A-B-Cylindrical-papilla-in-Callicostellopsis-meridensis-Muell-Hal-Broth-A-Immature.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-B-Cylindrical-papilla-in-Callicostellopsis-meridensis-Muell-Hal-Broth-A-Immature_fig1_261698068
Mielichhoferia emergens: The Marvelous Moss of the Mniaceae Family
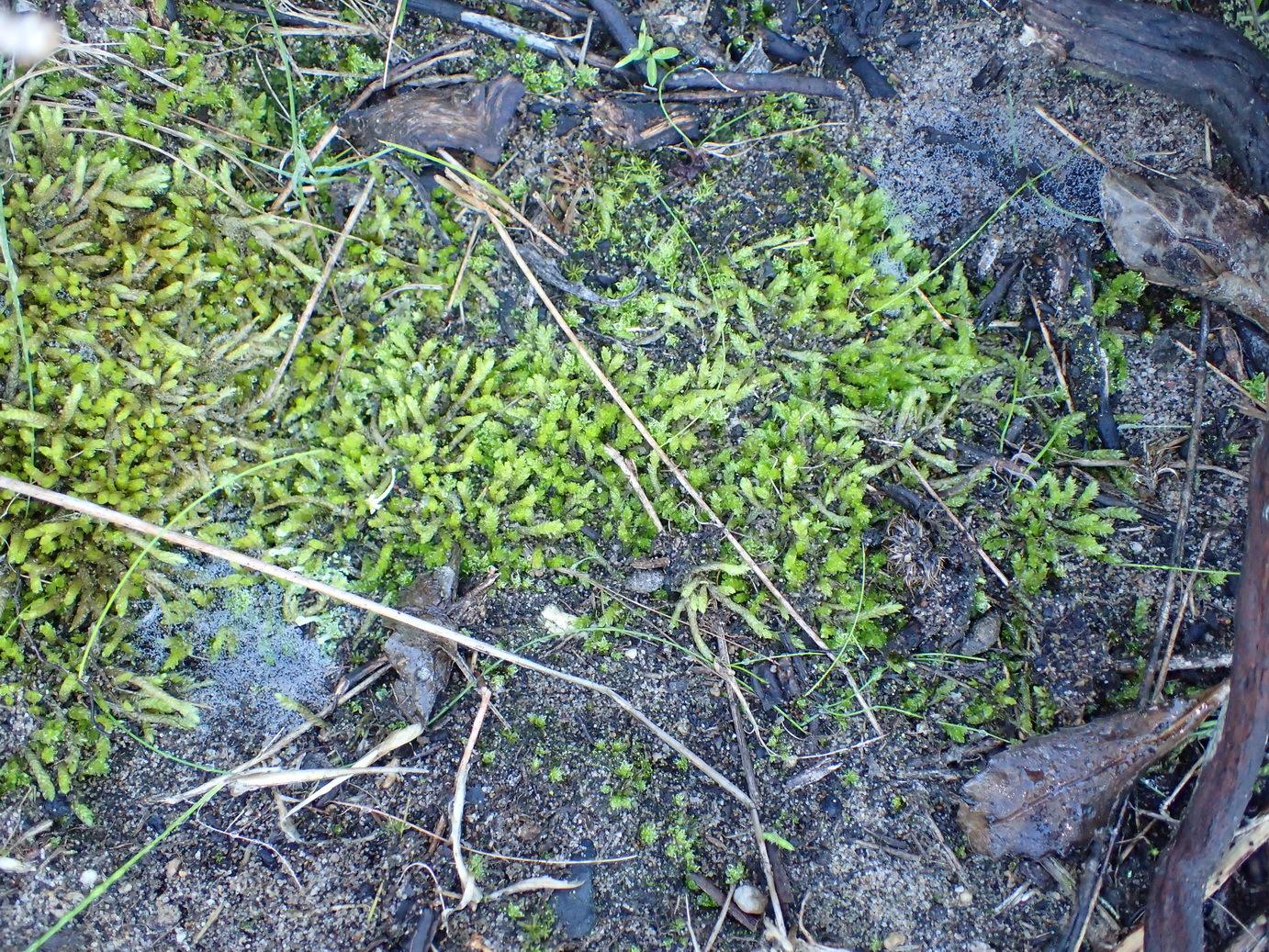

original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552
Introduction
Mosses may be small, but they play a big role in many ecosystems around the world. One particularly fascinating species is Mielichhoferia emergens (Müll.Hal.) Broth., also known simply as Mielichhoferia. This moss of the Mniaceae family has some unique characteristics that make it stand out in the world of bryophytes. Let’s take a closer look at this marvelous little plant!
