209774.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4887
Introduction
The world of bryophytes, or non-vascular plants, is a fascinating one, and among its many wonders is the

141736.jpg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=14071
Pohlia cruda (Hedw.) Lindb. moss, a member of the Mniaceae family. Often simply referred to as Pohlia, this unassuming plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Pohlia cruda, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These ancient plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, have been around for over 400 million years and are among the oldest land plants on Earth. Despite their diminutive size, they play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.

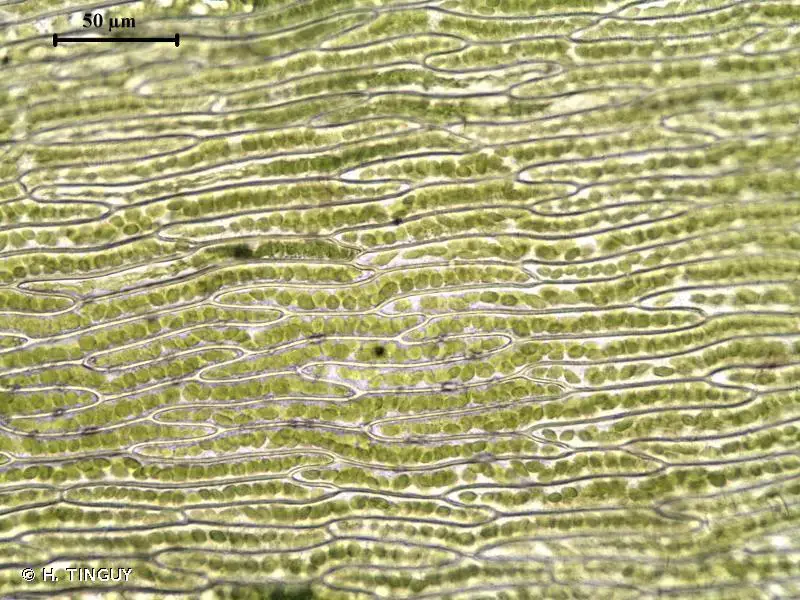
2022-02-03-11-58-12-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/pohlia-cruda/
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
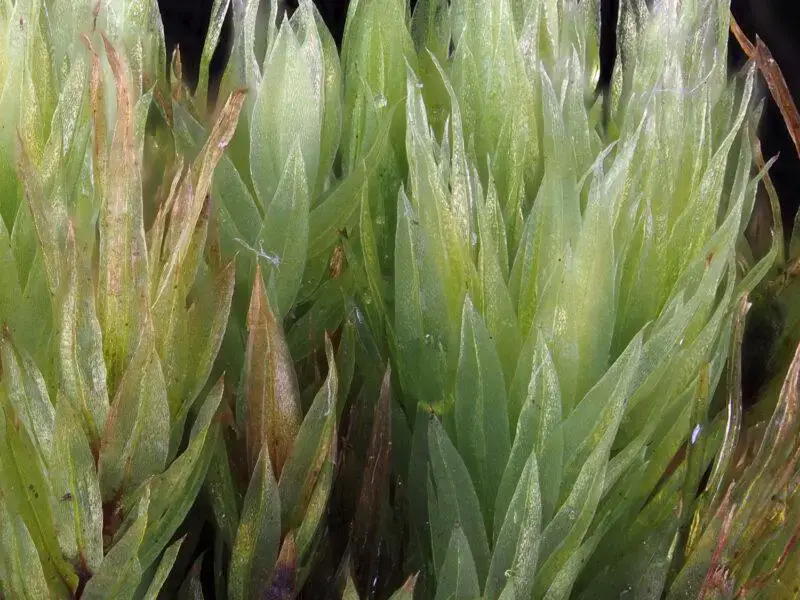
Pohlia cruda is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, green to yellowish-green tufts or cushions. Its leaves are ovate-lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a short awn or hair-like projection. This characteristic, along with the crisped and contorted leaves when dry, makes Pohlia cruda relatively easy to identify in the field.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a cosmopolitan distribution, meaning it can be found on almost every continent, from the Arctic regions to the tropics. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, including disturbed areas, roadsides, fields, and even urban environments. Pohlia cruda is particularly adept at colonizing bare, nutrient-rich soils, making it a pioneer species in many ecosystems.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small stature, Pohlia cruda plays a vital role in its environment. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense cushions provide microhabitats for various invertebrates, contributing to biodiversity.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Pohlia cruda is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, its leaves curl inward, protecting the delicate inner tissues from excessive water loss. This trait, known as poikilohydry, allows the moss to survive in harsh environments and quickly rehydrate when moisture becomes available.
Case Studies/Examples
In urban areas, Pohlia cruda has been observed colonizing disturbed sites, such as construction areas or abandoned lots. Its presence can be an indicator of soil quality, as it tends to thrive in nutrient-rich environments. Interestingly, this moss has also been found growing on the roofs of buildings, demonstrating its adaptability to unique habitats.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Bryales |
| Family | Mniaceae |
| Genus | Pohlia |
| Species | cruda |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Apex | Costa extending beyond leaf apex, forming a short awn |
| Habitat | Disturbed areas, roadsides, fields, urban environments |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan |
Conclusion
The Pohlia cruda (Hedw.) Lindb. moss, a member of the Mniaceae family, may be small in stature, but its impact on the environment is significant. From stabilizing soils to providing microhabitats, this unassuming plant plays a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance. As we continue to explore the fascinating world of bryophytes, we are reminded of the importance of appreciating and protecting even the smallest of nature’s wonders. Perhaps the next time you encounter a patch of Pohlia cruda, you’ll pause and reflect on the remarkable resilience and adaptability of this humble moss.