Nardia_feuille.jpg from: https://bryologiewallonie.blogspot.com/2022/07/nardia-insecta-lindb.html
Introduction
The world of mosses is a fascinating and often overlooked realm, home to a diverse array of species that play crucial roles in various ecosystems. Among these unsung heroes is the Nardia breidleri (Limpr.) Lindb., a member of the Gymnomitriaceae family, commonly known as Nardia. This unassuming moss may appear small, but its significance in the natural world is anything but insignificant.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Nardia breidleri, it’s essential to understand the broader context of mosses. These diminutive plants belong to the division Marchantiophyta, also known as the Bryophytes. Within this division, the class Jungermanniopsida encompasses the leafy liverworts, including the Gymnomitriaceae family, to which our subject belongs.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
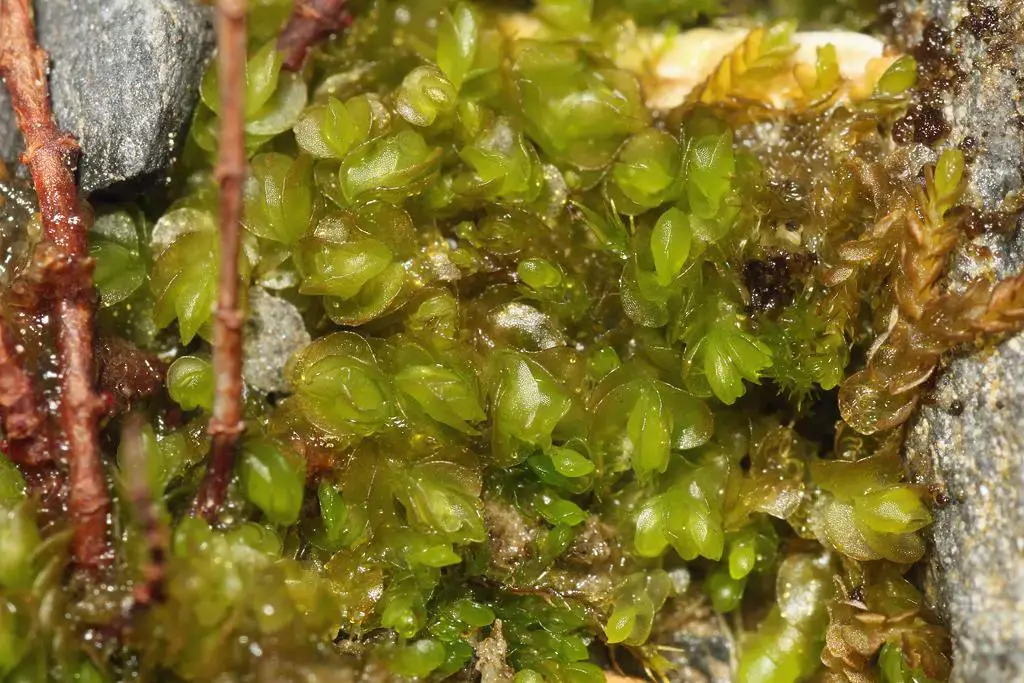

Nardia+scalaris+11jul11+%25282a%2529.jpg from: https://moonmoths.blogspot.com/2011/07/brechfa-forest-bryos.html
Nardia breidleri is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions. Its stems are slender and irregularly branched, with overlapping leaves arranged in two rows. The leaves themselves are deeply divided into two or three lobes, giving the plant a distinctive appearance. When viewed under a microscope, the leaf cells reveal intricate patterns and structures that aid in identification.

drepanocladus-lycopodioides.jpg from: https://www.iucn.org/our-union/commissions/group/iucn-ssc-bryophyte-specialist-group
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a widespread distribution, found across various regions of the Northern Hemisphere, including Europe, Asia, and North America. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often growing on decaying logs, stumps, or soil in coniferous and mixed forests. Nardia breidleri is particularly fond of areas with high humidity and cool temperatures, making it a common sight in boreal and montane ecosystems.
Brachythecium-acuminatum-Hedw-Aust-A-Dry-plant-6-B-Wet-plant-6-C-D_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Brachythecium-curtum-Lindb-Limpr-A-Dry-Plant-5-B-Wet-Plant-5-C-E-Stem_fig4_238738619
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Nardia breidleri plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide shelter and moisture for a variety of invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.

Pohlia-lutescens-Limpr-H-Lindb-KTUB-1608-A-habit-B-shoot-wet-C-leaf-D-F_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Distribution-map-of-Astragalus-turkmenensis-and-A-physodes-subsp-acikirensis-in_fig2_238073109
One of the remarkable adaptations of Nardia breidleri is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. During dry spells, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, demonstrating its resilience in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest, researchers found that Nardia breidleri played a crucial role in the recovery of forest ecosystems after disturbances such as logging or wildfires. Its ability to rapidly colonize disturbed areas and create a suitable microclimate facilitated the establishment of other plant species, accelerating the process of forest regeneration.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Gymnomitriaceae |
| Genus | Nardia |
| Species | Nardia breidleri (Limpr.) Lindb. |
| Common Name | Nardia |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Two rows, overlapping |
| Leaf Shape | Deeply divided into 2-3 lobes |
Conclusion
The Nardia breidleri (Limpr.) Lindb., a humble moss of the Gymnomitriaceae family, may be small in stature, but its impact on the natural world is profound. From stabilizing soil and facilitating forest regeneration to providing shelter for countless organisms, this unassuming plant plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us not overlook the importance of these tiny, yet mighty, mosses. Who knows what other secrets and marvels they may hold, waiting to be discovered?