Background on Mosses
Before diving into the specifics of M. emergens, it’s helpful to understand a bit about mosses in general. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead having structures that serve similar functions. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in a wide range of habitats worldwide.
Morphology and Identification
Mielichhoferia emergens is a small, tufted moss. Its stems reach about
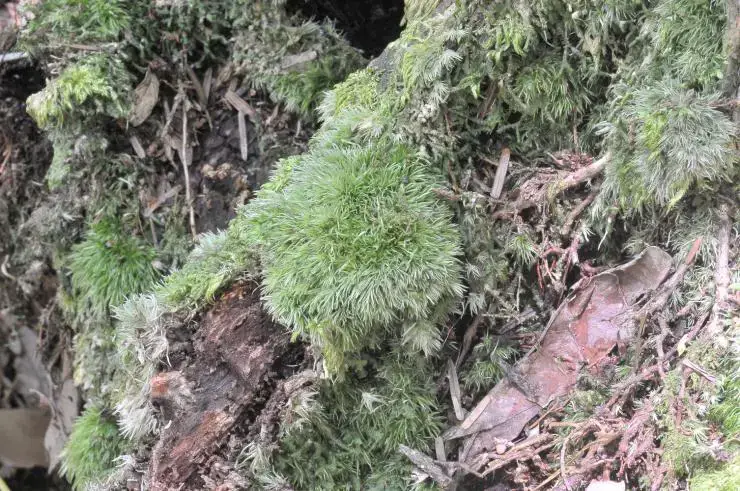

7037e79d418c961c5141889e083833ce.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/2355523fe7d6b11d4b7a8ac495911fd7
1-2 cm tall. The leaves are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and have a single costa (midrib). Leaf margins are entire or slightly toothed near the apex.
One of the most distinctive features of M. emergens is its capsule morphology. The capsules are held on long setae (stalks) and are pyriform (pear-shaped) when young, becoming urceolate (urn-shaped) with age. Capsules have a well-developed peristome, a ring of tooth-like structures surrounding the opening.
Global Distribution and Habitat
M. emergens has a widespread but scattered distribution. It is found in Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. This species typically grows on damp, acidic rocks like granite and sandstone, often near streams or in sheltered crevices. It is a pioneer species, one of the first to colonize bare rock surfaces.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, M. emergens plays important roles in its ecosystem:
- Erosion control: Moss mats help stabilize soil and prevent erosion.
- Water retention: Mosses act like sponges, absorbing and slowly releasing water.
- Habitat for micro-organisms: Many tiny invertebrates make their homes among moss stems and leaves.
M. emergens has several adaptations that allow it to thrive in its rocky habitat:
- Desiccation tolerance: This moss can survive periods of drying out, rehydrating when moisture is available again.
- Spore dispersal: The elevated capsules help shoot spores far from the parent plant to colonize new areas.
- Acid tolerance: M. emergens can grow on acidic substrates that other plants struggle with.
Conclusion
Mielichhoferia emergens may be a small and inconspicuous plant, but it has a fascinating biology and plays an important ecological role. Its unique capsule morphology, pioneer nature, and adaptations to harsh environments make it a marvelous moss indeed! Next time you’re out in nature, take a moment to appreciate the miniature world of mosses at your feet. You never know what wonders you might discover!