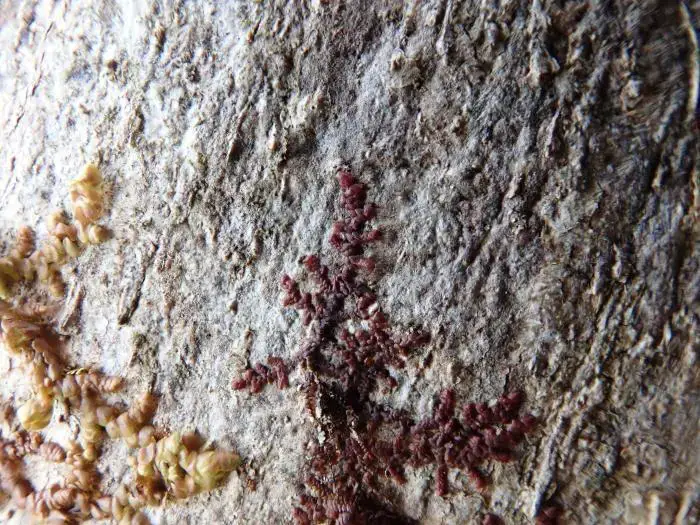

frullania-microphylla-t00376-68.jpg from: https://azoresbioportal.uac.pt/pt/especies-dos-acores/frullania-microphylla-11835/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Frullania seriata Gottsche ex Steph. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the
206983.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6679
Frullaniaceae family. Often referred to simply as Frullania, this diminutive yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s embark on an engaging journey to unravel the secrets of this intriguing species.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Frullania seriata, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. Belonging to the division
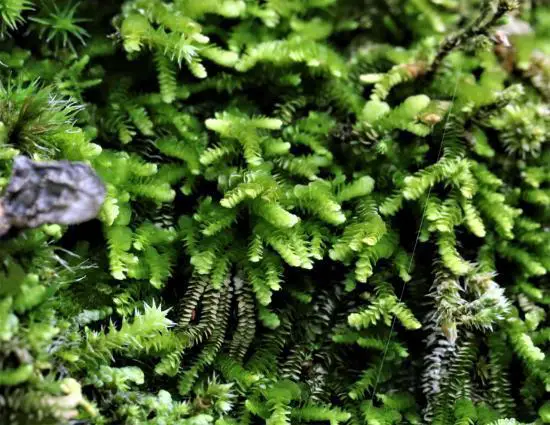

38875045.jpeg from: https://www.yclky.net/productinfo/1713539.html
Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida, Frullania seriata is a true marvel of nature.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Frullania seriata is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the surfaces it inhabits. Its delicate, flattened stems are adorned with overlapping leaves arranged in two rows, giving it a distinctive feathery appearance. The leaves themselves are intricately divided, with each lobe further subdivided into smaller segments, creating a lacy pattern that is both intricate and visually striking.
One of the most remarkable features of Frullania seriata is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. During the sexual reproductive cycle, it produces tiny, urn-shaped capsules that release spores, ensuring the propagation of the species. Asexually, it can also spread through fragmentation, allowing small pieces of the moss to establish new colonies.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Frullania seriata is widely distributed across various regions of the world, thriving in both temperate and tropical climates. It can be found growing on tree bark, rocks, and even soil, showcasing its adaptability to different substrates. This moss prefers moist and shaded environments, often inhabiting forests, woodlands, and other areas with high humidity levels.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Frullania seriata plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to the overall biodiversity of the area and serves as a microhabitat for various tiny organisms, such as tardigrades and mites. Additionally, its ability to absorb and retain moisture helps regulate the local microclimate, creating a favorable environment for other plant and animal species.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Frullania seriata is its tolerance to desiccation. During periods of drought, it can enter a dormant state, curling up its leaves to minimize water loss. Once favorable conditions return, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered a thriving population of Frullania seriata growing on the bark of ancient Douglas fir trees. This moss played a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of the forest ecosystem, providing a habitat for various invertebrates and contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Frullania seriata Gottsche ex Steph. |
| Family | Frullaniaceae |
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Two rows, overlapping |
| Leaf Shape | Divided into lobes and segments |
| Reproduction | Sexual (spores) and asexual (fragmentation) |
| Habitat | Tree bark, rocks, soil |
| Distribution | Widespread in temperate and tropical regions |
Conclusion
The Frullania seriata Gottsche ex Steph. moss, a member of the Frullaniaceae family, is a true marvel of nature that deserves our appreciation and admiration. Its intricate morphology, adaptations, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study for moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike. As we continue to explore the intricate world of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and preserve these often-overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems?