Oligotrichum-nepalense-GLSm-A-Habit-dry-B-Stem-leaf-in-ventral-view-C-Stem.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Oligotrichum-nepalense-GLSm-A-Habit-dry-B-Stem-leaf-in-ventral-view-C-Stem_fig5_326282845
Exploring the Fascinating World of Oligotrichum austroaligerum G.L.Sm. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are small but mighty plants that play important roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Oligotrichum austroaligerum G.L.Sm., a moss in the Polytrichaceae family. Also known simply as Oligotrichum, this moss has some unique characteristics worth exploring. Let’s dive in and learn more about this fascinating bryophyte!
Background on Mosses
Before we get into the specifics of Oligotrichum austroaligerum, it’s helpful to understand some basics about mosses in general:
- Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta
- They lack true roots, stems, and leaves like other land plants
- Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds
- They play key roles in nutrient cycling, water retention, and providing habitat for other organisms
Now that we have that background, let’s focus on our star species.
Morphology and Identification
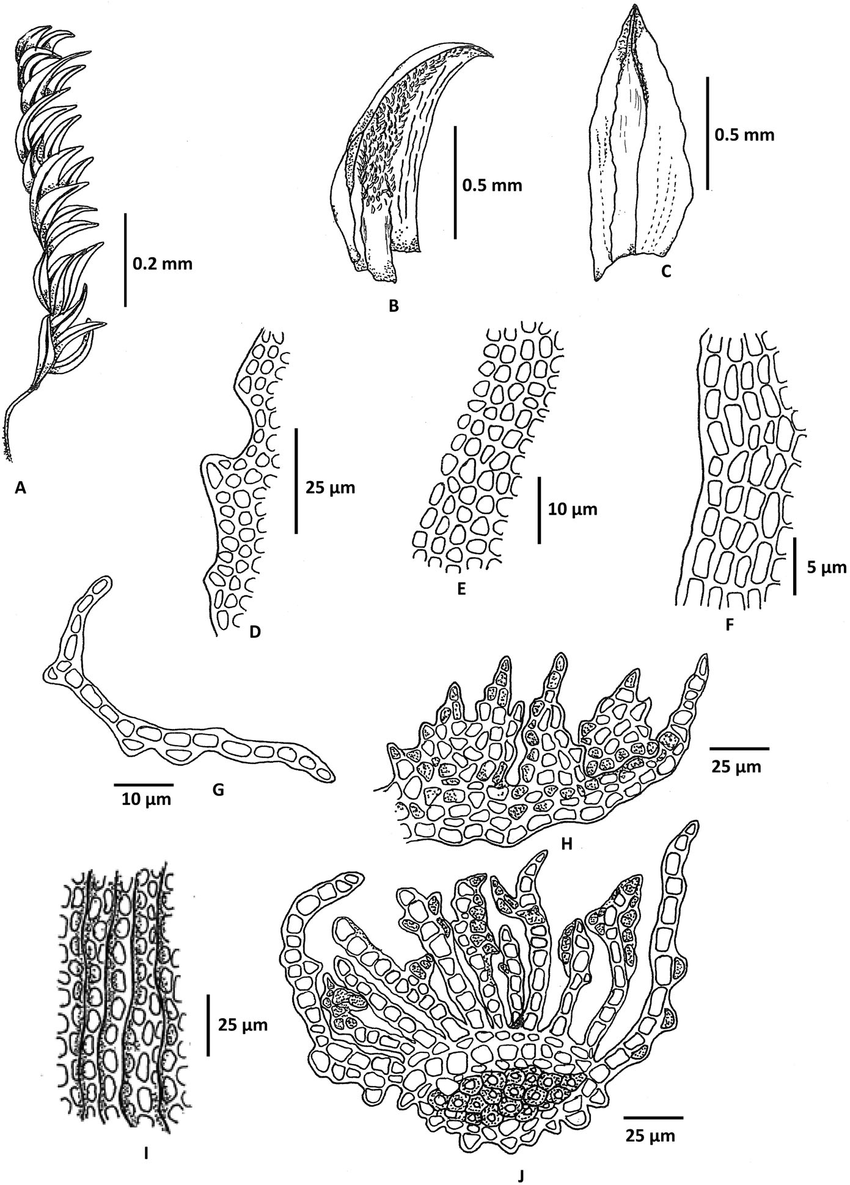
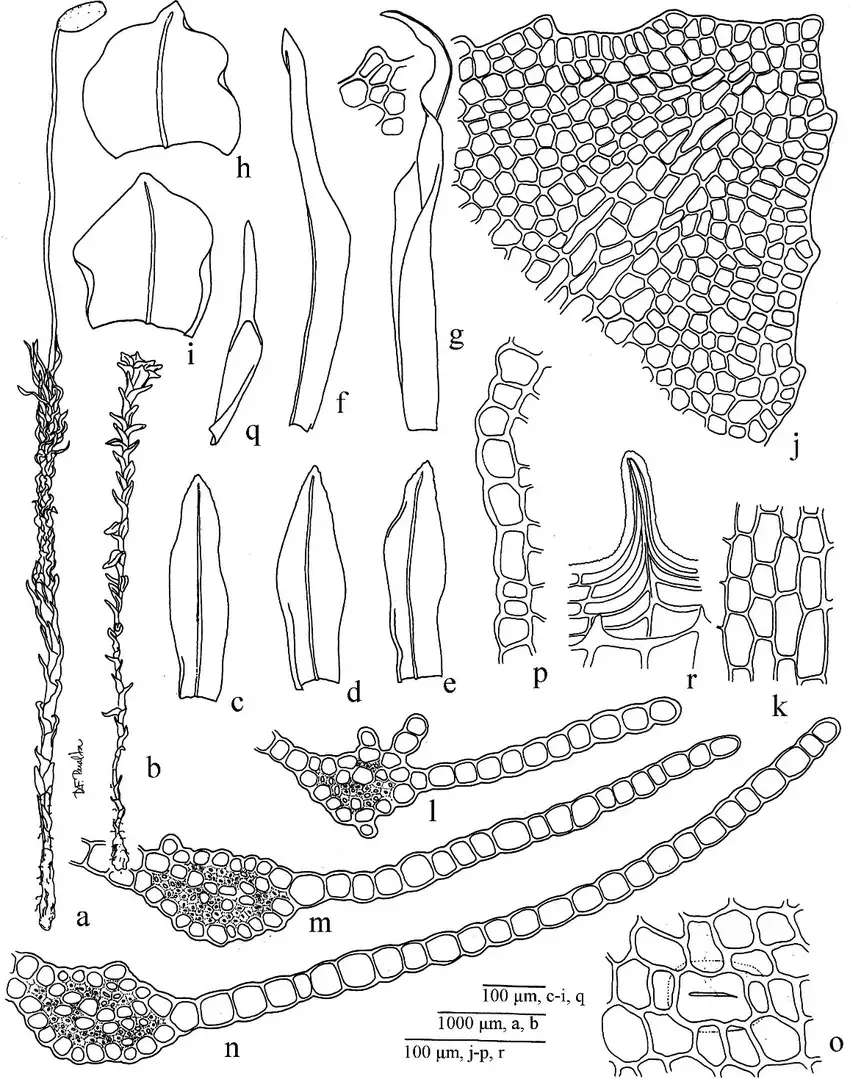
Oligotrichum austroaligerum is a acrocarpous moss, meaning it has upright growth and its sporophytes develop at the tips of the stems. Some key identifying features include:
- Stems are usually unbranched and grow up to 2-3 cm tall
- Leaves are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and have toothed margins near the tips
- Leaf midribs are broad and extend to the leaf tips
- Lamellae (ridges of photosynthetic tissue) are present on the upper leaf surface

