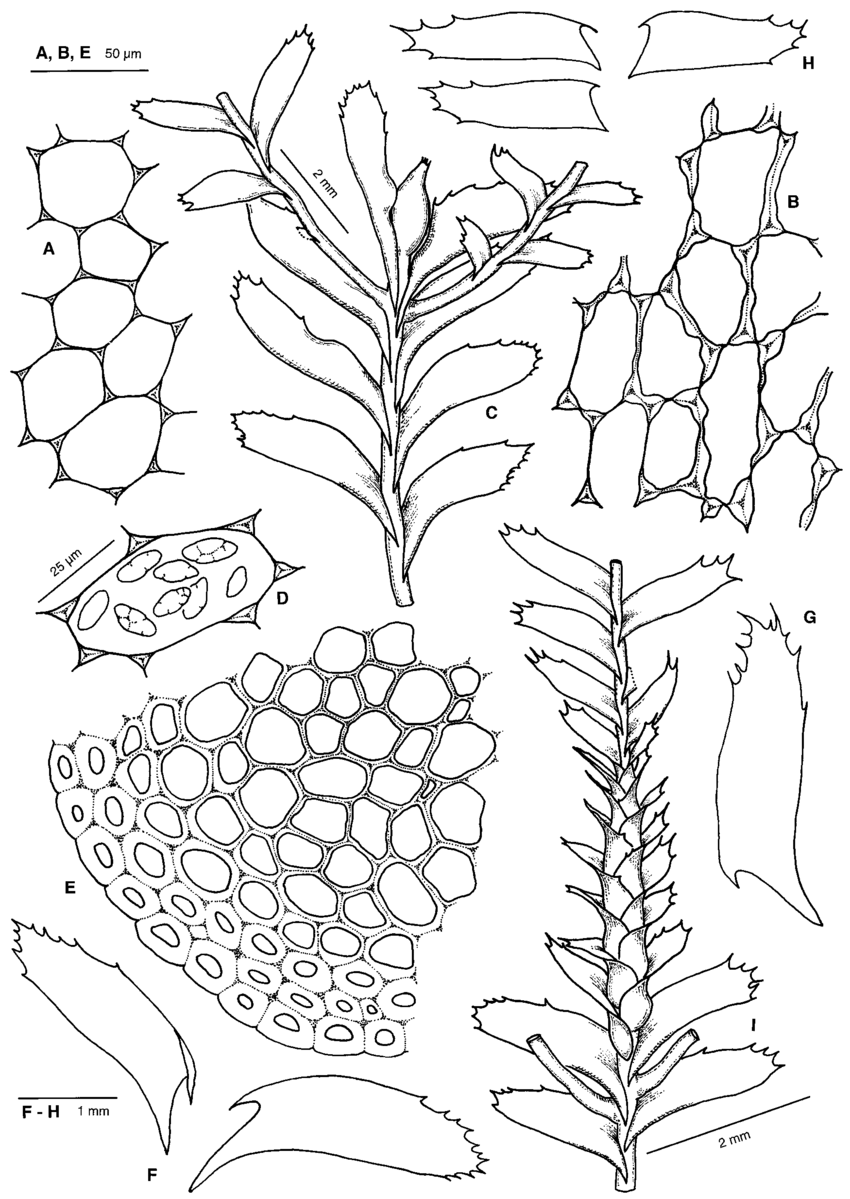
Plagiochila-rutilans-Lindenb-var-rutilans-A-B-Cells-from-center-of-upper-leaf.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plagiochila-rutilans-Lindenb-var-rutilans-A-B-Cells-from-center-of-upper-leaf_fig1_232669371
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Plagiochila frondescens var. rigida (Nees) Lindenb., commonly known as Plagiochila, stands out as a remarkable member of the Plagiochilaceae family. This unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide, offering a glimpse into the intricate beauty and resilience of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification.

Plagiochila-frondescens-a-Habit-b-Leaf-c-Leaf-cell.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plagiochila-frondescens-a-Habit-b-Leaf-c-Leaf-cell_fig1_337031290
Plagiochila frondescens var. rigida (Nees) Lindenb. belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida, which encompasses a diverse array of liverworts and mosses. These bryophytes play a crucial role in various ecosystems, serving as indicators of environmental health and contributing to the intricate web of life.
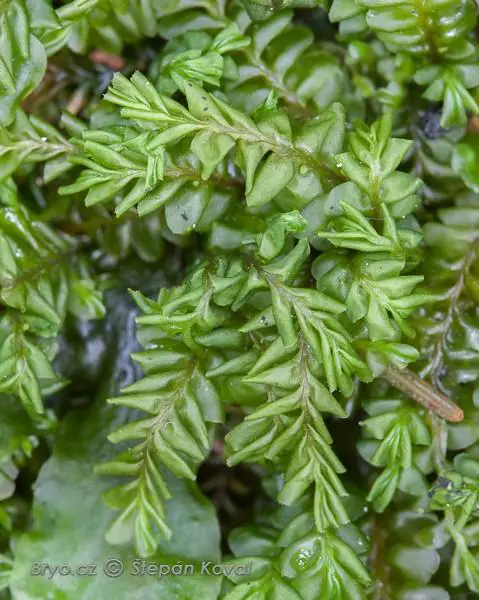

4490_Plagiochila_porelloides_2009_09_11_img_1084.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=default&gallery=plagiochila_porelloides&id=4490
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Plagiochila frondescens var. rigida (Nees) Lindenb. is a striking moss that exhibits a distinctive appearance. Its frondose growth habit, characterized by flattened, ribbon-like stems, sets it apart from many other mosses. The stems are adorned with overlapping leaves, creating a intricate and visually appealing pattern. These leaves are often deeply lobed or divided, adding to the moss’s unique charm.
One of the most remarkable features of Plagiochila is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. During the sexual reproductive cycle, it produces sporophytes that bear spore capsules, allowing for the dispersal of spores and the establishment of new colonies. Asexual reproduction occurs through the formation of gemmae, specialized reproductive structures that can develop into new individuals without the need for fertilization.
Global Distribution and Habitat
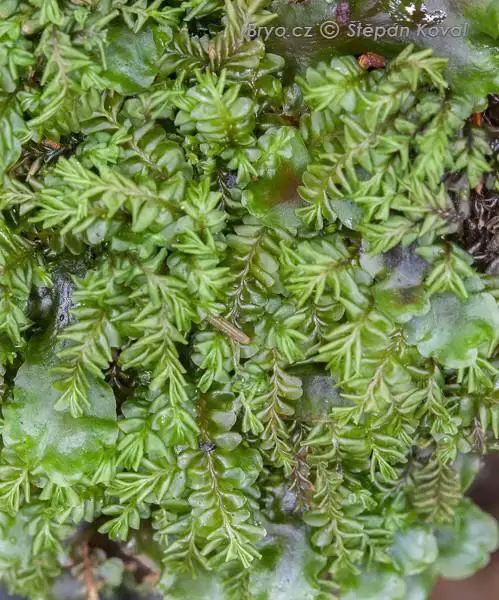

4488_Plagiochila_porelloides_2009_09_11_img_1081.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=default&gallery=plagiochila_porelloides&id=4488
Plagiochila frondescens var. rigida (Nees) Lindenb. is widely distributed across various regions of the world, thriving in a diverse range of habitats. From the temperate forests of North America and Europe to the tropical rainforests of South America and Southeast Asia, this resilient moss has adapted to a wide array of environmental conditions.
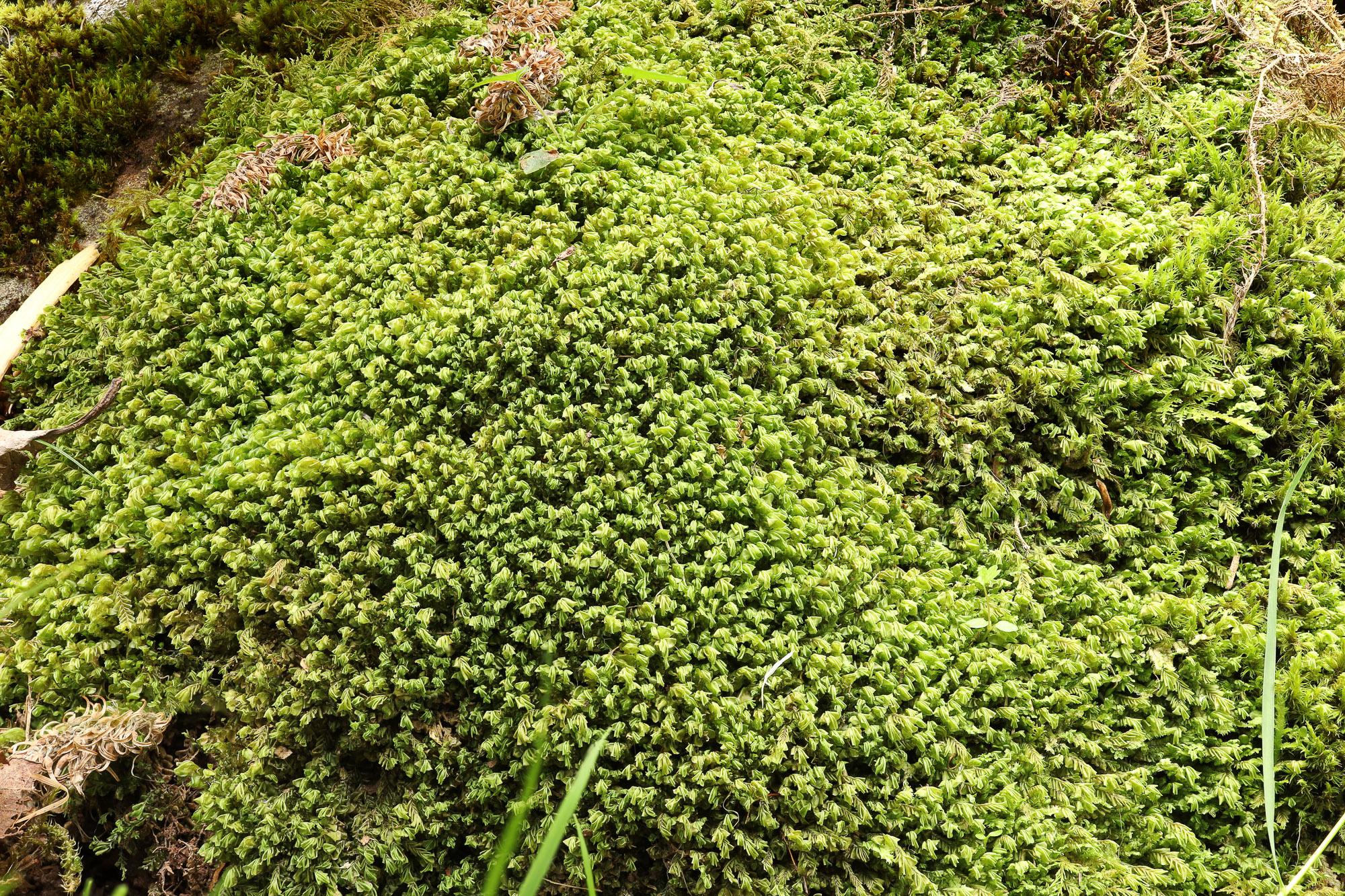

2020-07-16-14-52-16.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/plagiochila-porelloides/
