
spc_000266367_000024921.jpg from: https://www.orchidroots.com/detail/photos/266367/
Introduction

plaaus_pgd9886plasulweb2.jpg from: https://www.southernappalachianbryophytes.org/plagiochilaechinata.html
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Plagiochila gracillima Austin ex A.Evans moss stands out as a true marvel. Belonging to the Plagiochilaceae family, this delicate and intricate species, commonly referred to as Plagiochila

2021-02-06-14-13-44.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/plagiochila-asplenioides/
, has captured the hearts and minds of moss enthusiasts worldwide.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this remarkable moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. Plagiochila gracillima is a member of the phylum Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida, which encompasses a diverse array of liverworts and mosses. These bryophytes play a crucial role in various ecosystems, serving as indicators of environmental health and contributing to the intricate web of life.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Plagiochila gracillima is a true masterpiece of nature, with its delicate and intricate structure. This moss boasts a creeping habit, forming dense mats or cushions on the surfaces it inhabits. Its slender stems

s-l1600.jpg from: https://www.ebay.com/itm/155094129901
are adorned with overlapping leaves, arranged in a distinctive distichous pattern, resembling tiny green feathers. The leaves themselves are ovate to lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive midrib running along their length.
One of the most striking features of Plagiochila gracillima is its reproductive structures. The archegoniophores (female reproductive structures) and antheridiophores (male reproductive structures) are borne on separate plants, a characteristic known as dioicy. These structures are truly remarkable, with the archegoniophores resembling tiny umbrellas and the antheridiophores appearing as delicate spikes.
Global Distribution and Habitat

0239048-scaled.jpg from: https://makinodatabase.jp/plantsdatabase/corydalis-gracillima-c-y-wu-ex-govaerts-5/
Plagiochila gracillima is a widely distributed species, found across various regions of the world. It thrives in temperate and tropical regions, preferring moist and shaded environments. This moss can be found growing on tree trunks, rocks, and soil, often forming intricate carpets or cushions in these habitats.
While Plagiochila gracillima is not considered a threatened species, its presence is an indicator of a healthy and stable ecosystem. As such, it plays a vital role in monitoring environmental changes and serving as a barometer for the well-being of its surroundings.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like many bryophytes, Plagiochila gracillima plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. It serves as a pioneer species, colonizing bare surfaces and paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss acts as a sponge, absorbing and retaining moisture, creating a microhabitat for various invertebrates and microorganisms.
Plagiochila gracillima has evolved remarkable adaptations to thrive in its environment. Its dense cushion-like growth habit helps retain moisture and protect the delicate stems and leaves from desiccation. Furthermore, its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually through spores and vegetative propagules ensures its continued survival and dispersal.
Case Studies/Examples
One notable example of the ecological significance of Plagiochila gracillima can be found in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. In this temperate rainforest ecosystem, the moss plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of the forest floor. Its presence contributes to the overall biodiversity and serves as a indicator of the ecosystem’s health.
Technical Table
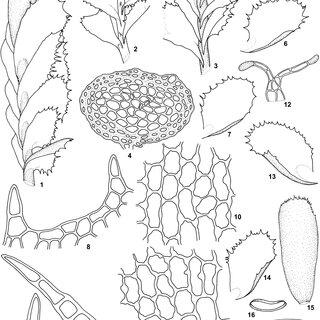
Plagiochila-alaskana-AEvans-1-A-portion-of-the-female-plant-with-gynoecium-in-lateral_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plagiochila-alaskana-AEvans-1-A-portion-of-the-female-plant-with-gynoecium-in-lateral_fig1_343281294

0061442-1419×2000.jpg from: https://makinodatabase.jp/plantsdatabase/corydalis-gracillima-c-y-wu-ex-govaerts/

0221287-1419×2000.jpg from: https://makinodatabase.jp/plantsdatabase/corydalis-gracillima-c-y-wu-ex-govaerts-3/

0238641-scaled.jpg from: https://makinodatabase.jp/plantsdatabase/corydalis-gracillima-c-y-wu-ex-govaerts-4/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta
 0222234-scaled.jpg from: https://makinodatabase.jp/plantsdatabase/corydalis-gracillima-c-y-wu-ex-govaerts-2/ |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Plagiochilaceae |
| Genus | Plagiochila |
| Species | gracillima Austin ex A.Evans |
| Growth Habit | Creeping, forming dense mats or cushions |
| Leaf Arrangement | Distichous (overlapping in two rows) |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to lanceolate |
| Reproductive Structures | Archegoniophores (female) and antheridiophores (male) |
| Habitat | Moist and shaded environments, on tree trunks, rocks, and soil |
| Distribution | Temperate and tropical regions worldwide |
Conclusion
The Plagiochila gracillima Austin ex A.Evans moss is a true testament to the beauty and complexity of nature. Its delicate structure, intricate reproductive mechanisms, and vital ecological roles make it a fascinating subject for moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the bryophyte world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and preserve these intricate and invaluable species for future generations to marvel at?