10980708275_f71ed608c8_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/109460077@N08/10980708275/
moss-diagram.jpg from: https://www.myxxgirl.com/beautiful/moss-anatomy-diagram-plantas-musgo-beautiful.htm
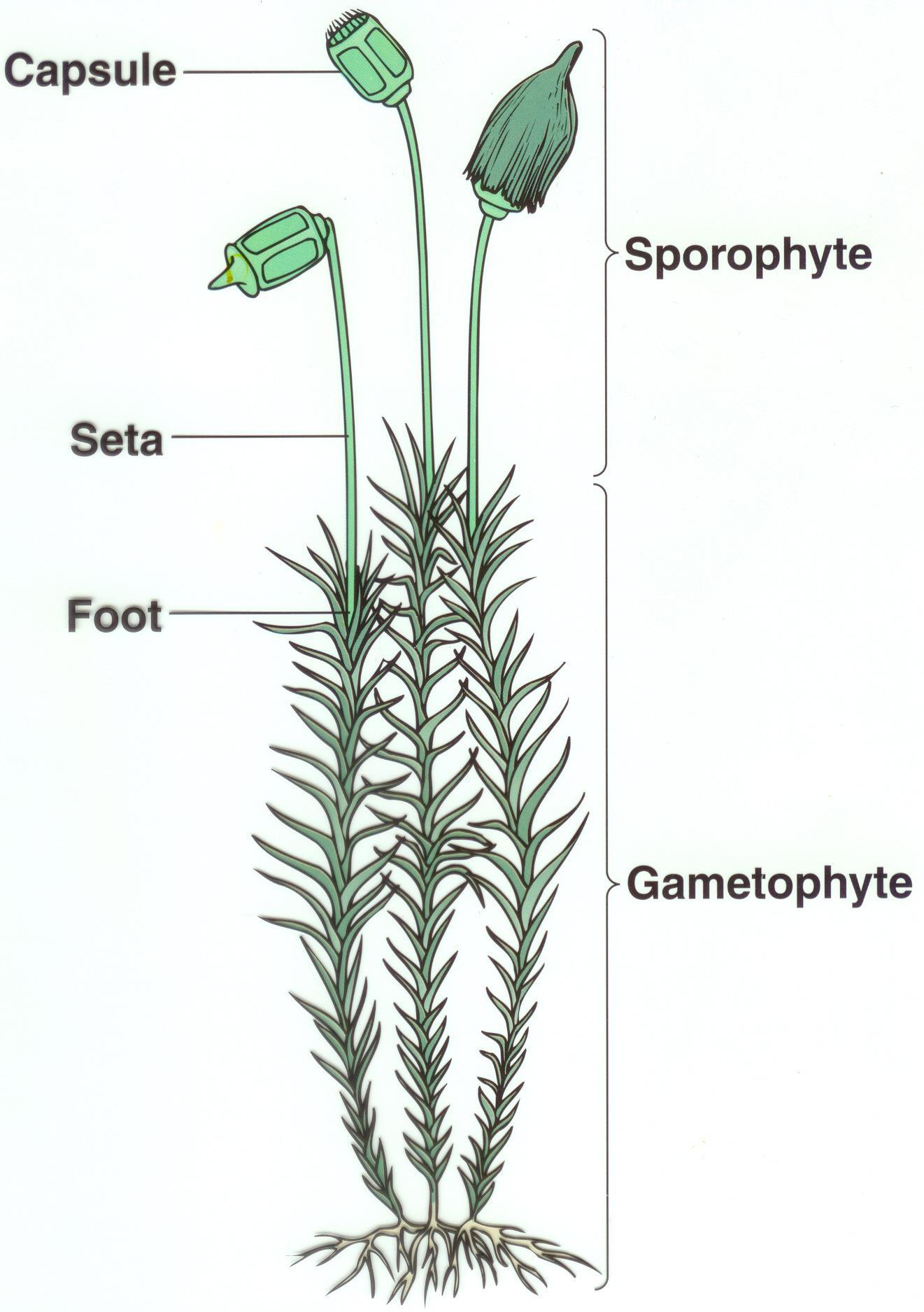
- Capsules (spore-bearing structures) are cylindrical and borne on
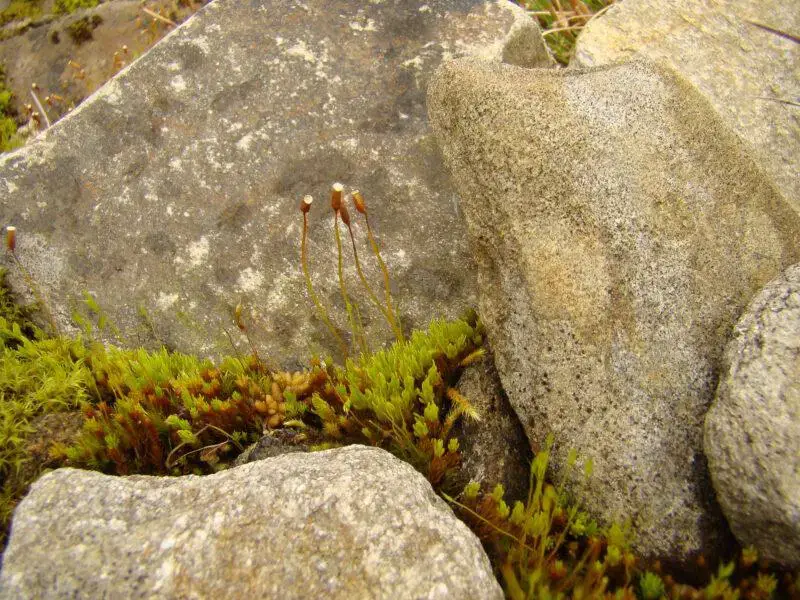