While Plagiochila can be found growing on various substrates, including soil, rocks, and tree bark, it often prefers moist and shaded environments. These conditions provide the ideal combination of moisture and protection from direct sunlight, allowing the moss to flourish and form lush, verdant carpets.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Plagiochila frondescens var. rigida (Nees) Lindenb. plays a vital role in the ecosystems it inhabits. As a pioneer species, it contributes to the formation of soil and the establishment of plant communities, paving the way for other organisms to thrive.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Plagiochila is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving itself once favorable conditions return. This resilience allows it to survive in environments where water availability can be unpredictable.
Case Studies/Examples
In the Pacific Northwest region of North America, Plagiochila frondescens var. rigida (Nees) Lindenb. is a common sight in the lush, temperate rainforests. Here, it forms vibrant carpets on the forest floor, contributing to the rich biodiversity of these ecosystems. Researchers have studied the moss’s role in nutrient cycling and its interactions with other organisms, such as fungi and invertebrates.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Plagiochilaceae |
| Genus | Plagiochila |
| Species | Plagiochila frondescens var. rigida (Nees) Lindenb. |
| Growth Habit | Frondose, flattened stems |
| Leaf Arrangement | Overlapping, deeply lobed or divided |
| Reproduction | Sexual (sporophytes, spore capsules) and asexual (gemmae) |
| Distribution | Widespread across temperate and tropical regions |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments on various substrates |
| Ecological Role | Pioneer species, soil formation, nutrient cycling |
| Adaptations | Desiccation tolerance, dormancy |
Conclusion
The Plagiochila frondescens var. rigida (Nees) Lindenb., or simply Plagiochila, is a true marvel of nature, showcasing the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. From its intricate morphology to its vital ecological roles, this moss serves as a reminder of the intricate beauty that often goes unnoticed in the natural world. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other secrets and marvels await discovery in the realm of these diminutive yet extraordinary organisms?