
medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/404140-Neohodgsonia-mirabilis
Neohodgsonia mirabilis: The Marvelous Moss
Introduction
Neohodgsonia mirabilis (Perss.) Perss., commonly known as Neohodgsonia, is a fascinating species of moss belonging to the Neohodgsoniaceae family. This unique moss has captured the attention of botanists and enthusiasts alike due to its distinctive morphology and ecological adaptations. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of Neohodgsonia and explore what makes it so marvelous.
Background
Neohodgsonia mirabilis is a species of Marchantiophyta, also known as liverworts and mosses, in the class Marchantiopsida. It was first described by the botanist Persson in 1954. The specific epithet “mirabilis” means “wonderful” or “marvelous” in Latin, reflecting the unique characteristics of this moss.
Morphology and Identification
One of the most striking features of Neohodgsonia is its thalloid gametophyte. Unlike many other mosses that have leafy stems, Neohodgsonia has a flattened, ribbon-like thallus. The thallus is typically

150px-Carpocephala_of_Neohodgsonia.jpg from: https://sv.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neohodgsonia_mirabilis
1-3 cm long and 2-5 mm wide, with a smooth, glossy surface. The underside of the thallus bears rhizoids, which are root-like structures that help the moss anchor itself to the substrate and absorb water and nutrients.
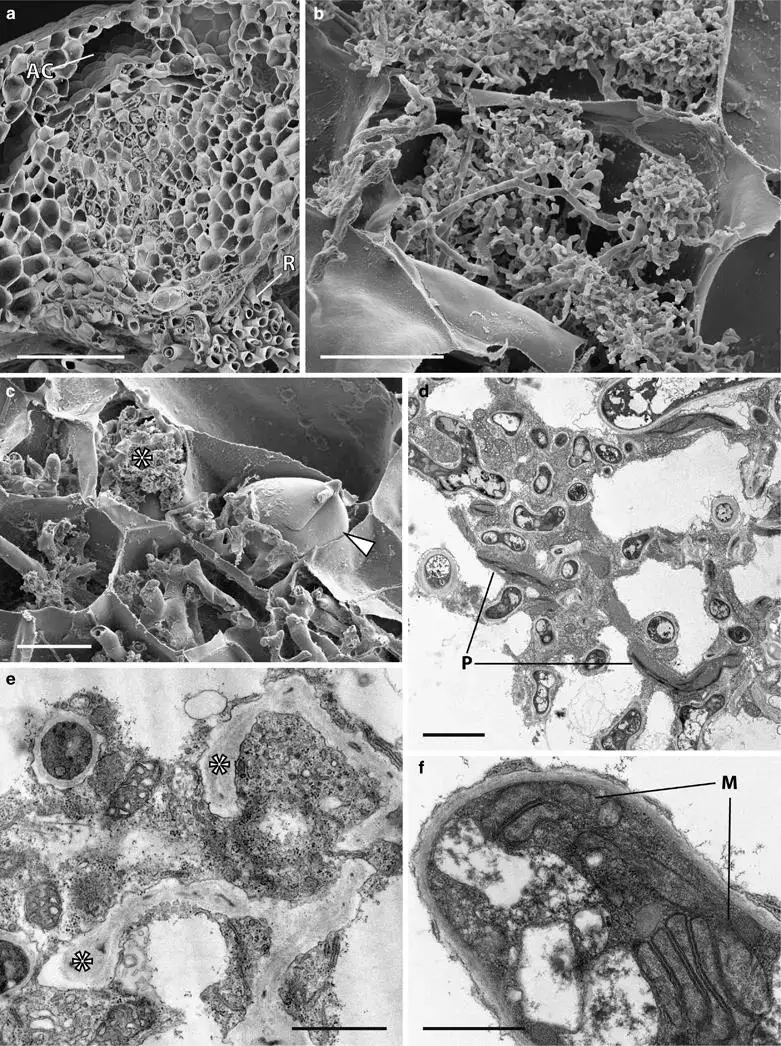
Cytology-of-Neohodgsonia-mirabilis-grown-at-440-and-1500-ppm-aCO2-Scanning-a-c.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Cytology-of-Neohodgsonia-mirabilis-grown-at-440-and-1500-ppm-aCO2-Scanning-a-c_fig4_284732877

how-to-get-rid-of-moss-in-lawns-2132201-hero-76e05f2164224eefba1a55518b1751ea.jpg from: https://www.thespruce.com/how-to-get-rid-of-moss-in-lawns-2132201
Neohodgsonia is dioicous, meaning that male and female reproductive structures are found on separate plants. The antheridia (male structures) are borne on short, upright branches, while the archegonia (female structures) are embedded in the thallus. After fertilization, the sporophyte develops, consisting of a capsule on a short seta (stalk). The capsule is spherical and cleistocarpous, meaning it lacks a lid and opens irregularly to release the spores.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Neohodgsonia mirabilis has a widespread but scattered distribution, occurring in Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. It is found in a variety of habitats, including moist, shaded rocks, cliffs, and soil banks in temperate and subtropical regions. Neohodgsonia often grows in association with other bryophytes and can form extensive mats in suitable conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
As a bryophyte, Neohodgsonia plays important ecological roles in its habitats. It contributes to nutrient cycling,

An-inconspicuous-moss-endemic-to-sub-Antarctic-Patagonia-T-mirabilis-Photograph-Omora.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/An-inconspicuous-moss-endemic-to-sub-Antarctic-Patagonia-T-mirabilis-Photograph-Omora_fig1_235920490
water retention, and soil stabilization. The dense mats formed by Neohodgsonia can provide shelter and microhabitats for various invertebrates.
Neohodgsonia has several adaptations that enable it to thrive in its environments. The thalloid gametophyte

gettyimages-148286269.jpg from: https://www.newscientist.com/article/2101032-without-oxygen-from-ancient-moss-you-wouldnt-be-alive-today/
allows for efficient water and nutrient uptake, while the rhizoids help anchor the plant to the substrate. The cleistocarpous capsule is an adaptation for spore dispersal in moist conditions, as the spores are released gradually over time rather than all at once.

52312541018_d63f07e644_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/nickadel/52312541018/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Neohodgsoniaceae |
| Genus | Neohodgsonia |
| Species | N. mirabilis |
| Gametophyte | Thalloid, 1-3 cm long, 2-5 mm wide |
| Sporophyte | Spherical, cleistocarpous capsule on short seta |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded rocks, cliffs, and soil banks |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, Africa, Americas |
Conclusion
Neohodgsonia mirabilis is a marvelous moss that showcases the incredible diversity and adaptations of bryophytes. Its unique morphology, widespread distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject for study and appreciation. The next time you find yourself in a moist, shaded habitat, keep an eye out for this remarkable moss and ponder the wonders of the often-overlooked world of bryophytes. What other secrets might these tiny plants hold?

52311430457_ab50dcf2b5_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/nickadel/52311430457/

plagiomnium-venustrum1.jpg from: https://blogs.ubc.ca/salmonberry/walkin-in-the-woods/
Medusa_detta_Spira-Mirabilis.jpg from: https://pressitalia.net/2016/08/spira-mirabilis.html