Oligotrichum-hercynicum-female-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/oligotrichum-hercynicum/
setae (stalks) up to 2 cm long
With its distinct appearance, Oligotrichum is not easily confused with other mosses, especially when the capsules are present.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Oligotrichum austroaligerum has a subantarctic distribution, found in the southern parts of South America, Australia, and New Zealand. It grows on soil or rock in open habitats, often in alpine or subalpine areas.
Some of the specific locations where this moss has been documented include:
Oligotrichum-denudatum-a-Female-gametophyte-b-Male-gametophyte-c-e-Leaves-f-g.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Oligotrichum-denudatum-a-Female-gametophyte-b-Male-gametophyte-c-e-Leaves-f-g_fig5_232670414

Sheet20Moss20Light20Green20CH20Bunch201-scaled-1-1200×1200.jpg from: https://wholesale.bynaturedesign.ca/product/sheet-moss-dried/

200155.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/433975
| Region | Country/Island | Elevation Range |
|---|---|---|
| South America | Argentina, Chile | 500-1500 m |
| Australia | Australian Alps | 1400-2200 m |
| New Zealand | South Island | 800-1800 m |
As you can see, Oligotrichum prefers high-elevation, mountainous environments in the southern hemisphere.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Oligotrichum austroaligerum plays important roles in its ecosystems:
- Helps retain moisture and prevent soil erosion

Oligotrichum-crossidioides-PCChen-TLWan-ex-WXXu-RLXiong-A-Habit-moist.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Oligotrichum-crossidioides-PCChen-TLWan-ex-WXXu-RLXiong-A-Habit-moist_fig1_326282845
- Provides microhabitats for invertebrates and other small organisms
- Participates in nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter
- Acts as a pioneer species, colonizing bare ground after disturbances
To survive in its often harsh habitats, Oligotrichum has several adaptations:
- Thick cell walls to prevent water loss and provide structural support
- Lamellae to increase surface area for photosynthesis
- Ability to dry out and rehydrate quickly to tolerate periods of drought
- Production of secondary compounds that may deter herbivores or have antimicrobial properties
These traits allow Oligotrichum to thrive in environments where many other plants cannot.
Conclusion
From its distinct morphology to its important ecological roles, Oligotrichum austroaligerum is a truly remarkable moss. Its adaptations allow it to survive in challenging mountain habitats, where it helps shape the environment for other species.
Next time you’re hiking in the subantarctic mountains, keep an eye out for this small but mighty plant! And consider this: what other secrets might the miniature world of mosses hold? The more we study these ancient and important plants, the more we realize how much there is still to discover.

Oligotrichum-falcatum-Steere-A-Habit-dry-B-Habit-moist-showing-innovation-C.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Oligotrichum-falcatum-Steere-A-Habit-dry-B-Habit-moist-showing-innovation-C_fig4_326282845

oligotrichum_gay.jpg from: https://musgosdechile.cl/oligotrichum.html