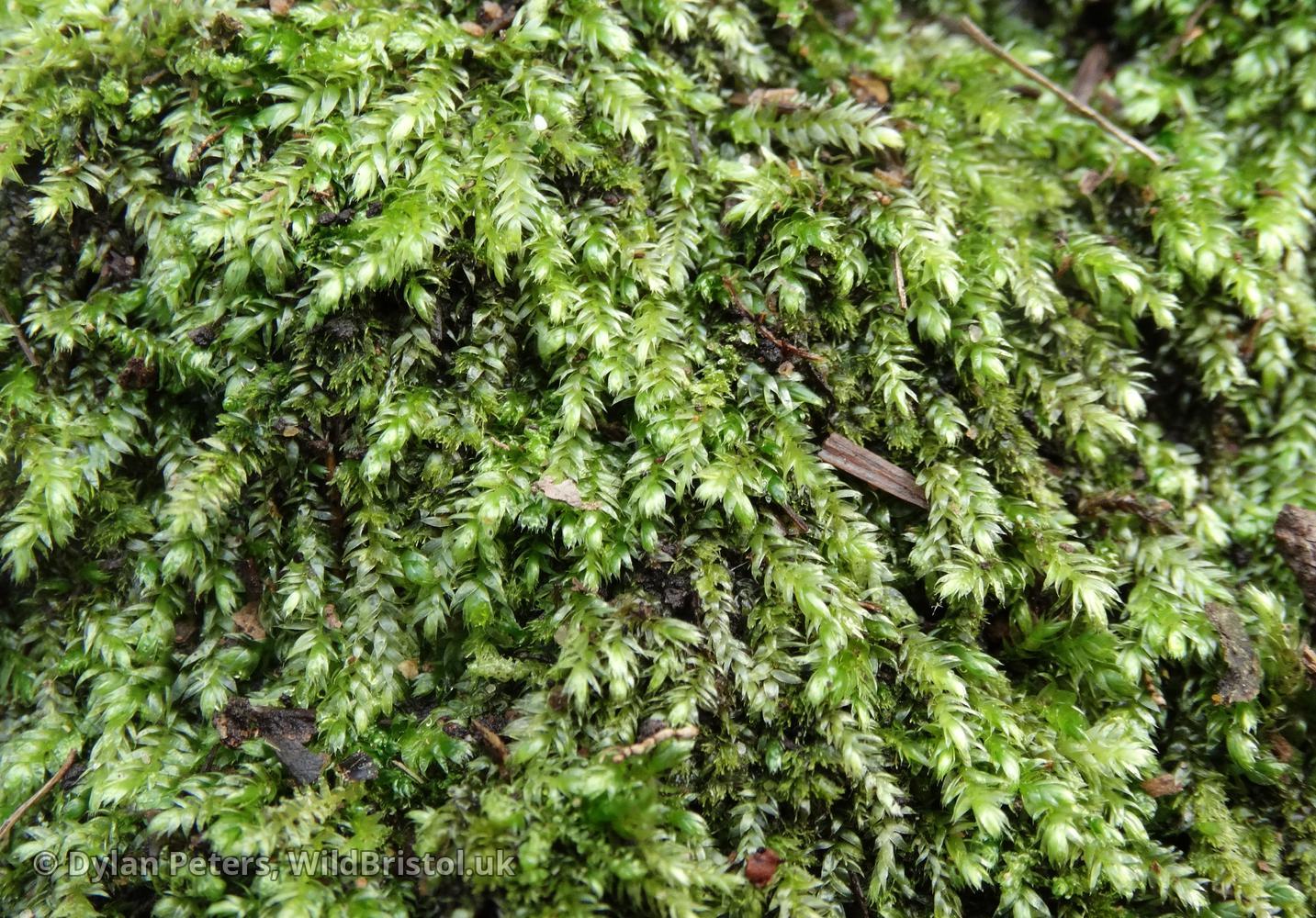

220223161130_DSC00779.JPG.full.JPG from: https://wildbristol.uk/groups/ferns-horsetails-mosses-liverworts/elegant-silk-moss/
(lid) and a peristome (toothed structure surrounding the mouth of the capsule).
Global Distribution and Habitat
Mielichhoferia elegans Herzog has a wide distribution, occurring in various regions across the globe. It can be found in Europe, Asia, North America, and South America. This moss species typically inhabits moist, shaded environments, such as rock crevices, cliff faces, and soil banks in montane forests and subalpine areas. It often grows in calcareous substrates, thriving in limestone and dolomite regions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Mielichhoferia elegans Herzog plays significant ecological roles in its habitats. As a
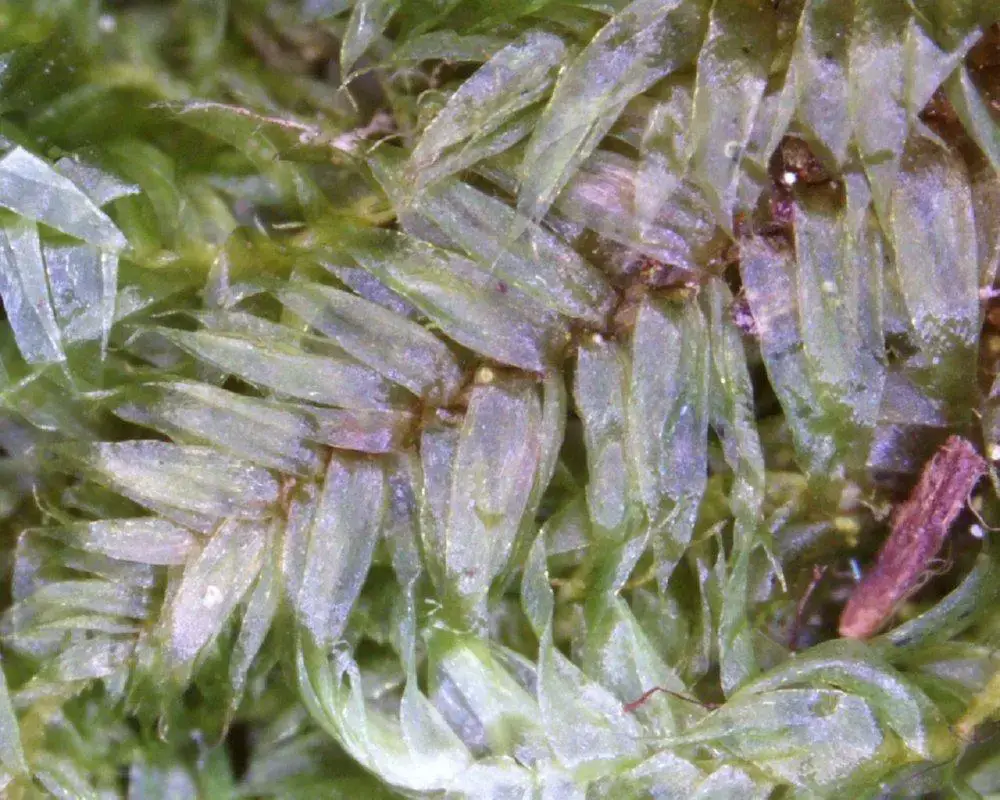

Pseudotaxiphyllum-elegans-shoot-tip-1.jpg from: http://blogs.ubc.ca/biology321/?page_id=977
pioneer species, it colonizes bare rock surfaces and contributes to the formation of soil by trapping organic matter
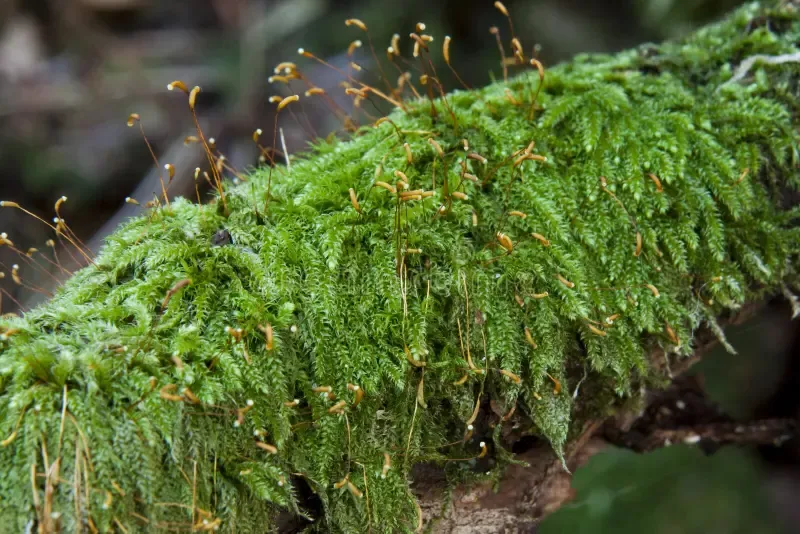

seligers-herzogiella-moss-herzogiella-seligeri-seligers-herzogiella-moss-herzogiella-seligeri-seligers-herzogiella-moss-old-267237873.jpg from: https://www.dreamstime.com/photos-images/seligers.html
and facilitating the growth of other plant species. Its dense tufts help in moisture retention and prevent soil erosion. Additionally, Mielichhoferia elegans Herzog serves as a
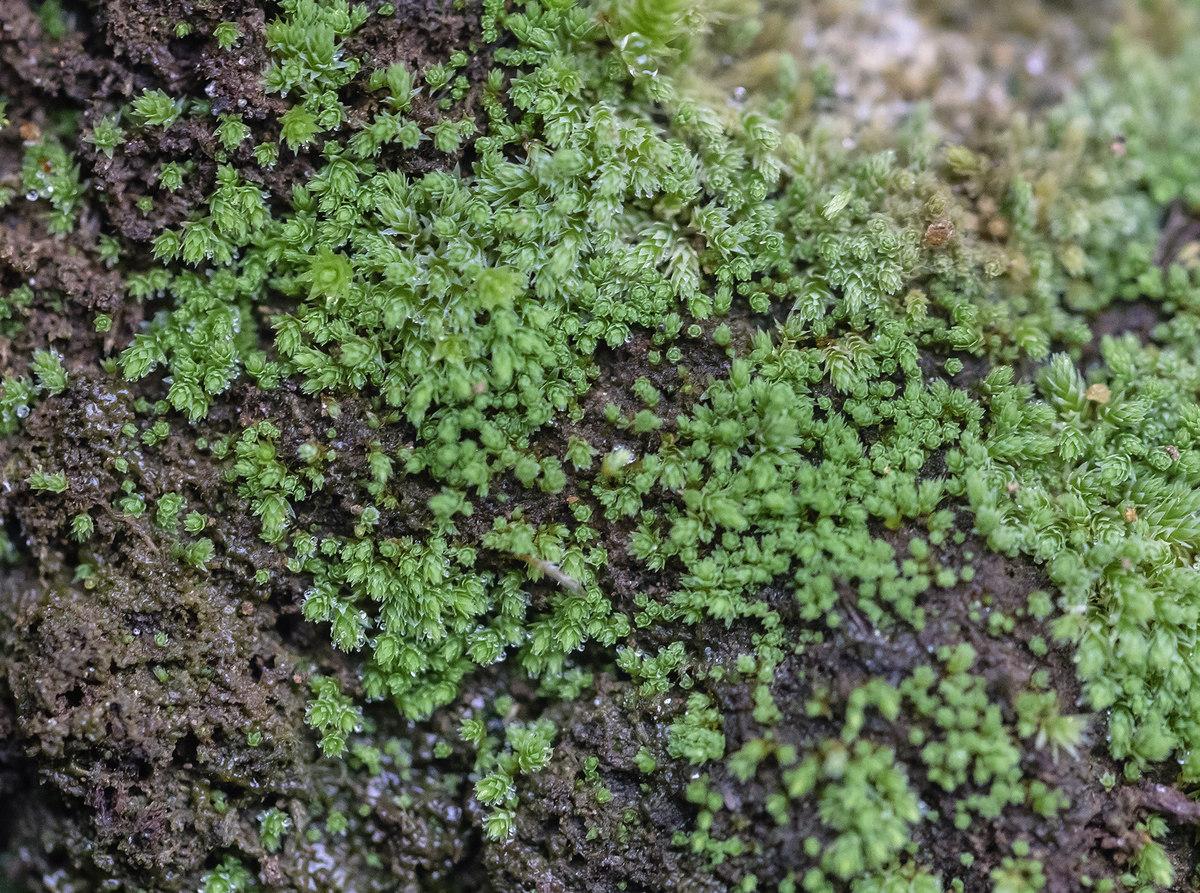

9383.jpg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=13070

3fc87660ab853b20bc330a658e746d94.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.ca/pin/xanthoria-elegans–312366924138785860/
microhabitat for various invertebrates and microorganisms, promoting biodiversity in its ecosystems.
This moss species has developed adaptations to thrive in its specific habitats. Its compact growth form and dense tufts help in minimizing water loss and protecting against desiccation. The elongated leaf cells and thin cell walls enhance water absorption and retention. Furthermore, the erect capsules and peristome teeth facilitate spore dispersal by wind, enabling the moss to colonize new areas effectively.

0231.jpeg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=8820
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Plant height | 1-3 cm |
| Leaf shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf apex | Pointed |
| Leaf margins | Serrated |
| Leaf cells | Elongated, thin-walled |
| Seta length | 1-2 cm |
| Capsule shape | Erect, cylindrical |
| Operculum | Conical |
| Peristome | Present |
Conclusion
Mielichhoferia elegans Herzog is a fascinating moss species that exemplifies the remarkable adaptations and ecological significance of bryophytes. Its distinct morphology, wide distribution, and pioneering nature make it a subject of interest for bryologists and nature enthusiasts. As we continue to study and appreciate the intricate world of mosses, Mielichhoferia elegans Herzog reminds us of the vital roles these tiny plants play in maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystems. So, the next time you come across a lush, green carpet of moss, take a closer look—you might just be in the presence of the captivating Mielichhoferia elegans Herzog.